R.SpinaDipartimento di Ingegneria Meccanica e Gestionale, Politecnico di Bari, Bari, Italy
Abstract
This paper studies the fabrication of a plastic arm of the body interior of a medium-sized car in order to evaluate the beneficial effects of using sequential injection moulding (SIM). The main requirement for the component is optimal surface finishing to maintain an excellent surface appearance. The author has investigated the product fabrication by evaluating different hot runner systems, gating and product configurations. The SIM phases for the production of parts with these complex geometries have been studied in order to assess the product manufacturability and process feasibility through finite element (FE) analyses. FE analyses ere used to study the filling, post-filling and cooling phases of the injection process. Using the FE system, a deeper investigation of thermal stress and strain distributions was performed to predict defect presence in the final product.
부품은 우수한 표면 외관을 유지하기 위한 최적의 표면 마감 처리입니다. 저자는 다양한 핫 러너 시스템, 게이팅 및 제품 구성을 평가하여 제품 제작을 조사했습니다.
유한 요소(FE) 분석을 통해 제품 제조 가능성 및 공정 타당성을 평가하기 위해 이러한 복잡한 형상을 갖는 부품 생산을 위한 SIM 단계가 연구되었습니다. FE 분석은 사출 공정의 충전, 충전 후 및 냉각 단계를 연구하는 데 사용되었습니다.
FE 시스템을 사용하여 최종 제품의 결함 존재를 예측하기 위해 열 응력 및 변형률 분포에 대한 심층 조사가 수행되었습니다.
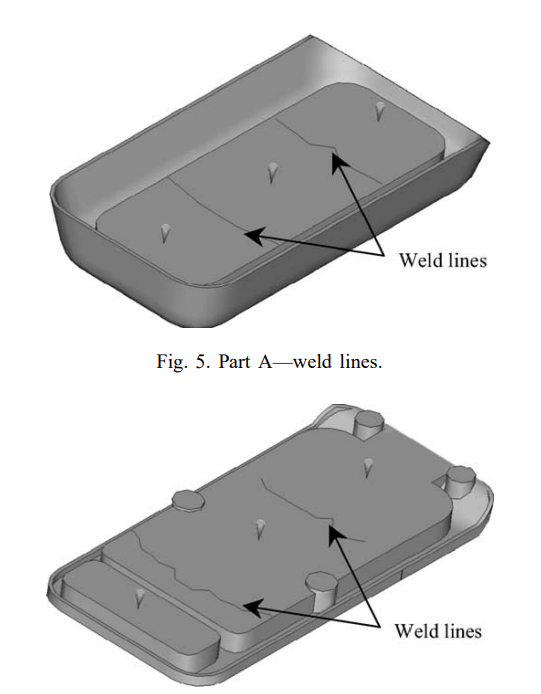
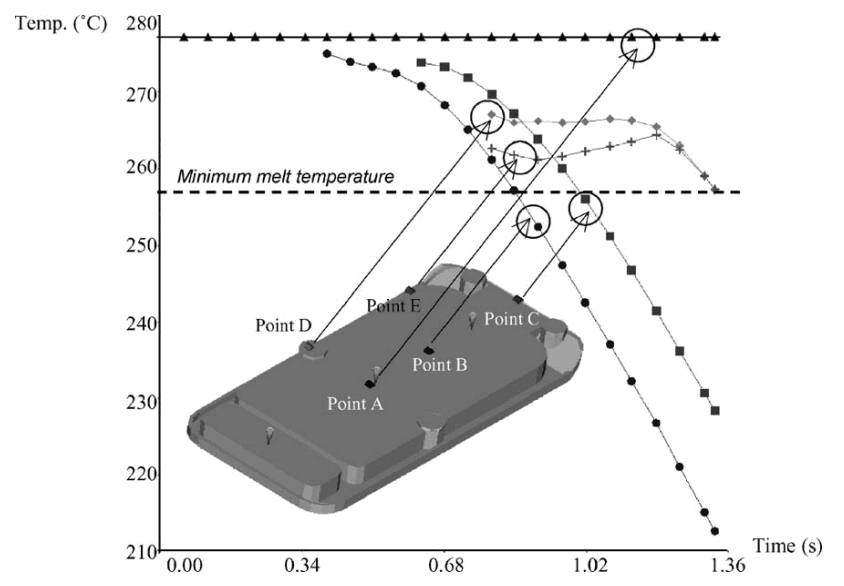
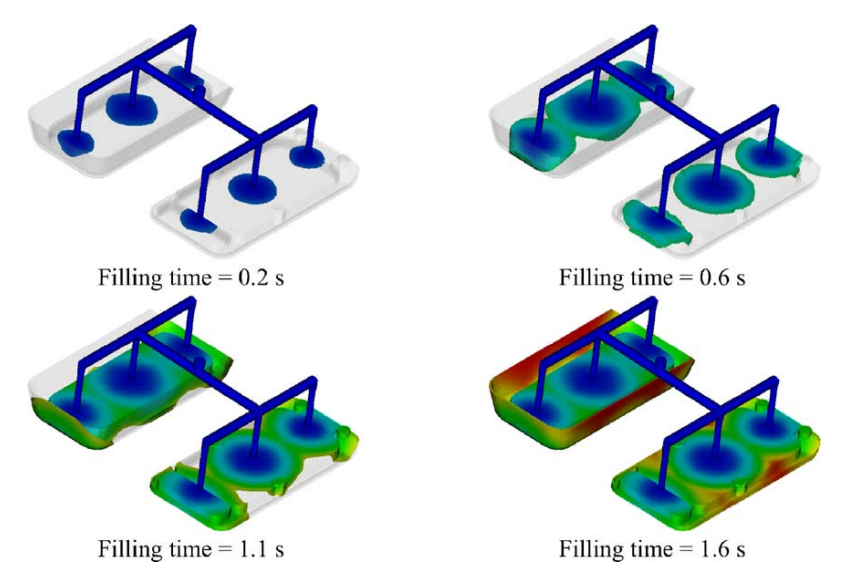
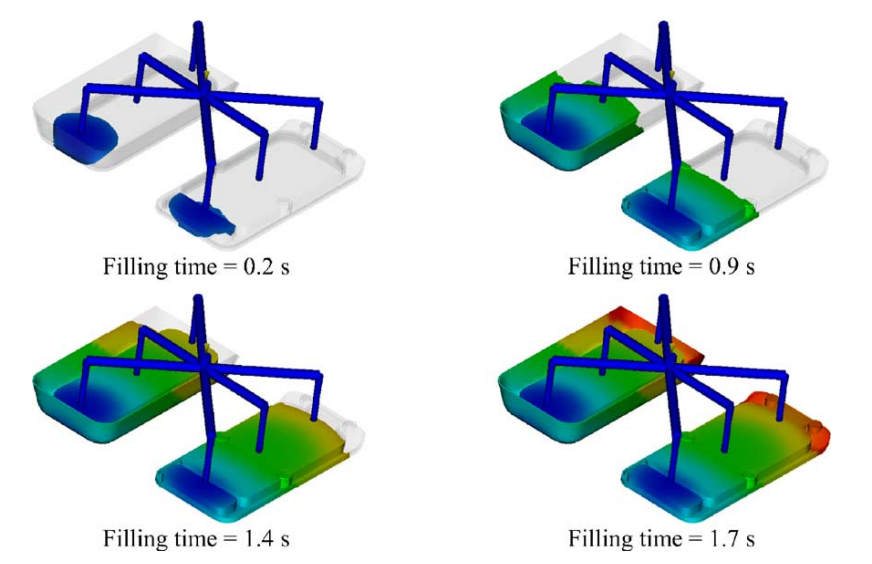
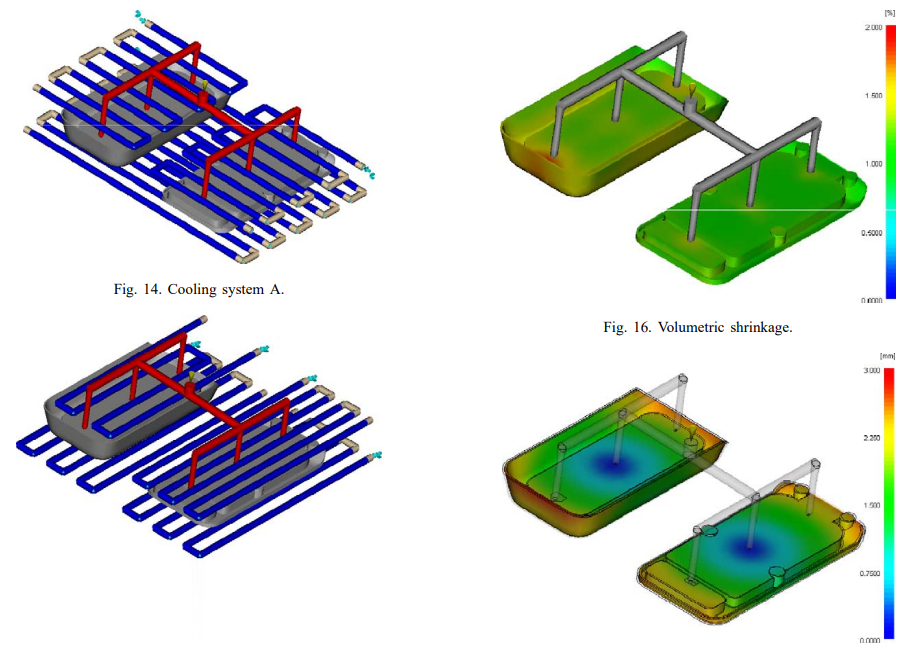
Fig. 17. Total deflection.
Keywords
Sequential injection mouldingFinite element methodAutomotive
Conclusions
The research has confirmed the advantages of using sequential injection moulding for the fabrication of aesthetic automotive parts. This research has also showed that valve timing could be performed without taking into account the cooling analysis. This feature speeded up the following analyses by designing an efficient cooling system based on the temperature field of the filling step.
The proposed methodology evaluated the efficiency sequential injection moulding in process improvement by avoiding weld lines before production set-up. The FE numerical simulations allowed the deflections of warped surfaces to be estimated and in-depth analyses to be performed in order to aid process engineers on how to position gates and/or modify mould design.
Moreover, the proposed approach can be enhanced by directly monitoring and optimizing process parameters on the control system of the injection-moulding machine. Further research must be addressed towards the use of pressure sensors in order to increase the prediction capabilities of FE software.
Cited by (45)
- Efficiency and agility of a liquid CO
2 cooling system for molten metal systems2021, Case Studies in Thermal EngineeringShow abstract - The die turning injection (DTI) process for the fabrication of hollow parts2012, Journal of Materials Processing TechnologyShow abstract
- Neuro Fuzzy Based Runner Selection for Plastic Injection Moulding Design2022, Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems
- Rapid numerical estimation of pressure drop in hot runner system2021, Micromachines
- A literature review on injection moulding process based on runner system and process variables2021, IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering
- Advanced melt rheology control: A filling defects investigation for hot runner based injection molding2021, ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Proceedings (IMECE)