This article introduces the paper ['Design and Analysis of Permanent Mould for Small Internal Combustion Engine Piston'] published by ['Jordan Journal of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering'].
1. Overview:
- Title: Design and Analysis of Permanent Mould for Small Internal Combustion Engine Piston
- Author: Olurotimi Akintunde Dahunsia, Olatunji Oladimeji Ojob*, Ikeoluwa Ogedengbea, Omeiza Bayode Maliki
- Publication Year: 2020
- Publishing Journal/Academic Society: Jordan Journal of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering
- Keywords: Permanent Mould, Mould Design, Piston, Casting, Mechanical properties; Aluminum alloy;
2. Abstracts or Introduction
The abstract of the paper states that the research addresses the issue of piston waste due to the short service life of generators in areas with unreliable power supply. The study focuses on designing, thermally analyzing, and fabricating a permanent mould for casting 950 Watts generator pistons from recycled piston waste. The mechanical and microstructural properties of the as-cast pistons were evaluated and compared to LM13 alloy. The results indicated the production of defect-free pistons, with slight compositional changes compared to LM13, while maintaining comparable properties.
3. Research Background:
Background of the Research Topic:
The research background highlights the increased use of portable generators in regions with poor electrical infrastructure, leading to generators exceeding their recommended service life and causing piston burnout. This results in frequent piston replacements and a growing volume of piston waste. The paper identifies an opportunity to recycle these waste pistons to create a sustainable piston market. Pistons are critical components in internal combustion engines, requiring good strength and heat resistance. Al-Si alloys are widely used for pistons due to their desirable properties such as thermal conductivity, high strength-to-weight ratio, and castability.
Status of Existing Research:
Existing research is focused on improving piston performance and material properties through various casting techniques and material modifications. The paper mentions studies on:
- High pressure die casting vs. permanent mold casting of Al-Si-Cu-Ni-Mg alloy [13].
- Squeeze casting of Al-Si piston alloy reinforced with Ni and nano-Al2O3 particles [14].
- Thermal barrier coatings on Al-Si piston alloys [7].
- Grain refiners and modifiers in hyper-eutectic Al-15Si-4Cu alloy [6].
- Fracture analysis of automotive piston material [15].
- Comparison of Al-Si pistons with aluminum pistons [16].
- Recycling of Al-Si pistons from scraps [17] [18].
These studies indicate ongoing efforts to enhance the mechanical properties and performance of Al-Si alloy pistons through different casting methods and material enhancements. However, the paper points out that defected pistons and undesirable results are often associated with casting processes like sand casting, highlighting the need for more reliable methods.
Necessity of the Research:
The research is necessary to investigate self-support casting processes, specifically permanent mould casting, to achieve reproducible piston production from recycled materials without the need for mould preparation for each casting. This addresses the environmental concern of piston waste and aims to establish a sustainable manufacturing approach for piston production, particularly relevant in regions with high generator usage and piston waste accumulation.
4. Research Purpose and Research Questions:
Research Purpose:
The primary research purpose is to design, analyze, and fabricate a permanent mould for casting 950 Watts generator pistons using recycled Al-Si alloy. The study aims to evaluate the effectiveness of the designed mould in producing defect-free pistons and to assess the mechanical and microstructural properties of the as-cast pistons.
Key Research:
The key research focuses on:
- Conceptual design of a permanent mould with a non-destructive core for 950 Watts generator pistons.
- Thermal analysis of the designed mould to understand heat transfer characteristics.
- Fabrication of the designed permanent mould.
- Casting of pistons using the fabricated mould and recycled Al-Si alloy.
- Evaluation of the mechanical and microstructural properties of the as-cast pistons.
- Comparison of the as-cast piston properties with those of LM13 alloy.
Research Hypotheses:
The paper does not explicitly state research hypotheses. However, implicitly, the research operates under the hypothesis that a properly designed permanent mould can effectively cast defect-free pistons from recycled Al-Si alloy, achieving comparable mechanical and microstructural properties to standard piston alloys like LM13.
5. Research Methodology
Research Design:
The research employs a design and experimental methodology. It involves the conceptual design of a permanent mould, followed by thermal simulation and experimental validation through mould fabrication and casting experiments.
Data Collection Method:
Data was collected through:
- Thermal Simulation: Temperature distribution data within the mould and core was obtained using COMSOL Multiphysics software.
- Mechanical Testing: Tensile strength and hardness of the as-cast pistons were measured.
- Microstructural Analysis: Optical microscopy was used to examine the microstructure of the as-cast pistons.
- Chemical Composition Analysis: The chemical composition of the as-cast pistons was determined and compared to LM13 alloy.
Analysis Method:
- Thermal Simulation Analysis: The temperature distribution plots were analyzed to assess the heat transfer characteristics of the mould and core during the casting process.
- Mechanical Property Comparison: The tensile strength and hardness values of the as-cast pistons were compared to the properties of LM13 alloy.
- Microstructural Evaluation: Micrographs were analyzed to identify the microstructural features, such as dendrites and grain structures, and to assess the presence of defects.
- Compositional Comparison: Chemical composition analysis results were compared to the standard composition of LM13 alloy to identify any deviations.
Research Subjects and Scope:
The research subjects are:
- Design and analysis of a permanent mould for casting small internal combustion engine pistons.
- Casting of 950 Watts generator pistons using recycled Al-Si alloy scraps.
- Evaluation of the properties of the as-cast pistons.
The scope of the research is limited to:
- Conceptual design, thermal analysis, and fabrication of a permanent mould.
- Casting and characterization of pistons for 950 Watts generators.
- Use of recycled Al-Si alloy scraps as the casting material.
- Evaluation of mechanical and microstructural properties and comparison with LM13 alloy.
6. Main Research Results:
Key Research Results:
- Successful Mould Design and Fabrication: A permanent mould for casting 950W pistons was successfully designed and fabricated from mild steel (AISI 1065 carbon steel).
- Effective Thermal Dissipation: Thermal simulation showed that the steel mould facilitated satisfactory thermal dissipation during casting.
- Defect-Free Castings: Defect-free pistons were produced using the permanent mould, with no inherent matrix defects observed in the microstructure.
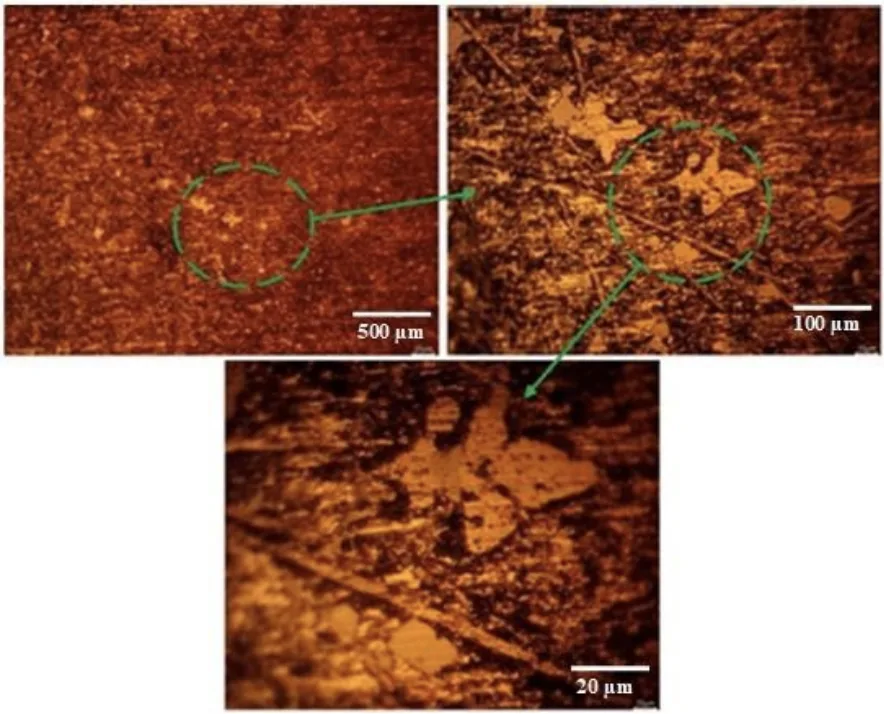
- Microstructure: The microstructure of the as-cast pistons consisted of solidification-induced dendrites and fine grain structures (Figure 11).
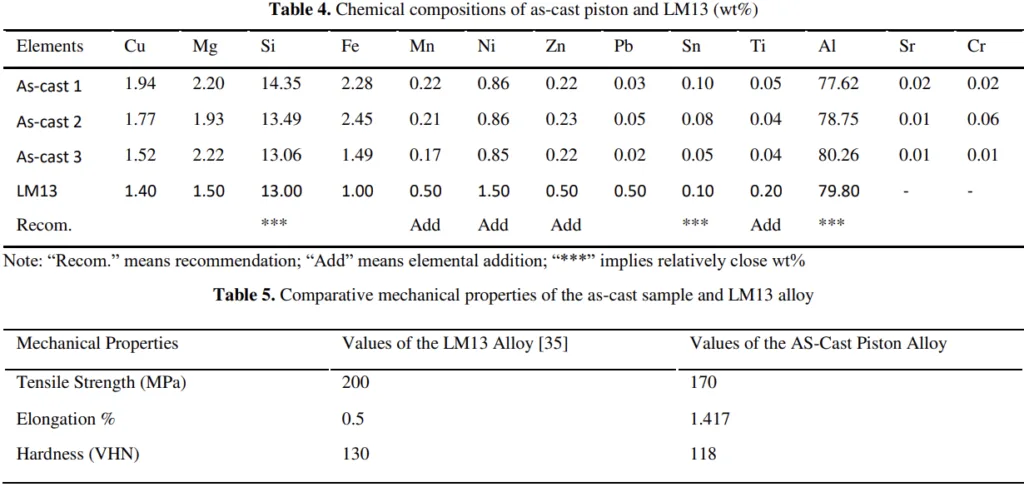
- Slight Compositional Variation: The chemical composition of the as-cast alloy showed slight variations compared to LM13 alloy (Table 4).
- Comparable Mechanical Properties: The average tensile strength and hardness of the as-cast pistons were slightly lower (15% and 9% respectively) than LM13, while elongation was significantly improved (Table 5).
Analysis of presented data:
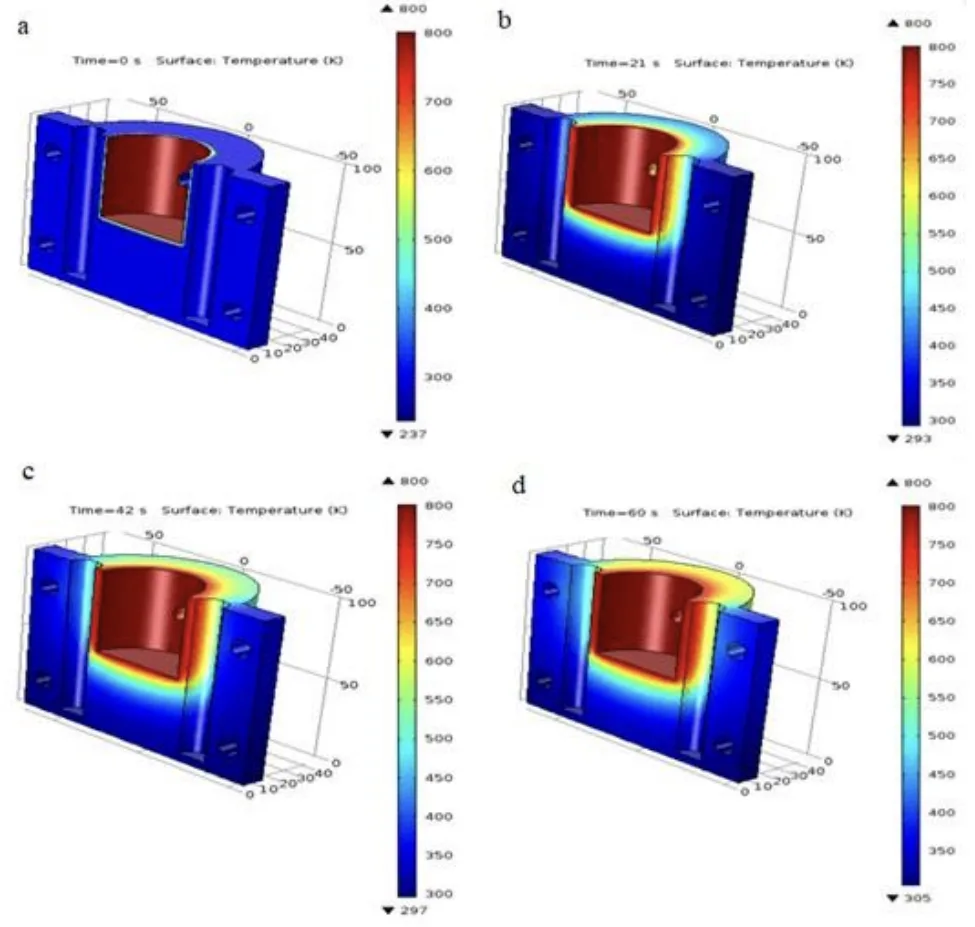
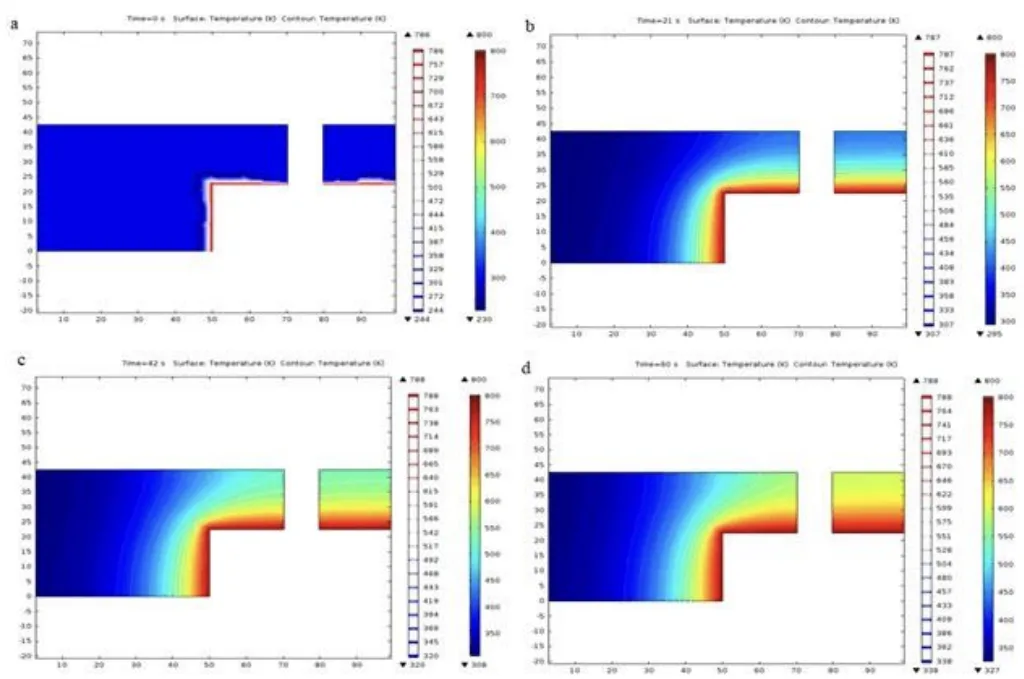
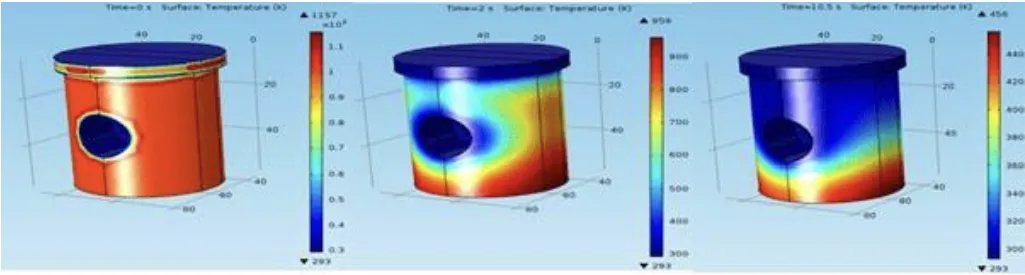
- Thermal Analysis: Figures 6, 7, and 8 illustrate the temperature distribution in the mould and core at different times after pouring. The analysis indicates effective heat transfer from the molten metal to the mould, with the mould acting as a heat sink. The core also contributes to heat dissipation, and the steel mould material's thermal conductivity facilitates rapid cooling.
- Microstructural Analysis: Figure 11 shows the microstructure of the as-cast piston, revealing a dendritic structure and fine grains, indicative of rapid solidification facilitated by the permanent mould. The absence of macro-pores suggests effective venting by the designed gating system.
- Mechanical Properties: Table 5 compares the mechanical properties of the as-cast piston with LM13 alloy. While tensile strength and hardness are slightly reduced, the improved elongation suggests enhanced ductility, potentially due to the refined microstructure.
- Compositional Analysis: Table 4 shows the chemical composition of the as-cast pistons compared to LM13. Minor variations are observed, which could be attributed to the recycling process and variations in the scrap material.
Figure Name List:
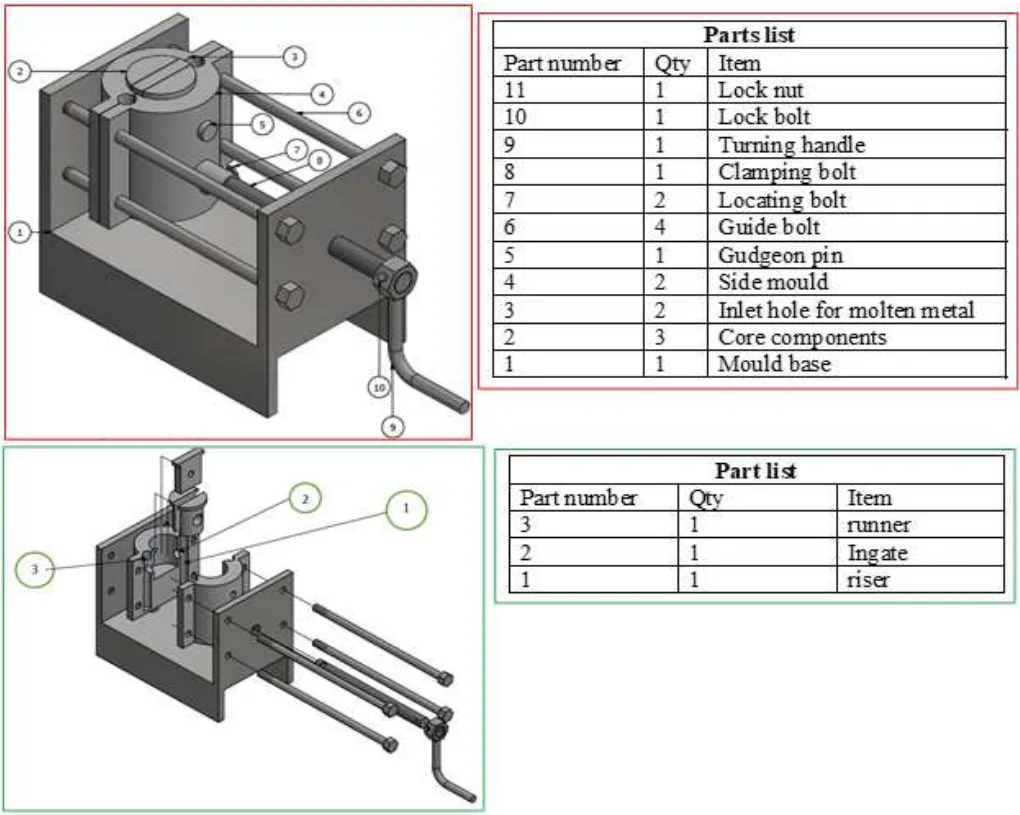

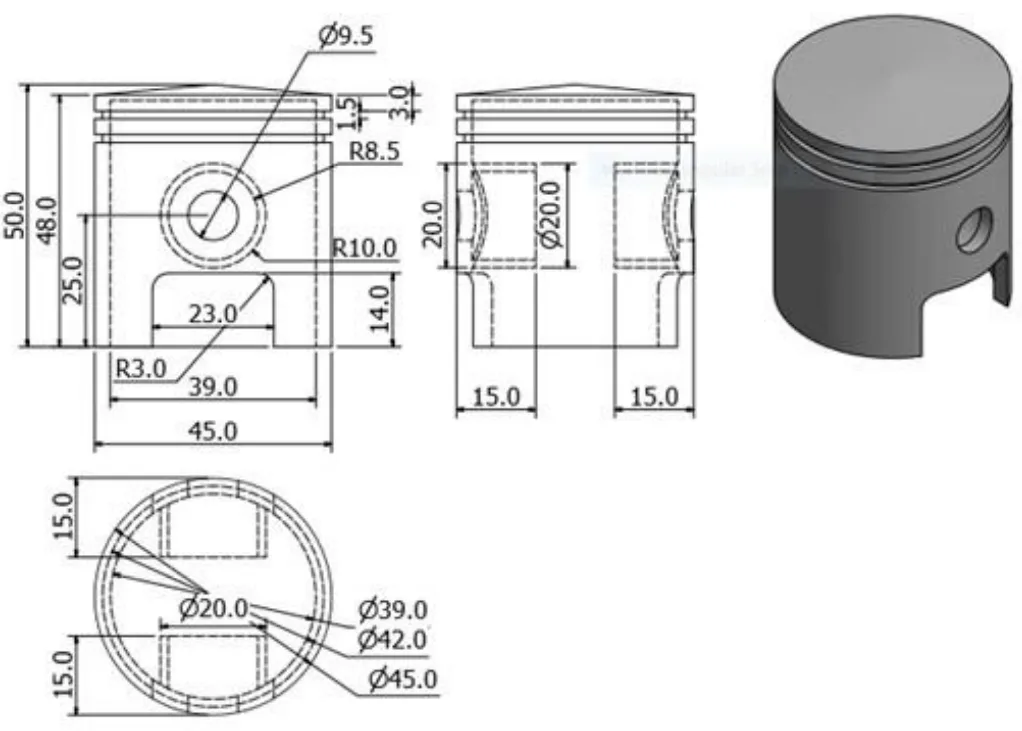
- Figure 1. Standard dimensions (mm) of a 950 W electric power generator piston
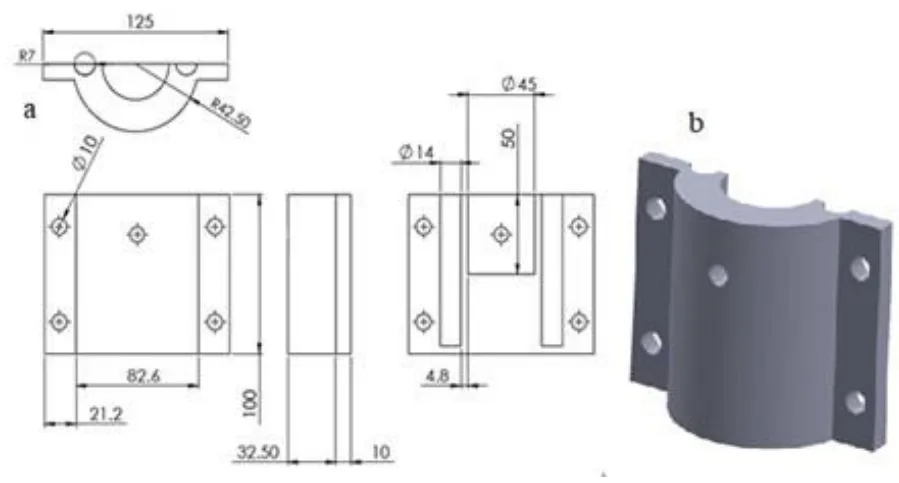
- Figure 2. Mould half (split mould) (a) projection views; (b) isometric drawing
- Figure 3. An assembled model of the permanent mould
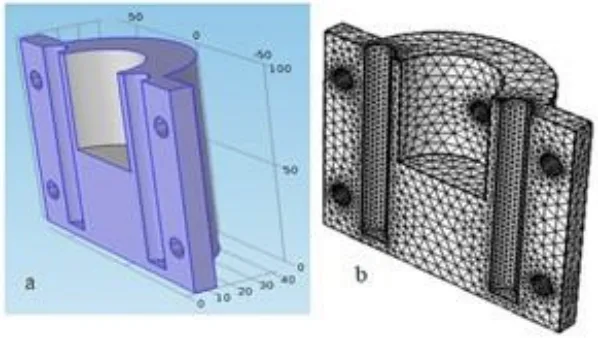
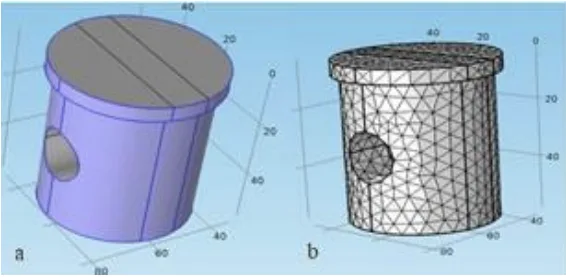
- Figure 4. Cast piston permanent mould on (a) Movable half of mould; (b) discretized mould
- Figure 5. Geometry of the piston core (a) unmeshed core; (b) discretized/meshed core
- Figure 6. Surface temperature distribution in the movable mould at different times (a) 0 s time; (b) 21 s time; (c) 42 s time and (d) 60 s time
- Figure 7. Thermal plot through the central section of the mould at different times (a) 0 s time; (b) 21 s time, (c) 42 s time, and (d) 60s time
- Figure 8. Surface temperature distribution around the piston core at different times (a) 0 s time; (b) 2 s time and (c) 10.5 s time
- Figure 9. Unmachined cast pistons
- Figure 10. Machined cast pistons
- Figure 11. Microstructure of the as-cast piston
7. Conclusion:
Summary of Key Findings:
The study successfully demonstrated the design, fabrication, and application of a permanent mould for casting 950 Watts generator pistons from recycled Al-Si alloy scraps. The key findings include the effectiveness of the steel mould in thermal dissipation, the production of defect-free pistons with a refined dendritic microstructure, and the achievement of mechanical properties comparable to LM13 alloy, with improved ductility.
Academic Significance of the Study:
This study contributes to the field of die casting by providing a detailed methodology for designing and analyzing permanent moulds for complex shapes like pistons. The thermal simulation and experimental validation provide valuable insights into the heat transfer phenomena during permanent mould casting. The research also highlights the potential of using recycled aluminum alloys for producing critical engine components, contributing to sustainable manufacturing practices.
Practical Implications:
The practical implications of this study are significant for regions facing challenges with piston waste management and the need for cost-effective piston production. The developed permanent mould technology offers a viable solution for recycling Al-Si piston scraps to manufacture new pistons, reducing waste and creating a sustainable supply chain. This approach can be particularly beneficial for local manufacturing and repair industries in developing economies.
Limitations of the Study and Areas for Future Research:
The study acknowledges that the surface finish of the as-cast pistons was slightly rough due to machining-induced roughness in the mould cavity. The suitability of the produced pistons for harsh service conditions was not directly evaluated. Future research directions include:
- Optimizing the mould cavity surface finish to improve the surface quality of as-cast pistons.
- Conducting performance testing of the as-cast pistons under engine operating conditions to validate their durability and reliability.
- Investigating the effect of elemental additions (Mn, Ni, Zn, Ti) to the recycled Al-Si alloy to further improve the mechanical properties and match the composition of LM13 more closely.
- Exploring the scalability of this permanent mould casting process for mass production.
8. References:
- [1] A. Ahmed, M.S. Wahab, A.A. Raus, K. Kamarudin, Q. Bakhsh, D. Ali, "Mechanical Properties, Material and Design of the Automobile Piston: An Ample Review". Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol. 9, No. 36, 2016, 1-7
- [2] S. Lombardo, I. Peter, M. Rosso, "Gravity Casting of Variable Composition Al Alloys: Innovation and New Potentialities". Materials Today: Proceedings, Vol. 10, 2019, 271-276
- [3] H. Pandey, A. Chandrakar, "Computer-Aided Modeling and Simulation of IC Engine Speculative Piston". International Journal of Innovations in Engineering and Technology, Vol. 4, 2014, 30-36.
- [4] R. Subbarao, S. V. Gupta, "Thermal and structural analyses of an internal combustion engine piston with suitable different superalloys". Materials Today: Proceedings, Vol. 22, 2020, 2950-2956
- [5] A.W. Orłowicz, M. Tupaj, M. Mróz, A. Trytek, "Combustion Engine Cylinder Liners Made of Al-Si Alloys". Archives of Foundry Engineering, Vol. 15, 2015, 71-74.
- [6] P.V. C. S. Rao, A. S. Devi, K.G. B. Kumar, "Influence of Melt Treatments on Dry Sliding Wear Behavior of Hypereutectic Al-15Si-4Cu Cast Alloys". Jordan Journal of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering, Vol. 6 (1), 2012, 55-61
- [7] V.R. Reghu, N. Mathew, P. Tilleti, S. V, P. Ramaswamy, "Thermal Barrier Coating Development on Automobile Piston Material (Al-Si alloy), Numerical Analysis and Validation". Materials Today: Proceedings, Vol. 22, Vol. 2020, 1274-1284
- [8] J. Kumar, D. Singh, N. S. Kalsi, S. Sharma, C. I. Pruncu, D. Y. Pimenov, K. V. Rao, W. Kapłonek, "Comparative study on the mechanical, tribological, morphological and structural properties of vortex casting processed, Al-SiC-Cr hybrid metal matrix composites for high strength wear-resistant applications: Fabrication and characterizations". Journal of Materials Research Technology, Vol. 9(6), 2020, 13607-13615
- [9] B.N. Yadav, D. Muchhala, A. Abhash, P. Singh, R. Kumar, D.P. Mondal, "Fabrication of ultra-light LM13 alloy hybrid foam reinforced by MWCNTs and SiC through stir casting technique". Materials Letters, Vol. 279, 2020, 128271
- [10] M. Goenka, C. Nihal, R. Ramanathan, P. Gupta, A. Parashar, J. Joel, "Automobile Parts Casting-Methods and Materials Used: A Review". Materials Today: Proceedings, Vol. 22, 2020, 2525-2531
- [11] M. Azadi, H. Bahmanabadi, F. Gruen, G. Winter, "Evaluation of tensile and low-cycle fatigue properties at elevated temperatures in piston aluminum-silicon alloys with and without nano-clay-particles and heat treatment". Materials Science & Engineering A, Vol. 788, 2020, 139497
- [12] G. Chirita, D. Soares, F.S. Silva, "Advantages of the centrifugal casting technique for the production of structural components with Al-Si alloys". Materials and Design, Vol. 29, 2008, 20-27.
- [13] J.-Y. Zhang, L.-J. Zuo, J. Feng, B. Ye, X.-Y. Kong, H.-Y. Jiang, W.-J. Ding, "Effect of thermal exposure on microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-Si-Cu-Ni-Mg alloy produced by different casting technologies". Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, Vol. 30, 2020, 1717-1730
- [14] H.F. El-Labban, M. Abdelaziz, E.R.I. Mahmoud, "Preparation and characterization of squeeze cast-Al-Si piston alloy reinforced by Ni and nano-Al2O3 particles". Journal of King Saud University - Engineering Sciences, Vol. 28, 2016, 230-239.
- [15] G. Zhang, J. Zhang, B. Li, W. Cai, "Characterization of tensile fracture in heavily alloyed Al-Si piston alloy". Progress in Natural Science: Materials International, Vol. 21, 2011, 380-385.
- [16] M.S. Divya, K.R. Gopal, "Design and Material Optimization of the Piston by using PRO E and ANSYS". International Journal of Advanced Scientific Technologies in Engineering and Management Sciences, Vol. 2, 2016, 14-20.
- [17] F.U. Ozioko, "Casting of Motorcycle Piston from Aluminium Piston Scrap using Metallic Mould". Leonardo Electronic Journal of Practices and Technologies, Vol. 21, 2012, 82-92.
- [18] S.O. Adeosun, E.I. Akpan, D. Abiodun, "Mould Temperature and Mechanical Properties of Cast Aluminum-Silicon Carbide Composite". International Journal of Materials and Chemistry, Vol. 3, 2013, 75-83.
- [19] M.B. Ndaliman, P.A. Pius, "Behavior of Aluminum Alloy Castings under Different Pouring Temperatures and Speeds". Leonardo Electronic Journal of Practices and Technologies, Vol. 11, 2007, 71-80.
- [20] R.G. Narayanan, Metal casting Processes, Indian Institute of Technology Gawahati [Internet] Available: https://www.slideshare.net/anjanpatel1/metal-casting-processes-89647585 [Accessed on 10th August 2017].
- [21] B.H. Hu, K.K. Tong, X.P. Niu, I. Pinwill, "Design and optimization of runner and gating systems for the die casting of thin-walled magnesium telecommunication parts through numerical simulation". Journal of Materials Processing Technology, Vol. 105, 2000, 128-133.
- [22] S.H. Wu, J.Y.H. Fuh, K.S. Lee, "Semi-automated parametric design of gating systems for die-casting die". Computers & Industrial Engineering, Vol. 53, 2007, 222-232.
- [23] Z. Jie, Z. Dongqi, W. Pengwei, W. Gang, L. Feng, D. Penglong, "Numerical Simulation Research of Investment Casting for TiB2/A356 Aluminum Base Composite". Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, Vol. 43, 2014, 0047-0051.
- [24] Α.Κ.Μ.Β. Rashid, Design of Gating and Feeding Systems [Internet]. Available: http://foundrygate.com/upload/artigos/K3ePtMbZRtz4gRWOTfVVjj3gbKc7.pdf [Accessed: 20th September 2017].
- [25] S. Santhi, B.R. Surya, S. Jairam, J. Jhansi, P.K.S. Subramanian, "Design of Gating and Riser System for Grate Bar Casting". Indian Foundry Journal, Vol 61, 2015, 19-23.
- [26] M.P. Groover, Fundamentals of modern manufacturing materials, processes, and systems. 3rd ed. John Wiley and Sons, Inc., 2007.
- [27] AZO Materials. AISI 1065 Carbon Steel (UNS G10650) [Internet] Available: https://www.azom.com/article.aspx?ArticleID=6575 [Accessed: 16th October, 2017].
- [28] S.K. Sharma, P.K. Saini, N.K. Samria, "Experimental Thermal Analysis of Diesel Engine Piston and Cylinder Wall". Journal of Engineering, 2015, 1-10.
- [29] H. Wang, G. Djambazov, K.A. Pericleous, R.A. Harding, M. Wickins, "Modelling the dynamics of the tilt-casting process and the effect of the mould design on the casting quality". Computers & Fluids, Vol. 42, 2011, 92-101.
- [30] S.M.H. Mirbagheri, M. Shrinparvar, A. Chirazi, "Modeling of metalo-static pressure on the metal-mould interface thermal resistance in the casting process". Materials and Design. Vol. 28, 2007, 2106-2112.
- [31] M.M.A. Rafique, J. Iqbal, "Modeling and simulation of heat transfer phenomena during investment casting". International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, Vol. 52, 2009, 2132-2139.
- [32] N. Gharaibeh, M. AlAjlouni, A. Al-Rousan, "Olive Mill Wastewater as Cutting Fluids: Effect on Surface Roughness of Aluminum". Jordan Journal of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering, Vol. 12(3), 2018, 161 – 166
- [33] R. Chen, Q. Xu, H. Guo, Z. Xia, Q. Wu, B. Liu, "Correlation of solidification microstructure refining scale, Mg
- [34] L. M. Shehadeh, I. S. Jalham, "The Effect of Adding Different Percentages of Manganese (Mn) and Copper (Cu) on the Mechanical Behavior of Aluminum". Jordan Journal of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering, Vol. 10 (1), 2016, 19-26
- [35] G.B. Mallikarjuna, K.V.S. Rao, R.H. Jayaprakash, "Preparation and Property Evaluation of Aluminium-Silica Composites by Casting Route". International Journal of Mechanical engineering and Robotics, Vol. 1, 2012, 118 – 124.
9. Copyright:
- This material is "Olurotimi Akintunde Dahunsia, Olatunji Oladimeji Ojob*, Ikeoluwa Ogedengbea, Omeiza Bayode Maliki"'s paper: Based on "Design and Analysis of Permanent Mould for Small Internal Combustion Engine Piston".
- Paper Source: https://doi.org/10.35191/jjmie.2020.14.4.07
This material was summarized based on the above paper, and unauthorized use for commercial purposes is prohibited.
Copyright © 2025 CASTMAN. All rights reserved.