This article introduces the paper "Materials in Automotive Engineering".
1. Overview:
- Title: Materials in Automotive Engineering
- Authors:
- Jeremija JEVTIC
- Radinko GLIGORIJEVIC
- Djuro BORAK
- Published Year: May 18th, 2007
- Published Journal/Conference: MACHINE DESIGN, Faculty of Technical Sciences, Novi Sad, 47th Anniversary of the Faculty
- Keywords:
- automotive materials
- CGI
- Al
- Mg-alloys
- plastic
2. Research Background:
- Social/Academic Context of Research Topic:
- The automotive industry worldwide is facing pressure to comply with strict emission regulations.
- A major challenge for the automotive industry is to improve performance and fuel economy while meeting increasingly stringent exhaust emission standards.
- The transport sector is a significant contributor to NOx and particulate emissions, as well as CO2 emissions from vehicles.
- Reducing vehicle weight is essential to achieve emission reduction goals.
- The greatest diesel engine problems are NOx and particulate emissions, and one way to reduce these is to increase cylinder peak-fire pressures.
- To meet these objectives, new stronger materials are needed for crankcases.
- Compacted graphite iron (CGI) is one of the best durability materials that supports modern HSDI engines without increasing size or weight.
- Limitations of Existing Research:
- The paper does not explicitly mention limitations of existing research, but it implies the need for alternatives to traditional materials like gray cast iron and aluminum alloys to meet new emission regulations and performance demands, thus highlighting the necessity for research into CGI, aluminum alloys, magnesium alloys, and plastics.
- Necessity of Research:
- There is an increasing need to reduce the weight of automotive components and develop stronger, lighter materials.
- Especially for heavy-duty diesel engines, reducing NOx and particulate emissions is critical, necessitating higher cylinder peak-fire pressures.
- Research is needed to explore and evaluate new materials suitable for engine components like crankcases.
3. Research Objectives and Research Questions:
- Research Objectives:
- To review the characteristics of compacted graphite iron in comparison with flake graphite cast iron and aluminum alloys, which are used for cylinder blocks.
- To provide a review of new aluminum and magnesium alloys, as well as plastics.
- Core Research Questions:
- What are the characteristics of compacted graphite iron (CGI) as a cylinder block material compared to conventional flake graphite cast iron and aluminum alloys?
- What are the characteristics and applicability of newly developed aluminum alloys, magnesium alloys, and plastics for lightweighting in the automotive industry?
- Research Hypothesis:
- While not explicitly stated as a hypothesis, the paper suggests that compacted graphite iron (CGI) exhibits superior properties in terms of strength, stiffness, and fatigue strength compared to flake graphite cast iron and aluminum alloys, making it suitable for high-performance diesel engine cylinder blocks.
4. Research Methodology
- Research Design:
- This research is a review paper analyzing and comparing the properties of various automotive materials.
- It analyzes material characteristics and application trends in the automotive industry based on existing research literature and data.
- Data Collection Methods:
- Data is collected through literature review of existing research papers, technical reports, and industry data.
- Material properties, performance data, and application examples of various materials are collected for comparative analysis.
- Analysis Methods:
- Comparative analysis of material characteristics is performed based on collected data.
- Tables (Table 1) and figures (Fig. 1, 2, 3) are used to visually compare material properties and performance.
- Advantages, disadvantages, and application areas of each material are analyzed, and their applicability in the automotive industry is evaluated.
- Research Subjects and Scope:
- The research focuses on materials for automotive engine cylinder blocks.
- The main materials studied are:
- Gray cast iron (CI)
- Compacted graphite iron (CGI)
- Aluminum alloy (Al-alloy)
- Spheroidal graphite iron (SGI)
- Additionally, trends in magnesium alloys (Mg-alloys) and plastics used for lightweighting in the automotive industry are briefly covered.
5. Key Research Findings:
- Core Research Findings:
- Characteristics of Compacted Graphite Iron (CGI):
- CGI has "about 75% higher strength, 40% higher stiffness and almost twice the fatigue strength of gray iron" (Fig. 1, Table 1).
- Compared to Al-alloy, CGI has "three times the fatigue strength."
- CGI's high strength and stiffness allow for higher cylinder pressures (up to 200 bars), making it suitable for high-performance diesel engines (Fig. 2).
- A diesel engine with CGI components can be as light as an aluminum diesel engine, resulting in better fuel economy and lower emissions.
- CGI has good dimensional stability, reducing cylinder liner deformation and oil consumption.
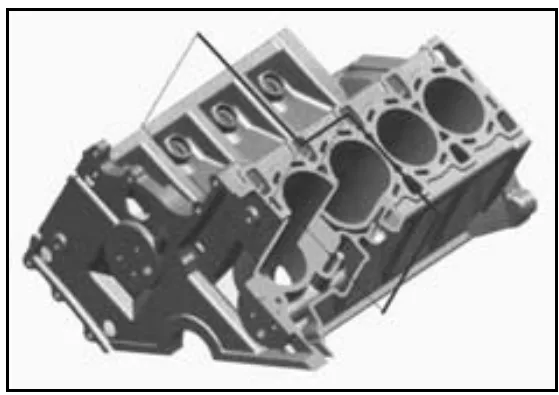
- CGI provides additional strength in the critical Z-shaped section between bulkheads of cylinder blocks in V-configuration engines (Fig. 4).
- Machinability of CGI is worse than gray iron, but new investigations suggest low titanium sulfide content can improve machinability (Fig. 3).
- Characteristics of Aluminum Alloys (Al-alloy):
- Aluminum alloys are effective for lightweighting, reducing body weight by "40 to 50%."
- Audi A2 and A8 models using aluminum bodies are "about 40% lighter" than comparable steel cars.
- Aluminum bodies offer stiffness, crashworthiness, strength, and durability.
- Aluminum alloys are highly recyclable.
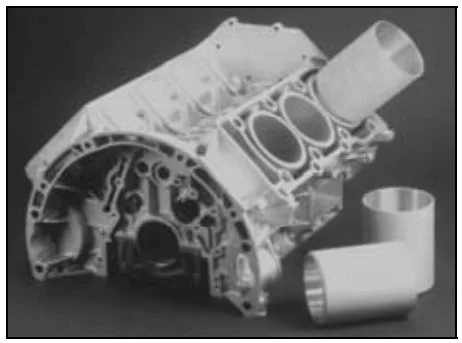
- New technologies are being developed for producing aluminum cylinder liners using die-casting (Fig. 7, 8).
- Characteristics of High Strength Steels:
- High strength steels contribute to lightweighting automotive components, accounting for "37%" of materials in the Mercedes-Benz E-Class model (Fig. 9).
- The body shell of the CLK Cabriolet model is made of high-strength steel alloys, accounting for "around 40%."
- VW Golf connecting rods have reduced weight through material optimization and application of high-strength steels.
- Porsche models use high-strength steel for door structures, making them "42% lighter."
- New steel grades (42CrMoS4, 45A) combine high strength and machinability.
- Characteristics of Magnesium Alloys (Mg-alloys) and Plastics:
- Magnesium alloys are expanding their application from automotive interiors to engine components and exterior body panels.
- Magnesium alloy crankcases can reduce weight by "25%" compared to aluminum versions.
- The Opel Vectra model uses a magnesium cross member, which is "4.3 kg lighter" than steel counterparts.
- Plastics, especially fiber-reinforced plastics, have high potential in the automotive industry, contributing to cost reduction and lightweighting.
- New plastic materials like nano-composites and natural organic fiber materials (flax, willow, hemp) are being developed.
- Carbon fiber is considered a future material for automotive parts.
- Characteristics of Compacted Graphite Iron (CGI):
- Statistical/Qualitative Analysis Results:
- Table 1: Comparison of cylinder block material characteristics (Gray iron, CGI, SGI, Aluminum alloy)
- Compares various properties such as pearlite content, tensile strength, elastic modulus, fatigue strength, hardness, and thermal conductivity.
- Fig. 1: Mechanical characteristics of cast iron (Tensile strength vs. Fatigue strength)
- CGI shows superior mechanical properties compared to flake graphite cast iron (CI).
- Fig. 2: Peak firing pressure limits of various materials for cylinder blocks
- CGI has a higher peak firing pressure limit than flake graphite cast iron and aluminum alloys.
- Fig. 3: Relative machining of various materials
- CGI has lower machinability than flake graphite cast iron, but new technology shows potential for improvement.
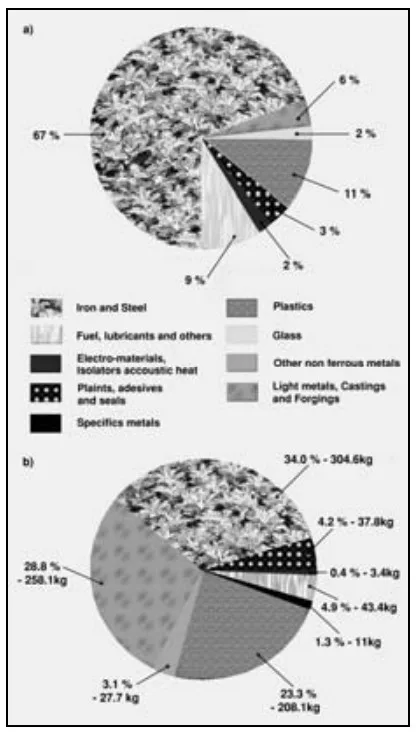
- Fig. 6: Material share in automobiles made in 1988 (a) and 1999 (b)
- Shows an increasing trend in the share of light metals (Light metals, Castings and Forgings).
- Fig. 9: Material share in E-class of Mercedes-Benc automobile
- Confirms the high proportion of high strength steel and light metals (Aluminum).
- Table 1: Comparison of cylinder block material characteristics (Gray iron, CGI, SGI, Aluminum alloy)
- Data Interpretation:
- CGI is an excellent material suitable for high-performance diesel engine cylinder blocks, contributing to lightweighting and emission reduction.
- Aluminum alloys play a crucial role in lightweighting car bodies, while magnesium alloys and plastics have high potential for lightweighting automotive components.
- High strength steels can replace conventional steel components to contribute to lightweighting.
- The automotive industry is actively utilizing various new materials to simultaneously pursue lightweighting, high performance, and environmental friendliness.
- Figure Name List:
- Fig. 1. Mechanical characteristics of cast iron
- Fig. 2. Peak firing pressure limits of various material for cylinder blocks
- Fig. 3. Relative machining of various materials
- Fig. 4. Z-shaped section of the cylinder block
- Fig. 5. Size and shape of graphite in CI, CGI and SGI under light (x 100) and SEL microscope
- Fig. 6. Materials share in an automobile made in 1988 (a) and 1999 (b)
- Fig. 7. Aluminium cylinder liner in conventional die-casting
- Fig. 8. Microstructure (100:1) of SAE 390 alloy
- Fig. 9. Materials share in E-class of Mercedes-Benc automobile
6. Conclusion and Discussion:
- Summary of Main Findings:
- New materials in the automotive industry offer new possibilities.
- The use of gray iron with compacted graphite instead of flake enables casting of high strength low weight cylinder blocks for engine families without any change in dimensions.
- Due to attractive properties of CGI, foundries in the Balkan area should develop and organize CGI casting technology.
- In light passenger cars, Al-alloys are widely used, and it is expected that magnesium alloys, plastics, and composites will also be more and more used.
- Gray cast iron and aluminum will be around for a great deal longer yet.
- The use of high and ultra-high strength steel will result in less weight and improved performances.
- Reduction in weight helps performance and makes emissions attainment easier, which in improves fuel economy.
- Academic Significance of Research:
- This research comprehensively presents trends in material development for lightweighting and high performance in the automotive industry.
- It highlights the superiority of compacted graphite iron (CGI) and analyzes the applicability of various new materials such as aluminum alloys, high-strength steels, magnesium alloys, and plastics, enhancing its academic value.
- It provides useful information for researchers in the field of automotive materials and contributes to setting future research directions.
- Practical Implications:
- Automakers should actively utilize various new materials such as CGI, aluminum alloys, high-strength steels, magnesium alloys, and plastics to pursue vehicle lightweighting and performance improvement.
- In particular, CGI is a very suitable material for high-performance diesel engine cylinder blocks, and it is necessary to consider developing production technology and expanding its application.
- Lightweighting leads to improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions, making it an important strategy to respond to tightening environmental regulations.
- Limitations of Research:
- This research is a review paper and does not present new experimental data or original analysis results.
- It focuses on a general comparison of the characteristics of various materials rather than in-depth analysis of specific materials.
- The scope and recency of cited references may be limited (based on a 2007 paper).
7. Future Follow-up Research:
- Directions for Future Research:
- Research on optimizing CGI casting technology and developing mass production technology.
- Research on developing new aluminum alloys, magnesium alloys, and composite materials.
- Research on the applicability and performance evaluation of various new materials for automotive components.
- Research on evaluating the durability, reliability, and economics of lightweight materials.
- Research on environmental impact assessment and recycling technologies for automotive materials.
- Areas Requiring Further Exploration:
- Development of technologies to improve CGI machinability.
- Cost-effectiveness analysis of lightweight materials.
- Life cycle assessment (LCA) of automotive materials.
- Research on lightweight materials suitable for future automobiles (electric vehicles, hydrogen vehicles, etc.).
8. References:
- Engine Technology Intern. 1/99, p.62
- Engine Technology Intern. 1/02,p.54
- Gligorijevic, R., Jevtic, J., Material development trends in automotive industry, Proceeding-YUDEKO 2002
- Engine Technology Intern. Sept 2001, p.12
- Sahm, A., New Aspects in CGI machining, Engine Expo 2002, Stuttgart 2002
- Slavnich, D., Lightweights punch in out, Automobile Engineer, March 2002, p.52
- MTZ 61 (2000) 4,p.244
- Stocker, P. et. al. The New Al-Si Cylinder Liner Technology for Die-Cast Aluminium Crankcases, MTZ 58,1997, 9,
- Auto Technology Intern. May 2001, p. 86
- Auto Technology Intern. 3(2003), p. 22
- Auto Technology Intern. Jun 2000, p.44
- Auto Technology Intern. 1/2001, p.40
- Gligorijevic, R.: Gray iron aluminium alloying as the method of improving damping properties and oxidation resistance at elevated temperatures, Foundry XXIX, 1982, No. 1-4, p. 15
9. Copyright:
- This material is based on the paper: Materials in Automotive Engineering by Jeremija JEVTIC, Radinko GLIGORIJEVIC, and Djuro BORAK.
This material is a summary based on the above paper, and unauthorized use for commercial purposes is prohibited.
Copyright © 2025 CASTMAN. All rights reserved.