This introduction paper is based on the paper "Challenges in Cooling Design of CPU Packages for High-Performance Servers" published by "Heat Transfer Engineering".
1. Overview:
- Title: Challenges in Cooling Design of CPU Packages for High-Performance Servers
- Author: Jie Wei
- Year of publication: 2008
- Journal/academic society of publication: Heat Transfer Engineering (Taylor & Francis Group)
- Keywords: CPU cooling, high-performance servers, thermal management, thermal interface materials, heat spreaders, power dissipation, heat sinks, asymmetric heat dissipation, package cooling
2. Abstract:
Cooling technologies that address high-density and asymmetric heat dissipation in CPU packages of high-performance servers are discussed. Thermal management schemes and the development of associated technologies are reviewed from a viewpoint of industrial application. Particular attention is directed to heat conduction in the package and heat removal from the package/heat sink module. Power dissipation and package cooling characteristics of high-performance microprocessors are analyzed. The development of a new metallic thermal interface technology is introduced, where thermal and mechanical performance of an indium-silver alloy in the chip/heat spreader assembly was studied. The paper also reports on research on other thermal management materials, such as diamond composite heat-spreading materials. Some actual package designs are described to illustrate the enhanced heat spreading capability of heat pipes and vapor chambers.
3. Introduction:
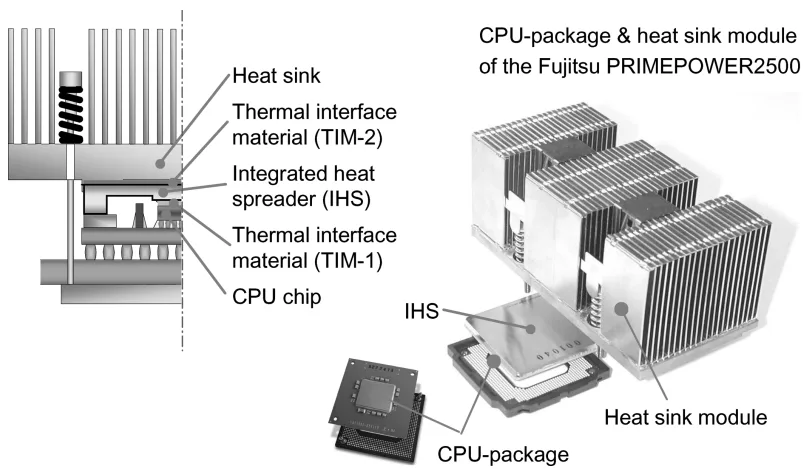
High-performance computer servers are essential for fields requiring significant data processing and computing. They demand high reliability, efficiency, and environmental compatibility alongside high performance. A major challenge is the continuously increasing power dissipation of high-performance microprocessors (CPUs). Miniaturization and design complexity also lead to highly asymmetric power distribution, creating localized "hot spots" with much higher power density than the chip average. These hot spots cause elevated local temperatures and large temperature gradients, negatively impacting processor performance, reliability, and cooling efficiency. Furthermore, the shrinking temperature budget (due to increased local ambient temperatures from high-density packaging and the desire for lower junction temperatures for reliability and leakage current suppression) intensifies thermal management challenges. Cooling capability at the package level is critical. A typical high-performance processor package structure (Figure 1) includes an integrated heat spreader (IHS) attached to the chip via a first-level thermal interface material (TIM-1). The IHS spreads heat and minimizes temperature gradients. An air-cooled heat sink is mounted on the IHS using a second-level thermal interface material (TIM-2), dissipating heat to the ambient air. This study analyzes processor power dissipation characteristics, reviews package cooling technologies, and discusses challenges related to high-density and asymmetric power dissipation, including new metallic thermal interface technology and composite heat-spreading materials.
4. Summary of the study:
Background of the research topic:
The increasing power dissipation, power density, and particularly the asymmetric power distribution (hot spots) in CPUs for high-performance servers pose significant thermal management challenges. These challenges are compounded by miniaturization trends and shrinking allowable operating temperature ranges, impacting server performance, reliability, and cooling efficiency. Effective cooling at the package level is crucial.
Status of previous research:
Various cooling technologies have been implemented for high-performance server CPU packages. Examples include:
- Single-chip packages with metallic TIM-1 and copper/aluminum heat sinks (e.g., Fujitsu PRIMEPOWER2500, SunFire-E25K).
- Direct chip attach with grease TIM (e.g., NEC SX-8).
- Multi-chip module (MCM) cooling using stacked designs with individual spreaders and common caps (e.g., IBM POWER4), small gap technology (SGT) for reduced thermal resistance (e.g., IBM POWER5, z-Server), or dual-layer interfaces (e.g., Hitachi M5800).
- Advanced air-cooling using thermosyphon-based heat sinks for MCMs (e.g., Fujitsu GS8900).
- Liquid cooling, including direct solder to water-cooled caps (e.g., Hitachi MP6000), pumped water circulation to cold plates attached to MCMs (e.g., Fujitsu GS8900 Turbo), and liquid spray impingement (e.g., Cray Supercomputer).
Purpose of the study:
This study aims to:
- Discuss cooling technologies addressing high-density and asymmetric heat dissipation in high-performance server CPU packages.
- Review thermal management schemes and associated technologies from an industrial application perspective.
- Analyze power dissipation characteristics and package cooling features of high-performance microprocessors.
- Introduce developments in metallic thermal interface technology (specifically In-Ag alloy).
- Report on research into advanced thermal management materials like diamond composites.
- Illustrate the enhanced heat spreading capabilities of heat pipes and vapor chambers in package designs.
Core study:
The core of the study involves:
- Analyzing CPU Power Dissipation: Examining trends (ITRS roadmap projections), average vs. hot spot densities (Figure 4), the impact of asymmetric power distribution on chip temperature (Figure 5), and the increasing significance and temperature dependency of leakage power (Figure 6, 7).
- Investigating Advanced Thermal Interface Materials (TIMs): Focusing on TIM-1 for chip-to-IHS connection, introducing a metallic In-10Ag composite, and evaluating its thermal performance compared to solders (Figure 9, Table 1). The impact of voids within TIM-1 on chip temperature distribution is simulated (Figure 8, 10, 11, Table 2).
- Evaluating Heat-Spreading Materials: Discussing the importance of high thermal conductivity and matched CTE for heat spreaders. Investigating the performance of composite materials (like diamond-silicon carbide, Al-diamond, Cu-diamond) compared to conventional materials (AlN, Cu) through numerical simulation (Figure 12, 13, Table 3).
- Assessing Enhanced Heat Sink Cooling: Exploring methods to extend air-cooling limits by improving heat spreading within the heat sink base using embedded heat pipes and vapor chambers, and experimentally comparing their performance and weight against conventional designs (Figure 14, 15, Table 4, 5).
5. Research Methodology
Research Design:
The paper employs a review and analysis approach. It synthesizes information from industry practices, published literature, technology roadmaps, and specific technical investigations (potentially including modeling, simulation, and experimental work conducted or cited by the author). It focuses on identifying challenges and presenting advancements in cooling technologies for high-performance server CPUs.
Data Collection and Analysis Methods:
- Literature Review: Citing and summarizing cooling solutions from various server manufacturers (Fujitsu, Sun, NEC, HP, IBM, Hitachi, Cray).
- Trend Analysis: Using data from the International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors (ITRS) to illustrate power density trends (Figure 4).
- Modeling and Simulation:
- Predicting chip temperature distribution based on power maps (Figure 5).
- Analyzing power consumption components (leakage vs. dynamic) based on modeling and test data (Figure 6, 7).
- Simulating the impact of voids in TIM-1 on chip temperature (Figure 10, 11, Table 2).
- Simulating the effect of different heat spreader materials on chip temperature distribution (Figure 12, 13).
- Material Characterization/Testing: Presenting thermal performance data for metallic interface materials (In-10Ag vs. solders) based on ASTM testing (Figure 9, Table 1).
- Experimental Testing: Evaluating and comparing the cooling performance and weight of different prototype heat sinks (including those with heat pipes and vapor chambers) in a wind tunnel setup (Figure 15, Table 5).
Research Topics and Scope:
The research covers thermal management challenges and solutions for CPU packages in high-performance servers. Key topics include:
- Characteristics of CPU power dissipation (density, asymmetry, hot spots, leakage current).
- Review of existing package cooling technologies (air and liquid).
- Advanced Thermal Interface Materials (TIMs), focusing on metallic TIM-1 (In-10Ag) and the impact of voids.
- Advanced heat-spreading materials (composites) and their effect on chip temperature uniformity.
- Technologies for enhancing air-cooling capability of heat sinks (heat pipes, vapor chambers).
The scope is primarily focused on package-level thermal management from an industrial perspective.
6. Key Results:
Key Results:
- CPU power density continues to rise, with projections nearing 50 W/cm² average and hot spots potentially reaching 200 W/cm², creating significant thermal challenges (Figure 4). Asymmetric power distribution leads to large on-chip temperature variations (Figure 5).
- Leakage power is becoming a substantial fraction of total CPU power consumption, exhibiting a strong exponential dependence on temperature, making junction temperature reduction critical (Figure 6, 7).
- A developed metallic TIM-1 using an In-10Ag composite shows lower thermal resistance compared to conventional Sn-Pb solders and offers favorable properties like ductility and a wide processing temperature range (Figure 9, Table 1).
- Voids in TIM-1, particularly above chip hot spots, significantly degrade thermal performance, causing localized temperature increases; simulations predict a >10°C rise for voids larger than 2.5 mm diameter (Figure 10, 11).
- Advanced heat spreader materials, such as diamond composites (k ≈ 600 W/m·K), offer superior thermal conductivity compared to traditional metals (Cu, AlN) or other composites, leading to more uniform chip temperatures and lower peak temperatures (Figure 12, 13, Table 3).
- Integrating heat pipes or vapor chambers into the base of large footprint heat sinks effectively enhances heat spreading, improving overall air-cooling performance (by 10-20% in tested cases) compared to solid metal bases, often with a simultaneous weight reduction (Figure 15).
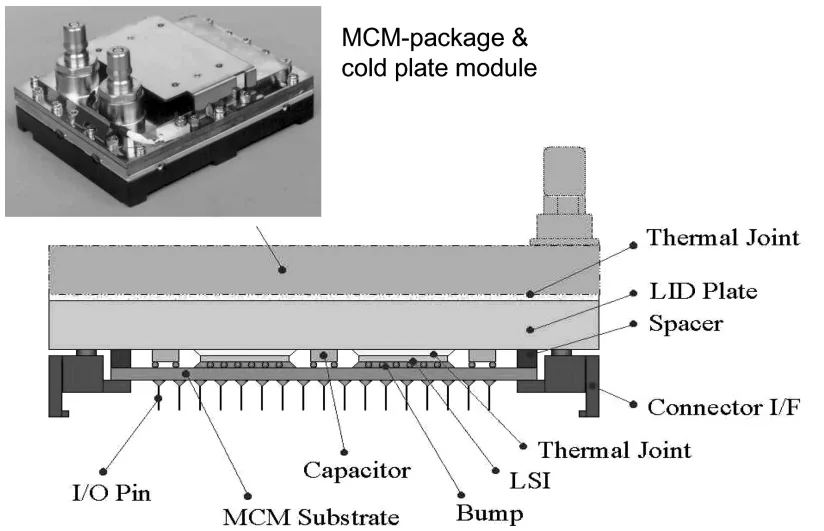
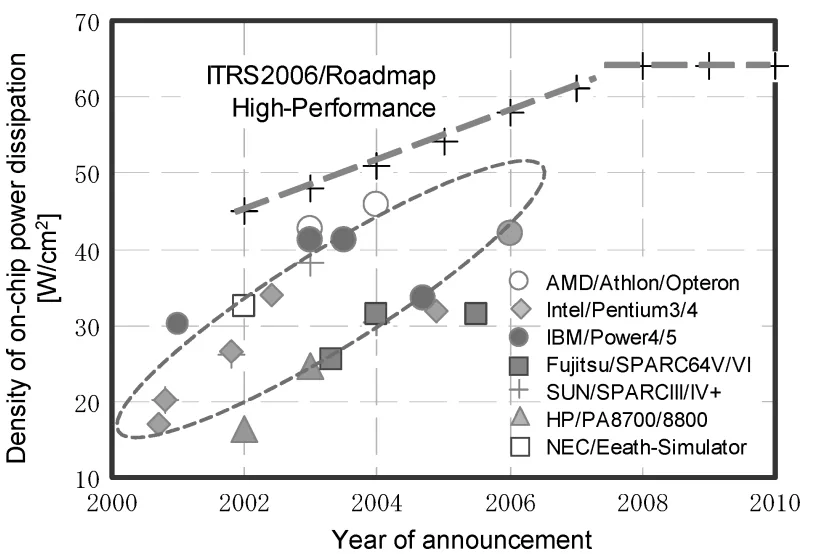
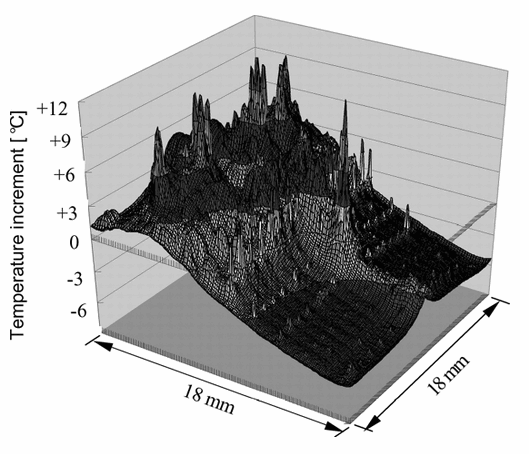
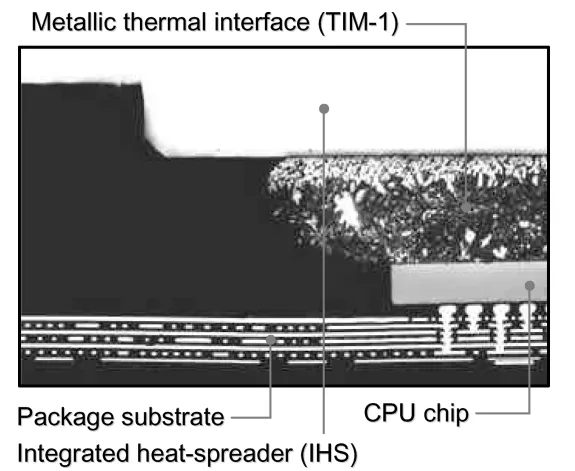
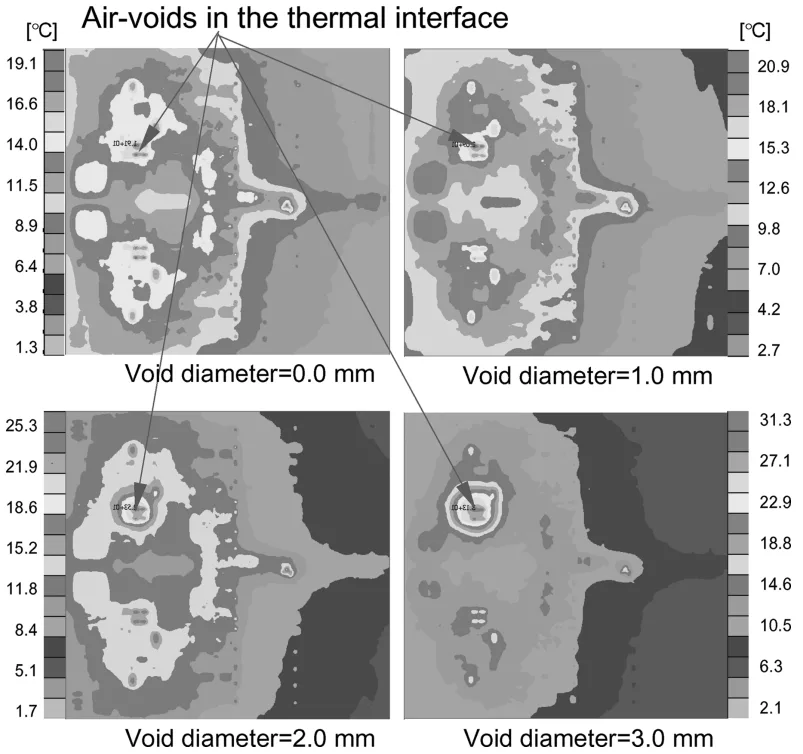
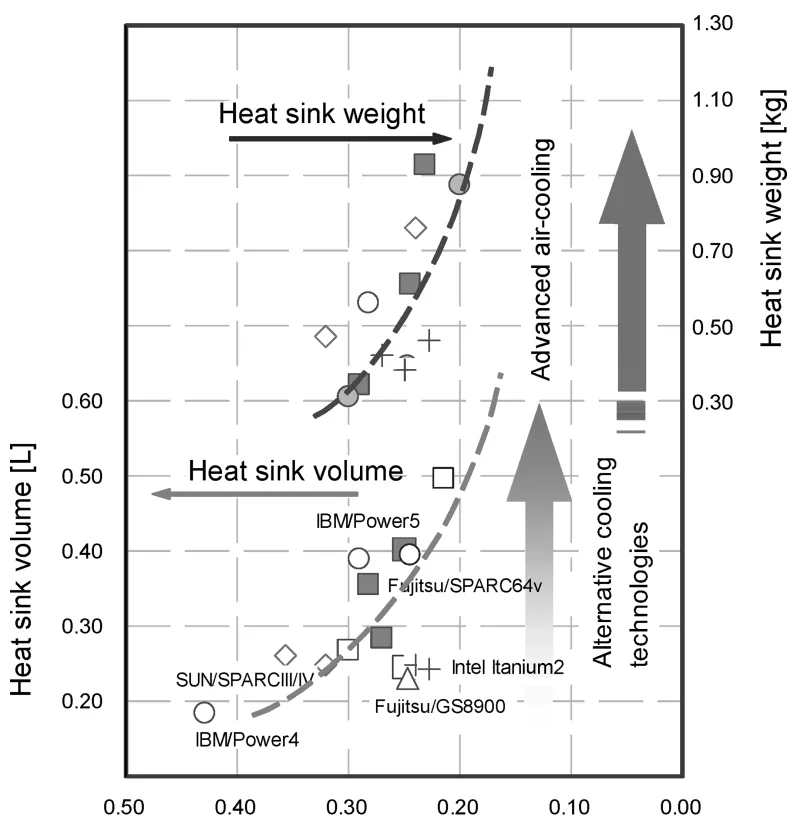
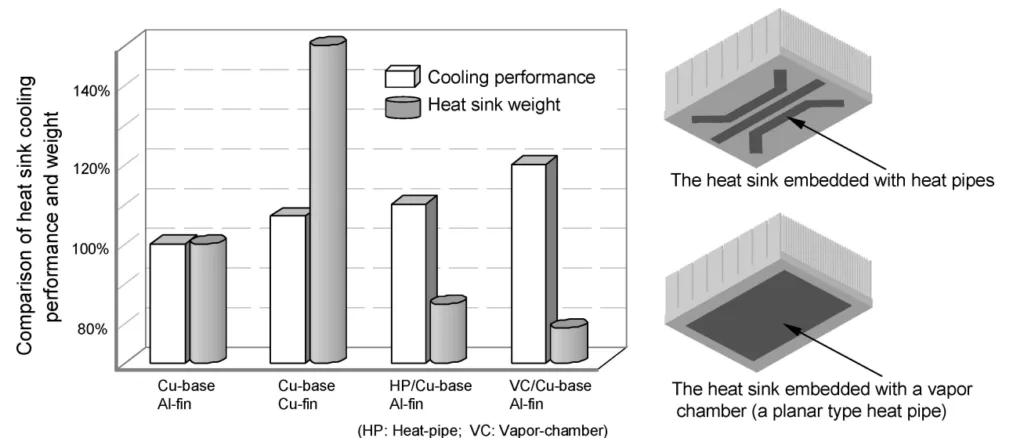
Figure Name List:
- Figure 1 A typical structure of CPU package and heat sink module.
- Figure 2 Air-cooled MCM packages of Fujitsu GS8900.
- Figure 3 Liquid-cooled MCM package of Fujitsu GS8900 (Turbo).
- Figure 4 Power density of high performance microprocessors.
- Figure 5 Temperature distribution on a test processor chip.
- Figure 6 Power consumption of the UltraSPARC64 V and VI processors.
- Figure 7 Temperature versus power consumption of UltraSPARC64 V processor.
- Figure 8 Cross-section of the package showing In-10Ag TIM-1.
- Figure 9 Thermal performance of several metallic interface materials.
- Figure 10 Impact of voids in TIM-1 on temperature distribution on the chip.
- Figure 11 Increase of junction temperature caused by voids in TIM-1.
- Figure 12 Effect of heat spreader materials on temperature distribution on the chip.
- Figure 13 Increase of junction temperature over the reference level plotted against the heat spreader thermal conductivity. (The reference level is the temperature of a chip having a total heat dissipation equal to the studied chip but uniform heat dissipation distribution.)
- Figure 14 Characteristics of air-cooled heat sinks for server packages.
- Figure 15 Comparison of various heat sinks in terms of their cooling performance and weights.
7. Conclusion:
Thermal management of CPU packages for high-performance servers faces significant challenges due to increasing power dissipation, density, asymmetry (hot spots), miniaturization, and device complexity. This paper discussed these challenges, reviewed characteristics of CPU power dissipation, and presented investigations into advanced thermal solutions. Key areas explored include advanced thermal interface materials (like metallic In-10Ag for TIM-1), high-conductivity heat-spreading materials (including composites), and methods to enhance the cooling capability of air-cooled heat sinks (using heat pipes and vapor chambers). The industry faces a critical need to extend the limits of cost-effective conventional cooling technologies while aggressively pursuing advanced solutions to meet the thermal demands of future high-performance processors.
8. References:
- [1] Wei, J., Challenges in Package-Level High Power Density Cooling, Proc. International Symposium on Transport Phenomena, Toyama, Japan, 2006.
- [2] Sauciuc, I., Prasher, R., Chang, J. Y., Erturk, H., Chrysler, G., Chiu, C. P., and Mahajan, R., Thermal Performance and Key Challenges for Future CPU Cooling Technologies, Proc. InterPACK’05, San Francisco, California, USA, 2005.
- [3] Prasher, R. S., Chang, J. Y., Sauciuc, I., Narasimhan, S., Chau, D., Chrysler, G., Myers, A., Prstic, S., and Hu, C., Nano Micro Technology-Based Next-Generation Package-Level Cooling Solutions, Intel Technology Journal, vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 285–296, 2005.
- [4] Wei, J., Thermal Management of Fujitsu High-Performance Servers, Fujitsu Scientific & Technical Journal, vol. 43, no. 1, pp. 122–129, 2007.
- [5] Xu, G., Follmer, L., and Cooley, J., Thermal Solution Development for the SunFireTM E25K server, Proc. SEMI-THERM, San Jose, California, USA, 2005.
- [6] Tanaka, S., Hamaguchi, H., Tsuzuki, H., Takahashi, I., Natori, M., and Nagata, T., Packaging Technology for SX-8, NEC Tech., vol. 58, no. 4, pp. 23–28, 2005.
- [7] Minichiello, A., and Belady, C., Thermal Design Methodology for Electronic Systems, Proc. ITherm, San Jose, California, USA, pp. 696–704, 2002.
- [8] Giraldo, M. D., Mechanical Packaging of HP’s Superdome Server, Proc. InterPACK’01, Kauai, Hawaii, USA, 2001.
- [9] Knickerbocker, J. U., Pompeo, F. L., Tai, A. F., Thomas, D. L., Weekly, R. D., Nealon, M. G., Hamel, H. C., Haridass, A., Humenik, J. N., Shelleman, R. A., Reddy, S. N., Prettyman, K. M., Fasano, B. V., Ray, S. K., Lombardi, T. E., Marston, K. C., Coico, P. A., Brofman, P. J., Goldmann, L. S., Edwards, D. L., Zitz, J. A., Iruvanti, S., Shinde, S. L., and Longworth, H. P., An Advanced Multi-chip Module (MCM) for High-Performance UNIX Servers, IBM J. Res. & Dev., vol. 46, no. 6, pp. 779–804, 2002.
- [10] Coico, P. A., Messina, G., Ostrander, S., Zitz, J., and Zou, W., Internal Thermal Management of IBM P-Server Large Format Multi-Chip Modules Utilizing Small Gap Technology, Proc. InterPACK’05, San Francisco, California, USA, 2005.
- [11] Harrer, H., Dreps, D. M., Winkel, T. M., Scholz, W., Truong, B. G., Huber, A., Zhou, T., Christian, K. L., and Goth, G. F., High-Speed Interconnect and Packaging Design of the IBM System z9 Processor Cage, IBM J. Res. & Dev., vol. 51, no. 1/2, pp. 1–16, 2007.
- [12] Kobayashi, F., Hardware Technology for the HITACHI MP5800 Series (HDS Skyline Series), IEEE Trans. Advanced Packaging, vol. 23, no. 3, pp. 504–514, 2000.
- [13] Yamada, O., Sawada, Y., Harada, M., Yokozuka, T., Yasukawa, A., Moriya, H., Saito, N., Kasai, K., Uda, T., Netsu, T., and Koyano, K., Improvement of the Reliability of the C4 for Ultra-High Thermal Conduction Module with the Direct Solder-Attached Cooling System (DiSAC), Proc. ECTC, Orlando, Florida, USA, pp. 1144–1148, 2001.
- [14] Fujisaki, A., Suzuki, M., and Yamamoto, H., Packaging Technology for High Performance CMOS Server Fujitsu GS8900, IEEE Trans. Advanced Packaging, vol. 24, no. 4, pp. 464–468, 2001.
- [15] Wei, J., Suzuki, M., Udagawa, Y., and Yamamoto, H., Thermal Management of Multiple MCMs with Low-Temperature Liquid Cooling, Proc. InterPACK’01, Kauai, Hawaii, USA, 2001.
- [16] Pautsch, G. W., An Overview on the System Packaging of the Cray SV2 Supercomputer, Proc. InterPACK’01, Kauai, Hawaii, USA, 2001.
- [17] Pautsch, A. G., and Shedd, T. A., Spray Impingement Cooling Using Single- and Multiple-Nozzle Arrays, Part I: Heat Transfer Using FC-72, Int. J. Heat and Mass Transfer, vol. 48, pp. 3167–3175, 2005.
- [18] International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors. Assembly and Packaging. 2005 ed. Available at: http://www.itrs.net/Links/2005ITRS/AP2005.pdf.
- [19] Sery, G., Borkar, S., and De, V., Life Is CMOS: Why Chase the Life After? Proc. Design Automation Conf., New Orleans, Louisiana, USA, pp. 78–83, 2002.
- [20] Deeney, J., Thermal Modeling and Measurement of Large High Power Silicon Devices with Asymmetric Power Distribution, Proc. IMAPS, Denver, Colorado, USA, 2002.
- [21] Warnock, J. D., Keaty, J. M., Petrovick, J., Clabes, J. G., Kircher, C. J., Krauter, B. L., Restle, P. J., Zoric, B. A., and Anderson, C. J., The Circuit and Physical Design of the Power4 Microprocessor, IBM J. Res. & Dev., vol. 46, no. 1, pp. 27–51, 2002.
- [22] Xu, G., Thermal Modeling of Multi-Core Processors, Proc. ITherm, San Diego, California, USA, pp. 96–100, 2006.
- [23] Iyengar, M., and Schmidt, R., Analytical Modeling for Prediction of Hot spot Chip Junction Temperature for Electronics Cooling Applications, Proc. ITherm, San Diego, California, USA, pp. 87–95, 2006.
- [24] June, M. S., and Sikka, K. K., Using Cap-Integral Standoffs to Reduce Chip Hot spot Temperatures in Electronic Packages, Proc. ITherm, San Diego, California, pp. 173–178, 2002.
- [25] Wei, J., Nori, H., Ishimine, J., and Fujisaki, A., Effects of Asymmetric Power Distributions on Thermal Management of High Performance LSI Processors, Proc. IFHT, Kyoto, Japan, pp. 37–39, 2004.
- [26] Mukhopadhyay, S., Raychowdhury, A., and Roy, K., Accurate Estimation of Total Leakage Current in Sealed CMOS Logic Circuits Based on Compact Current Modeling, Proc. Design Automation Conf., Anaheim, California, USA, pp. 169–174, 2003.
- [27] Krishnan, S., Garimella, S. V., Chrysler, G. M., and Mahajan, R. V., Towards a Thermal Moore’s Law, Proc. InterPACK’05, San Francisco, California, USA, 2005.
- [28] Kim, N. S., Austin, T., Blaauw, D., Mudge, T., Flaunter, K., Hu, J. S., Irwin, M. J., Kandemir, M., and Narayanan, V., Leakage Current: Moore’s Law Meets Static Power, IEEE Computer, vol. 36, no. 12, pp. 68–75, 2003.
- [29] Inoue, A., High Performance and High Reliability Technologies of the SPARC64 V/VI, Scientific System Research Symposium 2006, Tokyo, Japan, 2006 (in Japanese).
- [30] Dani, A., James, C., Matayabas, J. R., and Koning, P., Thermal Interface Material Technology Advancements and Challenges—An Overview, Proc. InterPACK’05, San Francisco, California, USA, 2005.
- [31] Stern, M. B., Gektin, V., Pecavar, S., Kearns, D., and Chen, T., Evaluation of High Performance Thermal Greases for CPU Package Cooling Applications, Proc. SEMI-THERM, San Jose, California, USA, 2005.
- [32] Wilson, J., Thermal Conductivity of Solders, Electronics Cooling, vol. 12, no. 3, pp. 4–5, 2006.
- [33] Koide, M., Fukuzono, K., Yoshimura, H., and Sato, T., High-Performance Flip-Chip BGA Technology Based on Thin-Core and Coreless Package Substrates, Proc. ECTC, San Diego, California, USA, pp. 1869–1873, 2006.
- [34] Standard Test Method for Thermal Transmission Properties of Thin Thermally Conductive Solid Electrical Insulation Materials, ASTM D5470-93. Available at: http://www.astm.org/
- [35] Gektin, V., Thermal Management of Voids and Delamination in TIMs, Proc. InterPACK’05, San Francisco, California, USA, 2005.
- [36] Wilson, J., Thermal Conductivity of Common Alloys in Electronics Packaging, Electronics Cooling, vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 6–7, 2007.
- [37] Zweben, C., Revolutionary New Thermal Management Materials, Electronics Cooling, vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 36–37, 2005.
- [38] Bollina, R., Landgraf, J., Wagner, H., Wilhelm, R., Knippscheer, S., and Tabernig, B., Performance, Production, and Applications of Advanced Metal Diamond Composite Heat Spreader, Proc. IMAPS, San Diego, California, USA, 2006.
- [39] Rowcliffe, D., Cemented Diamond Composites for Thermal Management Applications, Proc. IMAPS ATW, Denver, Colorado, USA, 2002.
- [40] Wei, J., Chan, A., and Copeland, D., Measurement of Vapor Chamber Performance, Proc. SEMI-THERM, San Jose, California, USA, 2003.
- [41] Wei, X., and Sikka, K., Modeling of Vapor Chamber as Heat Spreading Devices, Proc. ITherm, San Diego, California, USA, pp. 578–585, 2006.
- [42] Nakayama, W., Exploring the Limits of Air Cooling, Electronics Cooling, vol. 12, no. 3, pp. 10–17, 2006.
- [43] Ortega, A., The Evolution of Air Cooling in Electronic Systems and Observations about Its Limits, Proc. International Symposium on Transport Phenomena, Toyama, Japan, 2006.
- [44] Sauciuc, I., Chrysler, G., Mahajan, R., and Szleper, M., Air-Cooling Extension: Performance Limits for Processor Cooling Applications, Proc. SEMI-THERM, San Jose, California, USA, 2003.
- [45] Xu, G., Guenin, B., and Vogel, M., Extension of Air Cooling for High Power Processors, Proc. ITherm, Las Vegas, Nevada, USA, pp. 186–193, 2004.
- [46] Sauciuc, I., Chrysler, G., Mahajan, R., and Prasher R., Spreading in the Heatsink Base: Phase Change Systems or Solid Metals, in Thermal Challenges in Next Generation Electronic Systems, eds. Y. K. Joshi & S. V. Garimella, Millpress, Rotterdam, 2002.
9. Copyright:
- This material is a paper by "Jie Wei". Based on "Challenges in Cooling Design of CPU Packages for High-Performance Servers".
- Source of the paper: https://doi.org/10.1080/01457630701686727
This material is summarized based on the above paper, and unauthorized use for commercial purposes is prohibited.
Copyright © 2025 CASTMAN. All rights reserved.