This article introduces the paper "Automobile Lightweight Technology: Development Trends of Aluminum/Magnesium Alloys and Their Forming Technologies".
1. Overview:
- Title: Automobile Lightweight Technology: Development Trends of Aluminum/Magnesium Alloys and Their Forming Technologies
- Authors: Fu Penghuai, Peng Liming, Ding Wenjiang
- Publication Year: 2018
- Journal/Conference: Strategic Study of CAE
- Keywords: automobile, lightweight, aluminum alloy, magnesium alloy, forming technology, development trend
2. Background:
China is facing severe energy consumption, safety, and environmental problems due to continuous increases in vehicle production and ownership. Vehicle lightweighting technology is crucial for the sustainable development of the automotive industry, improving fuel economy, and reducing emissions. Lightweighting technologies comprise three primary components: lightweight designs, lightweight materials, and lightweight manufacturing processes. The feasibility of implementing new lightweighting technology depends on its cost-benefit ratio; adoption only occurs when benefits significantly outweigh cost increases. This study focuses on newly developed lightweight aluminum and magnesium alloys and the advancement of aluminum/magnesium forming technologies in the automotive sector.
3. Research Objectives and Questions:
- Research Objective: To review the development trends of aluminum and magnesium alloys, analyze the obstacles to their application in the automotive industry, and propose solutions to promote their wider use in China's automotive sector.
- Key Research Questions: What are the development trends of new lightweight aluminum and magnesium alloys and their forming technologies? What are the barriers to their application in the automotive industry? What are the viable solutions to promote the use of aluminum and magnesium alloys in China's automotive industry?
- Research Hypothesis: The development of new materials, new forming technologies, and new applications can promote the use of aluminum and magnesium alloys in the automotive industry.
4. Methodology:
- Research Design: Literature review.
- Data Collection Methods: Review of academic papers and industry reports related to aluminum and magnesium alloys.
- Analysis Methods: Analysis of development trends of aluminum and magnesium alloys, assessment of barriers to automotive application, and proposal of solutions.
- Research Scope: Aluminum and magnesium alloys, forming technologies, and automotive applications. Includes research and applications both inside and outside of China.
5. Main Findings:
- Key Findings: A review of the development of new aluminum and magnesium alloys, new forming technologies, and new applications. Suggestions for solutions to promote the use of aluminum and magnesium alloys in the automotive industry. For aluminum alloys, the development and application of new alloys such as JDA1 and JDA2, new forming technologies like vacuum die-casting and rheo-die casting, and new applications including engine brackets and car bodies were presented. For magnesium alloys, the development and application of high-performance alloys like JDM1-JDM4, new forming technologies such as flow forming, and new applications including engine cylinder heads and car bodies were detailed. Barriers to automotive lightweighting technologies included increased material costs, high R&D and production costs, increased maintenance costs, and insufficient maturity of anti-corrosion and joining technologies for magnesium alloys.
- Quantitative/Qualitative Analysis Results: Primarily qualitative analysis results were presented.
- Data Interpretation: Analysis and interpretation of data presented in the paper to understand the trends in the development and application of aluminum/magnesium alloys, identify barriers, and propose solutions.
- Figure Name List:
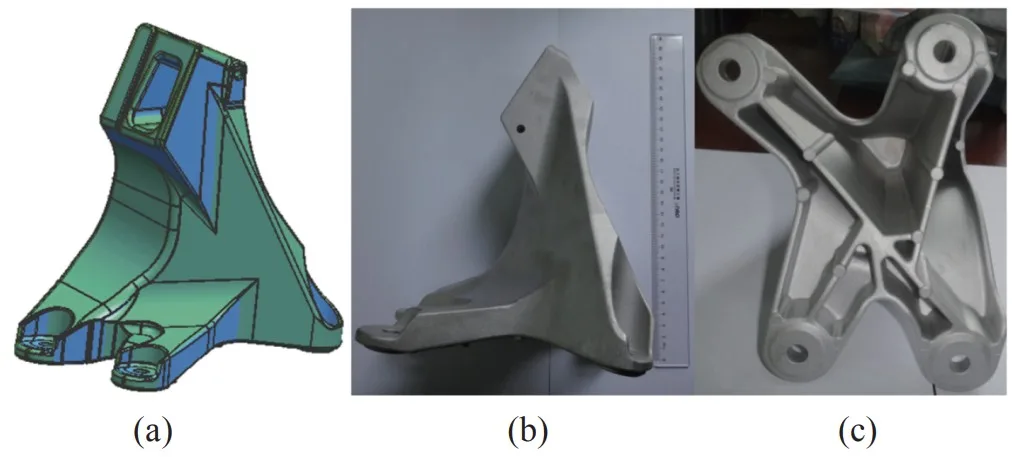
- Figure 1. Engine bracket (chassis system) made from the JDA1 aluminum alloy,
- Figure 2. Photographs of die cast aluminum alloy V6 engine blocks,
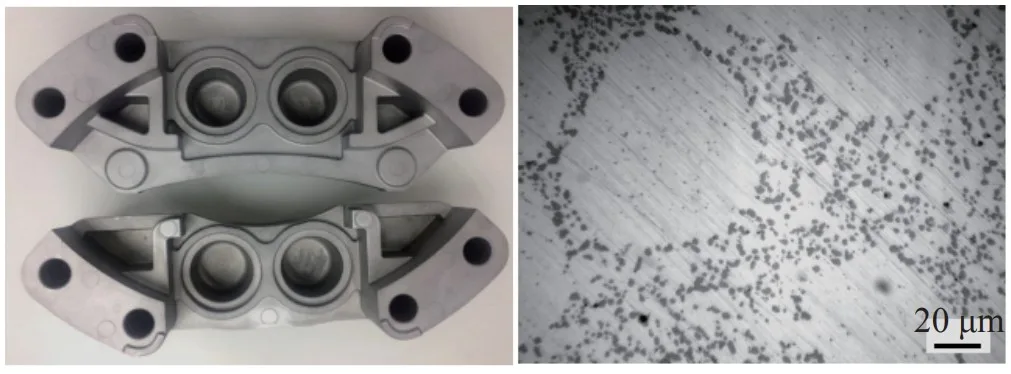
- Figure 3. Calipers (chassis system) produced by rheo-die casting of semi-solid aluminum alloy and their internal microstructure,
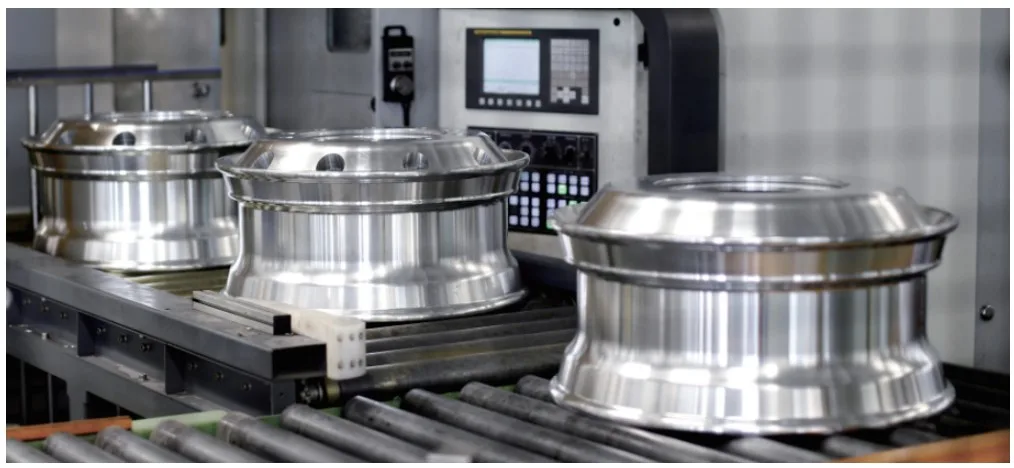
- Figure 4. Aluminum truck wheels produced via forging & flow forming by the Shandong Meika Wheel Co., Ltd,
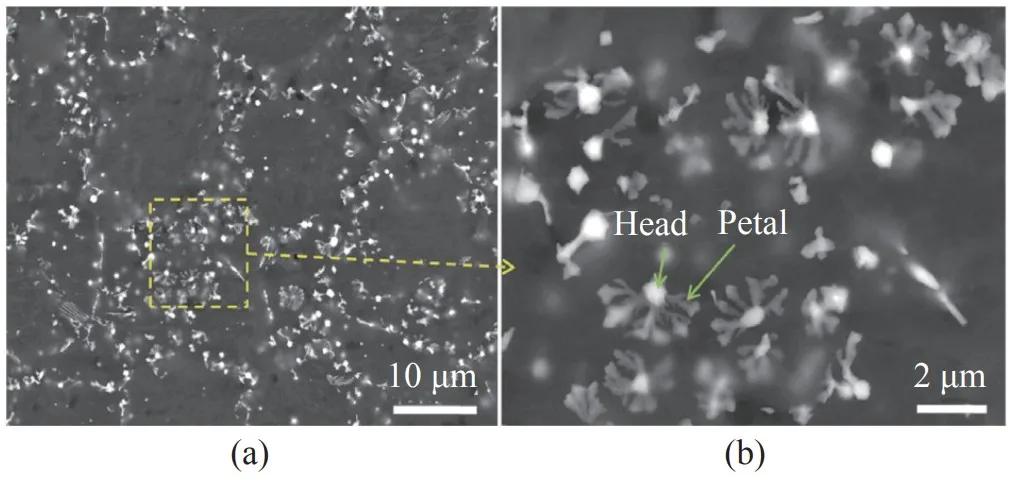
- Figure 5. Microstructure of the die-cast Mg-4A1-4Sm-0.3Mn alloy in the as-cast condition,
- Figure 6. Production of magnesium alloy wheels via extrusion process,
- Figure 7. JDM1 magnesium wheel produced by cast & flow forming technology,
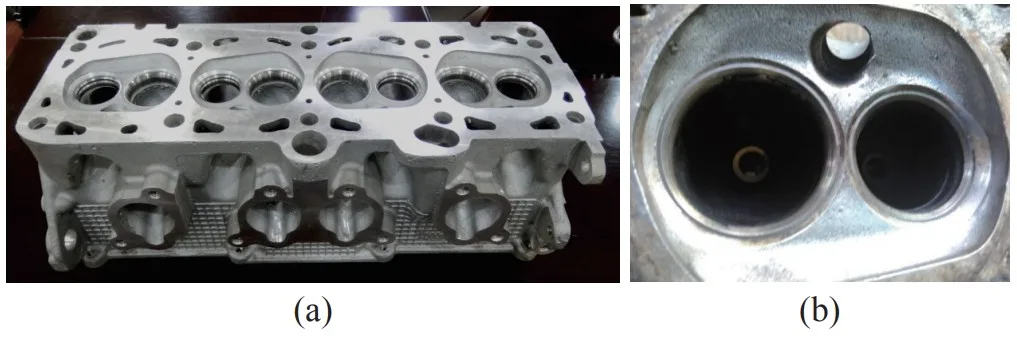
- Figure 8. Engine cylinder head made of JDM1 magnesium alloy


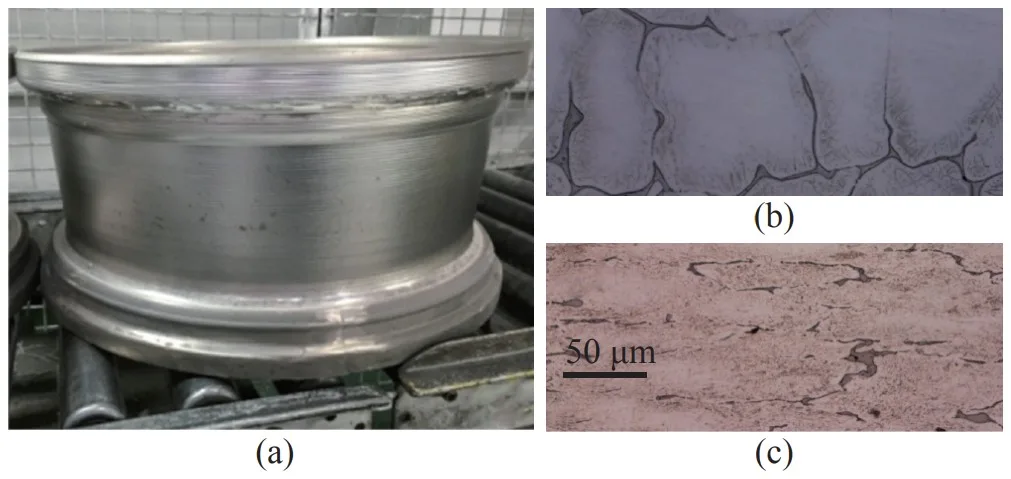
138 MPa, and 4.8 %, respectively; (c) the microstructure of the wheel rim after flow forming. In as-flow formed condition, the wheel has a yield strength, tensile strength, and elongation of 278 MPa, 317 MPa,
and 8.4%, respectively
6. Conclusions and Discussion:
This study analyzed the development trends of aluminum and magnesium alloys and the challenges to their application in the automotive industry, proposing solutions. The development of new materials, forming technologies, and applications contributes to automotive lightweighting. However, high material costs, high R&D and production costs, increased maintenance costs, and the immaturity of anti-corrosion and joining technologies for magnesium alloys pose significant challenges. The Chinese automotive industry needs to focus on material development, manufacturing process optimization, in-depth basic research, and leveraging die-casting processes to overcome these barriers.
7. Future Research:
Further research is needed on fundamental aspects of aluminum/magnesium alloys, developing new forming technologies, and expanding applications to various automotive components. Research on addressing magnesium alloy corrosion and improving joining technologies is particularly important. Collaboration with industry is also crucial for technology commercialization.
8. References:
- [1] Guo Y Q, Zhu X F, Yang Y, et al. Research state of lightweight material and manufacture processes in automotive industry [J]. Forging & Stamping Technology, 2015, 40(3): 1–6. Chinese.
- [2] Gong Y Y, Wang Z, Zhang Z P. New energy vehicles lightweight approach and its evaluation [J]. Automobile Applied Technology. 2017 (1): 5–6. Chinese.
- [3] Ingarao G, Gagliardi F, Anghinelli O, et al. Sustainability issues in sheet metal forming processes: An overview [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2011, 19(4): 337–347.
- [4] Zhang P, Li Z M, Liu B L, et al. Effect of chemical compositions on tensile behaviors of high pressure die-casting alloys Al-10SiyCu-xMn-zFe [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2016 (661): 198–210.
- [5] Zhang P, Li Z M, Liu B L, et al. Improved tensile properties of a new aluminum alloy for high pressure die casting [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2016 (651): 376–390.
- [6] Ji S, Watson D, Fan Z, et al. Development of a super ductile die cast Al-Mg-Si alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2012 (556): 824–833.
- [7] Fu P H, Peng L M, Jiang H Y, et al. Effects of heat treatments on the microstructures and mechanical properties of Mg-3Nd-0.2Zn0.4Zr (wt. %) alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2008 (486): 183–192.
- [8] Fu P H. Study on the microstructure, mechanical properties and strengthen mechanism of Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr alloys [D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Doctoral dissertation), 2009. Chinese.
- [9] He S M. Study on the microstructural evolution, properties and fracture behavior of Mg-Gd-Y-Zr (-Ca) alloys [D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Doctoral dissertation), 2007. Chinese.
- [10] Gao Y. Microstructure, properties and creep behavior of Mg-YGdZn-Zr alloys [D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Doctoral dissertation), 2009. Chinese.
- [11] Zjournal of Alloys and Compounds, 2014 (615): 703–711.
- [12] Su C Y, Li D J, Ying T, et al. Effect of Nd content and heat treatment on the thermal conductivity of MgNd alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016 (685): 114–121.
- [13] Yang Q, Guan K, Qiu X, et al. Structures of Al2Sm phase in a high-pressure die-cast Mg-4Al-4Sm-0.3Mn alloy [J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2016(675): 396–402.
- [14] Bian M Z, Sasaki T T, Suh B C, et al. A heat-treatable Mg-Al-CaMn-Zn sheet alloy with good room temperature formability [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2017 (138): 151–155.
9. Copyright:
This document is based on the paper: "Automobile Lightweight Technology: Development Trends of Aluminum/Magnesium Alloys and Their Forming Technologies" by Fu Penghuai, Peng Liming, and Ding Wenjiang.
DOI: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2018.01.012.
This document is a summary of the paper and its unauthorized commercial use is prohibited.
Copyright © 2025 CASTMAN. All rights reserved.