AUTHORS P. Jelínek1, E. Adámková1, F. Mikšovský1, J. Beňo1
ABSTRACT
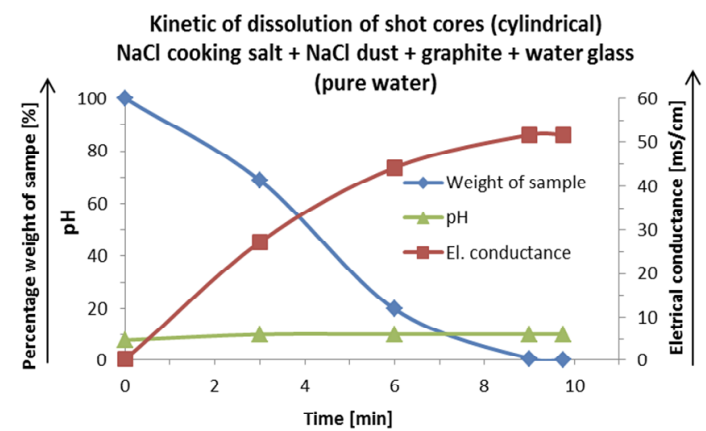
A number of technologies is developed that substitute simple metal cores in the high-pressure casting technology. Soluble cores, namely on the salt basis, represent the highest prospect. The contribution gives the results of the production of salt cores by high-pressure squeezing and shooting with using a binder. Special attention is paid to the shape of NaCl salt crystals with additives and the influence on strength properties of cores. A technology of bonding the salt cores is developing. Salinity of circulating water is studied and it is checked with the aid of electrical conductance.
KEYWORDS
salt cores, manufacture, squeezing, shooting, cooking salt, bonding of cores, salinity, cleaning water, electric conductance

BIBLIOGRAPHY
- Pacyniak, R. & Kaczorowski, R. (2010). Ductile cast iron obtaining by Inmold method with use of LOST FOAM process. Archives of Foundry Engineering. 10(1), 101-104. ISSN: 1897-3310.
- Michels, H., Bűnck, M. & Bűhrig – Polaszek, A. (2010). Suitability of lost cores in rheocasting process. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China. 20, 948-953. DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(10)60612-7.
- Dańko, J., Dańko, R. (2009). Theoretical and technological aspects of the production processes of foundry cores blown In 50. Konferencji Krzepniecie i Krystalizacja Metali (pp. 71-86). Katowice – Gliwice, Poland: Polska Academia Nauk, Komisja Odlewnictwa. ISBN: 978-83-929266-0-3. (in Polish).
- Holtzer, M., Dańko, R. (2009). Theory and practice of regeneration and utilization of waste molding and core. In 50. Konferencji Krzepniecie i Krystalizacja Metali (pp. 133-152). Katowice – Gliwice, Poland: Polska Akademia Nauk, Komisja Odlewnictwa. ISBN: 978-83-929266-0-3. (in Polish).
- Kallien, L., Bőhnlein, Ch., Dworak, A. & Műller, B. (2013). Ergebnisse aus dem Forschungsprojekt 3-D-Freiform –medienführende Kanäle im Druckguss. Giesserei Praxis. 100(12), 36-43. ISSN: 0016-9781.
- Fuchs, B., Eibisch, H. & Körner, C. (2013). Core viability simulation for salt core technology in high – pressure die casting. International Journal of Metalcasting. 7(3), 39-45. ISSN: 1939-5981.
- Fuchs, B., et. all (2014). Angepasste Wärmebehandlung von druckgegossenen Aluminiumstrukturbauteilen mit verlorenem Salzkerne. Giesserei Praxis. 101(06), 52-59. ISSN:0016-9781.
- Yaokawa, J., Miura, D., Anzai, K., Yamada, Y., & Yoshii, H. (2007). Strength of salt core composed of alkali carbonate and alkali chloride mixtures made by casting technique. Materials transactions. 48(5), 1034-1041.
- Stingl, P., & Shiller, G. (2009). Gichte und rückstandfreie Entkernung – Salzkerne für den Aluminiumguss. Giesserei-Erfahrungsaustausch. 6, 4-8.
- Adámková, E., Jelínek, P., & Študentová, S. (2013). Application of cooking salts in manufacture of water soluble cores for high pressure die casting (Aplikace kuchyňských solí při výrobě vodou rozpustných jader odlitků tlakového lití). Materials and technology. 61(11-12), 689-693. ISSN: 1580-2949, 1580-3414.
- Jelínek, P., Mikšovský, F., Beňo, J. & Adámková, E. (2013). Development of Foundry Cores Based on Inorganic Salts. Materials and technology. 47(6), 689-693. ISSN: 1580-2949, 1580-3414.
- Fuchs, B. & Körner, C. (2013). Dwell pressure induced compression of lost salt cores in high pressure die casting. International Foundry Research. 3, 18-23. ISSN: 0046-5933.
- Rupp, S. & Heppes, F. (2013). Combicore – Giesskerne für den Druckguss. Giesserei-Erfahrungsaustausch. 3/4, 6-9.
- Fabbroni, M. (2013) Lost Core Ein industrieller Prozesspfad für hochwertige Salzkerne. Giesserei Praxis. 100(07), 82-83. ISSN: 0016-9781.
- Kaneko, Y. & Morita, A. (1970) 6th SDCE international die casting congress. PAPER NO. 91, Cleveland, Ohio, November 16 – 19.
- Loper, C. R. et. all. (1985) The Use of Salt In Foundry Cores. AFS Transactions, 85 – 82, 545-560.
- Jelínek, P., Mikšovský, F., & Adámková, E. (2012). Influencing the strength characteristics of salt cores soluble in water. Slévárenství. 60(3-4), 85-89. ISSN: 0037-6825.
- Major–Gabryś, K., & Dobosz, M. (2009). A new ester hardener for moulding sands with water glass having slower activity. Archives of Foundry Engineering. 9(4), 125-128. ISSN: 1897-3310.