Mastering Metal Flow: A Technical Guide to Casting Defects and Remedies
This technical summary is based on the academic paper "Defects, Root Causes in Casting Process and Their Remedies: Review" by Vaibhav Ingle and Madhukar Sorte, published in the International Journal of Engineering Research and Application (2017).


Keywords
- Primary Keyword: Casting Defects and Remedies
- Secondary Keywords: High Pressure Die Casting, Casting Process Parameters, Blowhole Defect, Shrinkage Porosity, Cold Shut, Gas Porosity, Quality Improvement in Casting
Executive Summary
- The Challenge: The occurrence of casting defects due to uncontrolled process parameters leads to poor quality, low productivity, and high rejection rates in manufacturing.
- The Method: This paper reviews and synthesizes existing research to create a comprehensive guide classifying casting defects, their root causes, and proven remedies.
- The Key Breakthrough: The paper provides a clear, actionable framework categorizing defects into filling-related, shape-related, and thermal-related types, each with specific causes and corrective actions.
- The Bottom Line: A systematic understanding and control of process parameters, as outlined in this review, is essential for minimizing rejections and improving the quality and productivity of casting operations.
The Challenge: Why This Research Matters for HPDC Professionals
In the world of manufacturing, casting is a foundational process for creating complex shapes that would be difficult or uneconomical to produce otherwise. However, this process carries an inherent risk of failure at every stage. For engineers and managers, the emergence of defects is a constant challenge. Minor defects can sometimes be adjusted, but high rejection rates can lead to significant financial losses and production delays.
The core problem, as highlighted in this research, is the multitude of process parameters that must be perfectly controlled. Without a deep understanding of how each parameter influences the final product, organizations face uncertainty and defects. This paper addresses the critical need for a technical solution to minimize this uncertainty by providing a consolidated knowledge base on casting defects, their exact root causes, and their remedies, aiming to improve both quality and productivity on an industrial level.
The Approach: Unpacking the Methodology
This paper presents a comprehensive literature review, synthesizing the findings of numerous researchers to create a practical guide for die casters. The authors analyzed a wide body of work to identify recurring themes and proven solutions. For instance, they drew on the work of Rajesh Rajkolhe and J.G. Khan, who classified defects by appearance (filling-related, shape-related, thermal-related), and C. M. Choudhari et al., who demonstrated the use of simulation software to minimize defects by optimizing parameters like gating design and parting line orientation.
The methodology was to collate these disparate research findings into a single, accessible resource. By examining various studies—from analyzing defects in 4R cylinder blocks to using Design of Experiments (DOE) for Al-Si alloys—the authors have built a robust framework that connects specific defects to their underlying process-related causes and corrective actions.
The Breakthrough: Key Findings & Data
The paper's primary contribution is its clear, structured classification of common casting defects, complete with visual examples, causes, and actionable remedies.
Finding 1: Taming Filling-Related Defects (Blowholes & Cold Shuts)
Filling-related defects occur during the initial pour as molten metal fills the mold cavity. Two of the most common are blowholes and cold shuts.
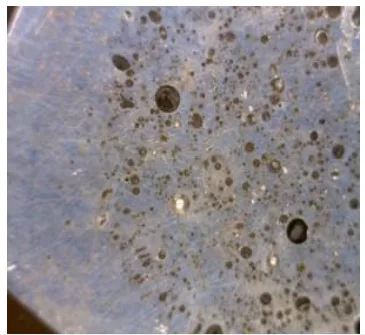
Blowholes: As described in the paper, a blowhole is a "rounded or ovel shape hole cavity on smooth or clean surface" (see "BLOW HOLES" figure). It forms when gas collects in a bubble, preventing liquid metal from filling the space.
- Causes: Poor venting of the mold or core, excessive moisture absorption by cores, and low pouring temperature.
- Remedies: Improve the venting of the core and provide dedicated venting channels.
Cold Shut: This defect is a crack-like seam with rounded edges that forms when two streams of molten metal fail to fuse properly inside the mold cavity (see "'Cold shut' defect on die cast part" figure).
- Causes: Lack of fluidity in the molten metal, faulty gating system design, or low pouring temperature.
- Remedies: Adjust to the proper pouring temperature, modify the gating system, and revise the overall part design.
Finding 2: Conquering Thermal-Related Defects (Cracks & Shrinkage)
Thermal-related defects arise from stresses and volume changes during the cooling and solidification phase.
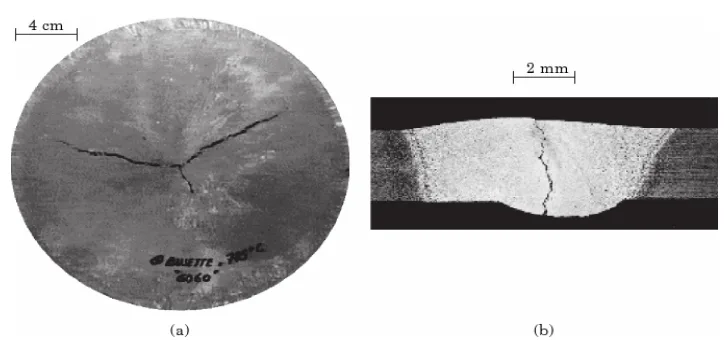
Cracks or Tears: These defects can be obvious or microscopic and appear as fractures in the casting (see "Cracks or tears" figure).
- Causes: Shrinkage of the casting within the die, thermal imbalance in the die, inadequate die design, or excessive porosity in critical regions.
- Remedies: Reduce dry strength, reduce pouring temperature, use chills and feeders, and reduce sharp corners in the design.
Shrinkage Porosity: This defect occurs when feed metal is not available to compensate for the reduction in volume as the metal solidifies. It often appears as small voids in the center of thick sections (see "Shrinkage Porosity" figure).
- Causes: The primary cause is the natural density increase as the alloy changes from a liquid to a solid state, causing it to shrink.
- Remedies: The general technique is to ensure that liquid metal under pressure continues to flow into the voids as they form during solidification.
Practical Implications for R&D and Operations
The findings from this review have direct applications for various technical teams within a manufacturing facility.
- For Process Engineers: This study suggests that adjusting key process parameters like pouring temperature, using a coarser sand, or modifying the gating system may contribute to directly reducing specific defects like cold shuts, sand inclusions, and gas porosity.
- For Quality Control Teams: The data and images in the paper, such as the visual distinctions between blowholes, gas porosity, and shrinkage porosity, can be used to refine and standardize visual inspection criteria, leading to more accurate defect identification.
- For Design Engineers: The findings indicate that part geometry, such as the presence of sharp corners or inadequate die draft, could influence crack formation during solidification, suggesting this is a valuable consideration in the early component design phase.
Paper Details
Defects, Root Causes in Casting Process and Their Remedies: Review
1. Overview:
- Title: Defects, Root Causes in Casting Process and Their Remedies: Review
- Author: Vaibhav Ingle, Madhukar Sorte
- Year of publication: 2017
- Journal/academic society of publication: Int. Journal of Engineering Research and Application (IJERA), Vol. 7, Issue 3, (Part -3) March 2017, pp.47-54
- Keywords: Casting defects and their root causes, remedies for casting defects.
2. Abstract:
Many industry aims to improve quality as well as productivity of manufacturing product. So need to number of process parameter to must controlled while casting process, so there are no of uncertainty and defects are face by organizations. In casting process industries are need to technical solution to minimize the uncertainty and defects. In this review paper to represent various casting defects and root causes for engine parts while casting process. Also provide preventive action to improve quality as well as productivity an industrial level.
3. Introduction:
Casting is a manufacturing process where molten metal is poured into a mold containing a hollow cavity of a desired shape and allowed to solidify. It is often used for complex shapes that are difficult to make by other methods. The process carries a risk of failure, and necessary action should be taken to obtain defect-free parts. Minor defects can be adjusted, but high rejection rates lead to significant costs. Therefore, it is essential for die casters to have knowledge of defect types, their exact root causes, and remedies. This review paper attempts to provide a comprehensive overview of casting-related defects with their causes and remedies to minimize rejection rates.
4. Summary of the study:
Background of the research topic:
Casting defects are a major concern in manufacturing as they directly impact product quality, productivity, and cost. The control of numerous process parameters is critical to achieving zero-defect parts, but this requires deep knowledge of how each parameter influences the final casting.
Status of previous research:
The paper reviews a wide range of existing research. Previous studies have identified various defects like blowholes, shrinkage, and cold shots (Rajkolhe, Khan). Researchers have explored different methods to mitigate these issues, including the use of simulation software to optimize process parameters (Choudhari et al.), Design of Experiments (DOE) to improve mechanical properties (Shailesh et al.), and statistical quality control (SQC) techniques (Vijayaram et al.). This paper consolidates these varied findings.
Purpose of the study:
The purpose is to present a comprehensive review of various casting defects, their root causes, and their remedies. The study aims to provide a practical guide for industry professionals to identify and prevent defects, thereby improving quality, productivity, and reducing rejection rates at an industrial level.
Core study:
The core of the study is the classification and analysis of casting defects. The paper categorizes defects into three main groups: Filling-related defects (e.g., Blowhole, Sand inclusion, Cold shut, Gas porosity), Shape-related defects (e.g., Mismatch, Distortion), and Thermal-related defects (e.g., Cracks, Shrinkage). For each specific defect, the paper provides a detailed description, a visual example, a list of possible causes, and a set of actionable remedies.
5. Research Methodology
Research Design:
The research design is a literature review. The authors have compiled, analyzed, and synthesized information from a variety of academic papers, technical articles, and industry studies related to casting defects.
Data Collection and Analysis Methods:
The method involved identifying and studying relevant publications to extract common casting defects, their scientifically-backed root causes, and industry-accepted remedies. This information was then organized into a systematic classification framework for clarity and practical application.
Research Topics and Scope:
The scope of the research covers a wide range of common defects found in the casting process. It focuses on identifying the root causes linked to process parameters, material properties, and design factors. The paper also provides corresponding remedies and preventive actions applicable to general casting processes.
6. Key Results:
Key Results:
- The paper successfully classifies casting defects into three primary categories: Filling-related, Shape-related, and Thermal-related.
- For Filling-related defects, key issues identified include Blowholes (caused by poor venting), Sand Inclusions (caused by mold erosion), Cold Shuts (caused by low metal fluidity), and Gas Porosity (caused by trapped gases).
- For Shape-related defects, the paper details Mismatch (caused by shifting molding flashes) and Distortion/Warp (caused by residual stresses).
- For Thermal-related defects, it highlights Cracks/Tears (caused by thermal imbalance and shrinkage stress) and Shrinkage (caused by the density change during solidification without proper feeding).
- For each defect, a list of specific causes and remedies is provided, offering a direct diagnostic tool for engineers.
Figure Name List:
- BLOW HOLES
- Sand inclusion defects
- "Cold shut" defect on die cast part
- Defect Diagnosis: Gas Porosity
- Mismatch defect
- Distortion or warp
- Cracks or tears
- Shrinkage Porosity

7. Conclusion:
The paper presents a new classification of defects for castings, identifying three main categories: filling-related, shape-related, and thermal-related defects. The study details how interactions between the melt flow, temperature, and environment lead to these issues. By referring to different research papers, the causes and remedies for various defects are listed. The authors conclude that this study will be helpful for industries to improve quality, enhance productivity, minimize rejections, and achieve higher quality castings.
8. References:
- [1]. Defects, Causes and Their Remedies in Casting Process: A Review Rajesh Rajkolhel, J. G. Khan2 Asst Professor1, 2, Mechanical Engineering Department1, 2, Shri Sant Gajanan Maharaj College of Engineering,
- [2]. "Review of Casting Defect Analysis to Initiate the Improvement Process"A.P.More, Dr.R.N.Baxi, Dr.S.B.Jaju Mechanical Engineering Department, G.H.Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur. 440016 (India)
- [3]. Defect formation in cast iron Lennart Elmquist School of Engineering Jönköping University, Sweden Tammerfors, Finland, November 8, 2012
- [4]. Analysis of Casting Defects and Identification of Remedial Measures A Diagnostic Study Dr D.N. Shivappal, Mr Rohit2, Mr. Abhijit Bhattacharya3 International Journal of Engineering Inventions ISSN: 2278-7461, www.ijeijournal.com Volume 1, Issue 6 (October2012) PP: 01-05
- [5]. Casting Defect Analysis using Design of Experiments (DoE) and Computer Aided Casting Simulation Technique Uday A. Dabade* and Rahul C. Bhedasgaonkar, (2013)
- [6]. Reduction of defects in grey cast iron castings by six sigma approach Raguramsingh., Syath Abuthakeer. ME Lean Manufacturing, PSG College of Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering, PSG College of Technology, Coimbatore, India.
- [7]. Process optimization as a tool in the analysis of steel casting defects By Dr.Hathibelagal Roshan, Chief Metallurgist Maynard Steel Casting Company Milwaukee
- [8]. Silver anniversary paper, div5 Porosity defects in iron casting from mold metal interface reaction. R.l.naro.aci international, inc,cleveland,ohio.
- [9]. Advanced techniques in casting defects and rejection analysis: a study in an industry Mr. Siddalingswami. S. Hiremath, Dr. S. R. Dulange Professor, Mechanical Engg. Solapur University, [IJIERT] ISSN: 2394- 3696 volume 2, issue 9, sep.-2015
- [10]. Modeling and simulation with experimental validation of Temperature distribution during solidification process in sand cast By C. M. Choudhari,, B. E. Narkhede, S. K. Mahajan
- [11]. Analysis of Casting Defect Through Diagnostic Study Approach Method, B.Chokkalingam & S.S.Mohamed Nazirudeen, Department of Foundry Technology, Coimbatore, India.
- [12]. New Approach to Casting Defects Classification and Analysis Supported by Simulation, V.V.Mane, Amlt Sata and Y.R. vire.
- [13]. Casting Defect Hand Book, American Foundry Society (AFS), Des Plaines II, 1972.
- [14]. Casting Defect analysis using Design of Experiments (DOE) and Computer aided Casting Simulation Technique, Uday A.Dabade and Rahul.C, Bhedasaonkar, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Walchand College of Engineering Sangli, India.
- [15]. Metal Casting Principal and Practice, T.V.Ramana Rao, India.
- [16]. Principal of Methoding and Casting Design, Professor Goutam Sutradhar
- [17]. B.ravi, "Casting Simulation and Optimization: Benefits, Bottlenecks”, Indian foundry journal, 2008, pp.3-5.
- [18]. Dr.M.Arasu (Head, Department of Foundry Technology, PSG Polytechnic College)
- [19]. Guo-fa MI, Xiand-yu, Kuang-fei WANG, Heng-Zhi FU Malcolm Blair, Raymond Monroe, Christoph Beckermann, Rishard Hardin, Kent Carlson and Charles Monroe
- [20]. A.Alagarsamy, Citation Corporation, Birmingham, Alabama
- [21]. "Review of Casting Defect Analysis to Initiate the Improvement Process”A.P.More, Dr.R.N.Baxi, Dr.S.B.Jaju Mechanical Engineering Department, G.H.Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur. 440016 (India)
- [22]. Defect formation in cast iron Lennart Elmquist School of Engineering Jönköping University, Sweden Tammerfors, Finland, November 8, 2012
- [23]. Analysis of Casting Defects and Identification of Remedial Measures A Diagnostic Study Dr D.N. Shivappal, Mr Rohit2, Mr. Abhijit Bhattacharya3 International Journal of Engineering Inventions ISSN: 2278-7461, www.ijeijournal.com Volume 1, Issue 6 (October2012) PP: 01-05
- [24]. Casting Defect Analysis using Design of Experiments (DoE) and Computer Aided Casting Simulation Technique Uday A. Dabade* and Rahul C. Bhedasaonkar, (2013)
- [25]. Reduction of defects in grey cast iron castings by six sigma approach Raguramsingh.M#1, Syath Abuthakeer.S*2 #ME Lean Manufacturing, PSG College of Technology, Coimbatore, India. Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, PSG College of Technology, Coimbatore, India. 2syathpsgtech@gmail.com
- [26]. Process optimization as a tool in the analysis of steel casting defects By Dr.Hathibelagal Roshan, Chief Metallurgist Maynard Steel Casting Company Milwaukee, WI 53217
- [27]. Silver anniversary paper, div5 Porosity defects in iron casting from mold metal interface reaction. R.l.naro. aci international, inc, Cleveland, ohio
- [28]. Modeling of shrinkage defects during solidification of long and short freezing materials A. eisa,, Y. Houbaertc, Zhian Xub, Rob Van Tol b, A.D. Santosa, J.F. Duartea, A.B. Magalha esa a FEUP - Faculdade de Engenharia da Universidade do Porto, Porto, Portugal b WTCM Foundry Center, Research Center of Belgium Metalworking Industry, 9052 Zwijnaarde, Gent, Belgium c UGent University of Ghent, Technologiepark Zwijnaarde 903, Gent, Belgium.
- [29]. New classification of defects and imperfection for aluminium alloy casting Elena Fiorese, Franco bollono and Gaiulio Timelli department of management and engineering international journal of metal casting vol.9 issue 1, 2015
- [30]. Casting defects and fatigue strength of die cast aluninium alloy M. Avalle, G. Belingardi, M.P. cavatorta, R. Deglione Department of mechanical engineering politechno de Torino Italy international journal of fatigue 24 2002
- [31]. Understanding the quality in aluminium casting G. K.Sigworth USAAmerican foundary society 2011
- [32]. temperature effect on tensile properties of precipation hardend alloy J.B.Ferguson, Hugo F. Lopez, Kyu Cho,and Chang Soo Kim expert of material science and technology USA
- [33]. Solidification charectristics and mechanical properties of aluminium silicon alloy containing sulfur J. Kajorncchairyakal, R. Sirichaivejakul, N moonrin, National metal and material technology center Bangkok
- [34]. The effect of microstructural charectristics and casting defects on the mechanical failure of Al based alloy Ildiko peter, Mario Rosso, Material science and chemical engineering department Italy
Expert Q&A: Your Top Questions Answered
Q1: The paper mentions that simulation software can help minimize defects. How exactly does it achieve this?
A1: According to the review of work by C. M. Choudhari et al., simulation software helps optimize the casting process faster and with better results than physical trials alone. It allows engineers to experiment with four key decisions: (1) part orientation and parting line, (2) core print design, (3) feeder design, and (4) gating design. By simulating these variables, it helps minimize bottlenecks and reduces the number of expensive and time-consuming trials required on the foundry shop floor.
Q2: What is the fundamental difference between a "blowhole" and "gas porosity" as described in the paper?
A2: The paper distinguishes them primarily by formation and appearance. A blowhole is described as a larger, rounded cavity that forms when a pocket of gas prevents liquid metal from filling a space, often occurring at high points in the mold. Gas porosity, on the other hand, is described as smaller bubbles trapped during solidification. These bubbles can come from various sources, including trapped air, hydrogen dissolved in aluminum alloys, or moisture from die lubricants, and are often internal.
Q3: The paper identifies "low pouring temperature" as a possible cause for multiple defects, including blowholes and cold shuts. Can you clarify the mechanism?
A3: The paper lists low pouring temperature as a cause for blowholes, gas porosity, and cold shuts. For cold shuts, the mechanism is direct: a lower temperature reduces the fluidity of the molten metal, so when two metal fronts meet, they are too cool to fuse together properly, creating a seam. While the paper doesn't detail the mechanism for blowholes, a lower temperature would similarly reduce fluidity, making it harder for the metal to displace gases, causing them to become trapped more easily.
Q4: What is the primary cause of "shrinkage porosity" according to this review?
A4: According to section 4.3.2, the primary cause is the natural change in density when a casting alloy transitions from a molten to a solid state. The solid state is denser, so the material shrinks in volume as it cools. If additional molten metal (feed metal) is not available to flow into the spaces created by this shrinkage, voids or porosity will form, typically at the center of the last sections to solidify.
Q5: For "Mismatch" defects, what are the specific remedies proposed in the paper?
A5: A mismatch defect is caused by the shifting of the cope and drag parts of the mold. In section 4.2.1, the paper provides direct remedies to correct this. It recommends to first check the pattern mounting on the match plate. Secondly, it advises to rectify and correct the dowels. Finally, it states that using a proper molding box and closing pins is essential to ensure alignment.
Conclusion: Paving the Way for Higher Quality and Productivity
This comprehensive review provides an invaluable roadmap for tackling the persistent challenge of Casting Defects and Remedies. By systematically categorizing defects and linking them to specific, controllable root causes, the paper empowers engineering and quality teams to move from reactive problem-solving to proactive defect prevention. The key breakthrough is the consolidation of this knowledge into a practical framework, enabling manufacturers to diagnose issues with greater accuracy and implement effective corrective actions, ultimately reducing costly rejections and improving productivity.
At CASTMAN, we are committed to applying the latest industry research to help our customers achieve higher productivity and quality. If the challenges discussed in this paper align with your operational goals, contact our engineering team to explore how these principles can be implemented in your components.
Copyright Information
- This content is a summary and analysis based on the paper "Defects, Root Causes in Casting Process and Their Remedies: Review" by "Vaibhav Ingle and Madhukar Sorte".
- Source: https://doi.org/10.9790/9622-0703034754
This material is for informational purposes only. Unauthorized commercial use is prohibited.
Copyright © 2025 CASTMAN. All rights reserved.