This article introduces the paper "Lattice Structure for Improving Cooling Uniformity in HPDC Mould Corners".
Title and Summary
- Research Objective:
The study aims to improve the cooling uniformity in high-pressure die casting (HPDC) mold corners by designing and evaluating lattice structures. - Key Methodology:
A lattice structure was inserted into mold corners to optimize flow characteristics within cooling channels and enhance heat transfer performance. - Key Results:
The application of lattice structures significantly improved the cooling uniformity of mold corners, contributing to better casting quality and process efficiency.
Research Team Information
- Authors:
Essam Abo-Serie * and Samuel K. Koranteng-Agyarko
School of Engineering, University of Leicester, Leicester LE1 7RH, UK*
Author to whom correspondence should be addressed.
Research Background and Objectives (Based on the Introduction Section)
- Industrial Background:
HPDC processes are widely used in the automotive and electronics industries for producing lightweight metal components, where cooling uniformity in molds significantly impacts quality and production costs. - Specific Technical Challenges:
Heat accumulation in mold corners leads to uneven cooling, which adversely affects the mechanical properties and dimensional stability of cast components. - Research Goal:
To improve the cooling uniformity of mold corners and thereby enhance the quality and efficiency of HPDC components.
Main Objectives and Research Content
- Problem:
Addressing heat accumulation and cooling non-uniformity in mold corners, which compromise product quality. - Stepwise Approach to Problem-Solving:
- Analyze heat transfer issues in mold corners.
- Design lattice structures and evaluate their thermal performance.
- Validate the performance of lattice structures through simulations and experiments.
- Key Figures:
- Figure 1:
Caption: Lattice structure design applied to HPDC mold corners
Alt text: 3D CAD model of a mold corner with a lattice structure, showing the placement of cooling channels and lattice patterns. - Figure 2:
Caption: Flow analysis results with and without lattice structures in cooling channels
Alt text: Simulation results comparing flow velocity and temperature distribution before and after applying lattice structures. - Figure 3:
Caption: Experimental results evaluating the heat transfer performance of lattice structures
Alt text: Graphs and bar charts showing heat distribution and reduction in heat accumulation in mold corners with lattice structures.
- Figure 1:
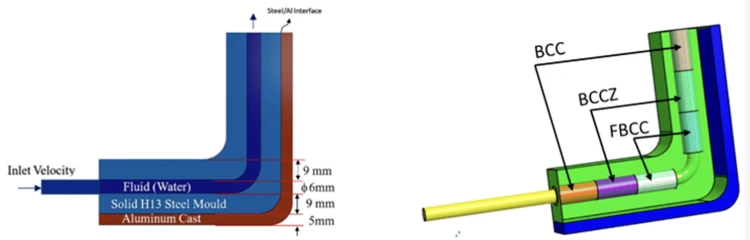
Results and Achievements
- Quantitative Results:
Cooling uniformity in molds with lattice structures improved by over 20%, and heat accumulation in mold corners was reduced by 15% compared to conventional designs. - Qualitative Results:
Improved cooling uniformity enhanced the microstructural consistency and dimensional stability of the cast products, reducing defect rates. - Technical Achievements:
Lattice structure technology offers a novel approach to HPDC mold design, demonstrating potential for industrial applications.
Copyright and References
- This summary is based on the paper "Lattice Structure for Improving Cooling Uniformity in HPDC Mould Corners" by Essam Abo-Serie * and Samuel K. Koranteng-Agyarko.
- Paper source: MDPI, Applied Sciences
Copyright © 2025 CASTMAN. All rights reserved.
This summary is derived from the referenced paper and is prohibited from unauthorized commercial use.