This article introduces the paper "Magnesium Alloys and Applications in Automotive Industry".
1. Overview:
- Title: Magnesium alloys and applications in automotive industry
- Author: Nima Khademian, Yaser Peimaei
- Publication Year: August 2021
- Publishing Journal/Academic Society: Fourth International Conference on Interdisciplinary Studies in Nanotechnology (Conference Paper)
- Keywords: Magnesium alloys, Manufacturing methods, Automobile, Micro/nanostructures
2. Research Background:
- Social/Academic Context of the Research Topic:
- The automotive industry is increasingly focused on improving fuel economy and reducing emissions.
- Light weighting of vehicles is a key strategy to achieve these goals.
- Substituting conventional heavier materials like steel and cast irons with lighter alternatives such as aluminum and magnesium is a growing trend.
- Magnesium, being the lightest structural metal, is considered a promising material for automotive applications.
- Limitations of Existing Research:
- While the paper doesn't explicitly detail limitations of prior research, it implies a continuous need for advancements in magnesium alloy technology and its application in vehicles.
- The ongoing desire to identify challenges, solutions, and opportunities related to magnesium use suggests that existing research is still evolving and requires further exploration.
- Necessity of the Research:
- Weight loss in vehicles is crucial for both combustion and electric vehicles to meet stringent fuel economy and emission standards.
- Reducing vehicle mass improves performance attributes such as acceleration, braking, and handling.
- Magnesium offers superior heat dissipation and heat transfer due to high thermal conductivity.
- Magnesium alloys exhibit excellent ability in shielding electromagnetic interruption.
- Magnesium alloys can reduce noise and vibrations compared to typical metals and increase stiffness.
- Weight reduction in dynamic structures is significantly more impactful than in static structures, making magnesium particularly beneficial for automotive components.
3. Research Purpose and Research Questions:
- Research Purpose:
- To investigate the challenges, solutions, and opportunities associated with utilizing magnesium in automotive applications.
- To provide an overview of the historical, current, and potential future structural applications of magnesium within the automotive industry.
- Key Research Questions:
- What are the advantages of employing magnesium alloys in automotive design and manufacturing?
- What are the primary challenges and limitations associated with the increased use of magnesium alloys in vehicles?
- What are the current applications of magnesium alloys in the automotive sector, and what are the potential areas for future expansion?
- How can manufacturing methods be optimized to facilitate greater adoption of magnesium alloys in vehicle production?
- Research Hypotheses:
- The paper does not explicitly state research hypotheses. The research is primarily exploratory and descriptive, aiming to synthesize existing knowledge and identify trends and future directions.
4. Research Methodology
- Research Design:
- The research employs a literature review approach, synthesizing information from existing studies, industry reports, and historical data related to magnesium alloys in the automotive industry.
- Data Collection Method:
- The study relies on secondary data gathered from published research papers, conference proceedings, and industry-related publications.
- Historical examples of magnesium applications in vehicles are also considered.
- Analysis Method:
- The analysis is primarily qualitative, focusing on summarizing and interpreting the existing body of knowledge on magnesium alloys in automotive applications.
- The paper identifies key trends, benefits, challenges, and future directions based on the reviewed literature.
- Research Subjects and Scope:
- The research focuses on magnesium alloys as a material and their specific applications within the automotive industry.
- The scope encompasses various aspects, including material properties, manufacturing methods (especially die casting), automotive component design, and the historical evolution of magnesium use in vehicles.
5. Main Research Results:
- Key Research Results:
- Light weighting is a major focus for fuel economy in the automotive industry, with 39% of companies prioritizing it in 2017.
- Magnesium alloys offer substantial weight savings compared to steel and aluminum, with potential weight reductions of up to 60%.
- Current average magnesium usage in vehicles ranges from 4-30 kg, with an industry target of exceeding 80 kg per vehicle by 2030.
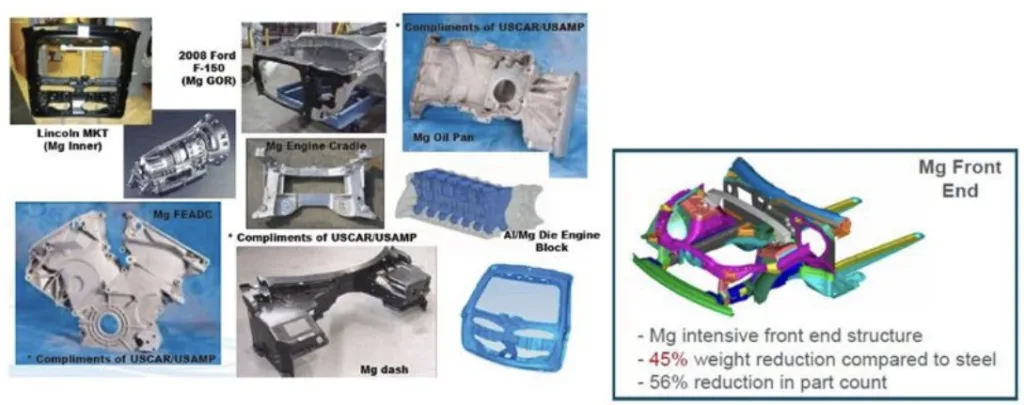
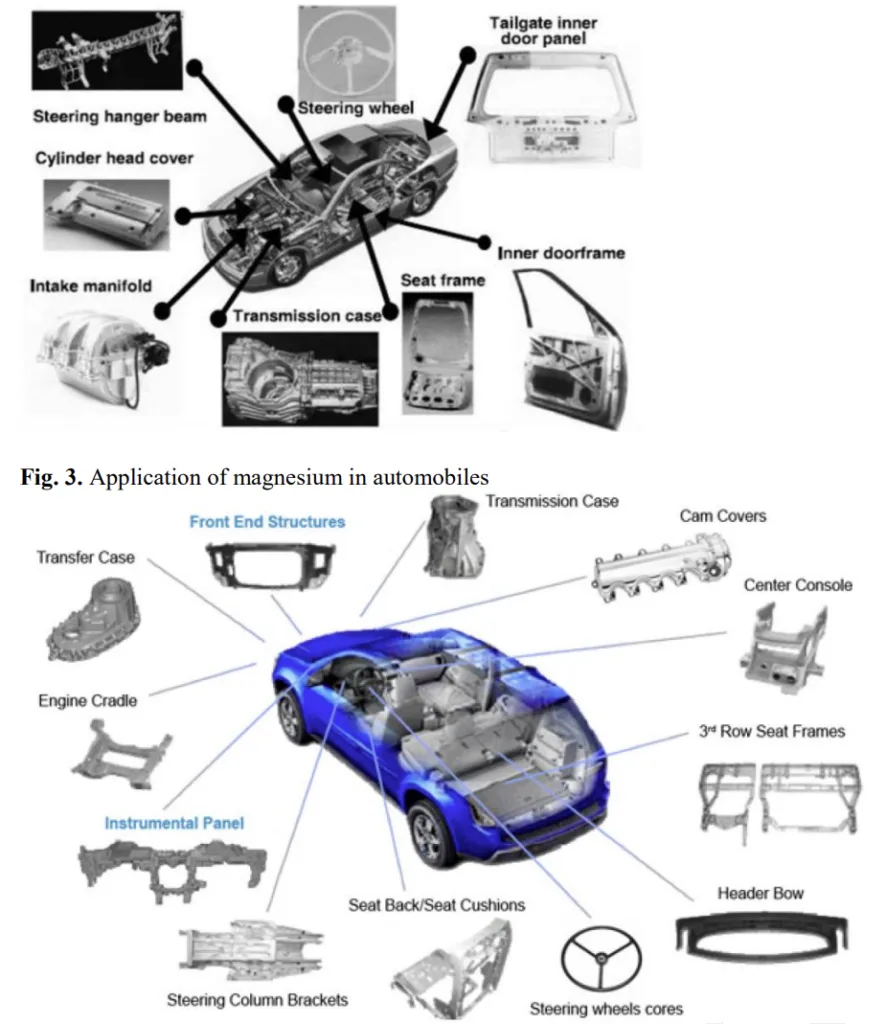
- Magnesium alloys are utilized in diverse automotive components, including chassis, interior parts (seat bases, instrument panels), exterior panels (roofs, frames), and powertrain components.
- Pressure die casting is the predominant manufacturing method for producing magnesium automotive parts due to its excellent casting properties and ability to create complex shapes with thin walls.
- Magnesium die castings made of high-ductility alloys like AM50 and AM20 offer a combination of high strength, extreme rigidity, low weight, and cost-effectiveness.
- Statistical/Qualitative Analysis Results:
- Fuel Economy Focus (2017 Data): 39% light weighting, 29% engine efficiency, 26% vehicle electrification, 6% downsizing.
- Weight Saving Potential: Aluminum (2.7 g/cm3) can save 50% weight, Magnesium (1.8 g/cm3) can save 60% weight, glass fiber composite (~1.1-2.5 g/cm3) can save 30% weight, and carbon fiber composite (~1.8 g/cm3) can save 60% weight.
- Vehicle Weight Breakdown: 35% body, 34% chassis and suspension, 27% powertrain, and 4% other.
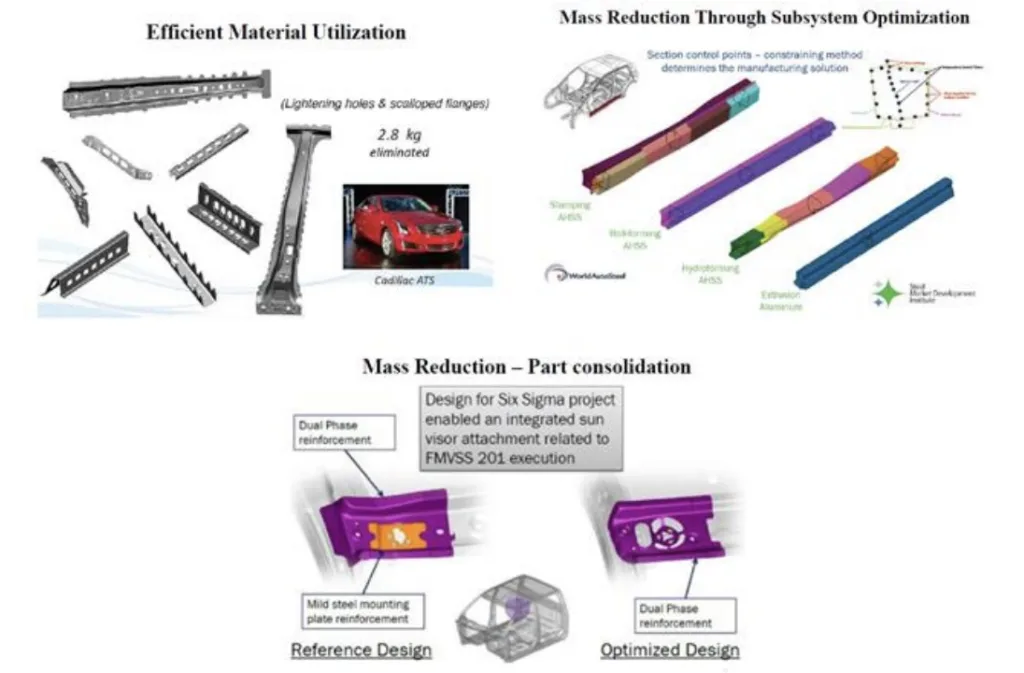
- Mass Reduction Example (Cadillac ATS): Efficient material utilization (lightening holes & scalloped flanges) eliminated 2.8 kg.
- Mass Reduction Example (USCAR Sigma project): Part consolidation in sun visor attachment design.
- Magnesium front end structure: 45% weight reduction compared to steel, 56% reduction in part count (USCAR/USAMP project).
- Data Interpretation:
- The data underscores the significant potential of magnesium alloys in achieving automotive weight reduction targets.
- The statistical breakdown of vehicle weight and fuel economy strategies highlights the importance of light weighting as a primary approach.
- Examples of mass reduction through efficient material utilization and part consolidation demonstrate practical engineering strategies for implementing magnesium in vehicle design.
- The success of magnesium die castings, particularly with alloys like AM50 and AM20, indicates their suitability for demanding automotive applications.
- Figure Name List:
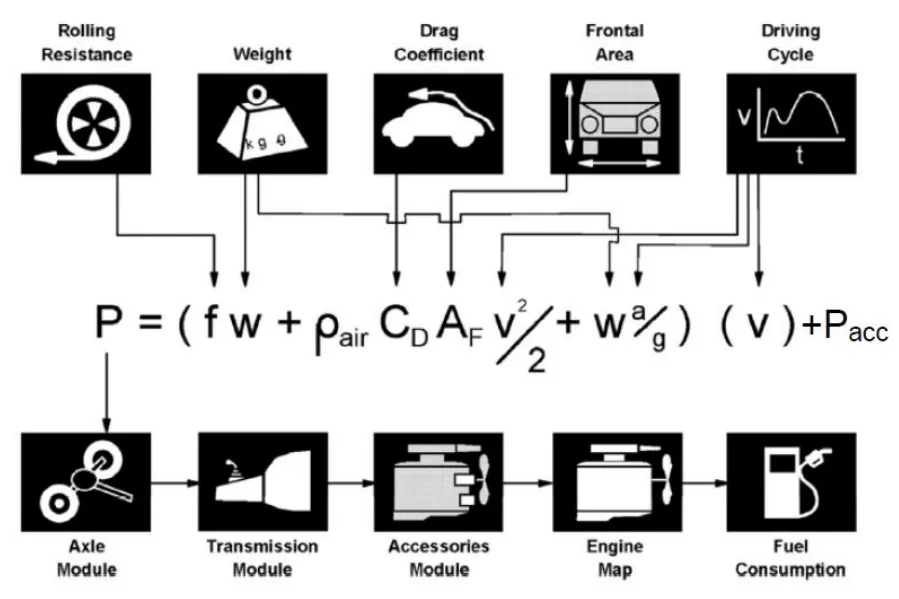
- Fig. 1. Fuel consumption
- Fig. 2. Improved part design
- Fig. 3. Application of magnesium in automobiles
- Fig. 4. Application of magnesium in automobiles
- Fig. 5. Application of magnesium in automobiles

6. Conclusion and Discussion:
- Summary of Main Results:
- Magnesium alloys present a compelling solution for reducing vehicle weight, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and enhanced vehicle performance.
- Die casting stands out as the most effective and widely used manufacturing process for magnesium automotive components.
- Despite the advantages, challenges persist in areas such as alloy development, optimizing manufacturing processes, and enhancing corrosion resistance to broaden magnesium's application scope.
- Academic Significance of the Research:
- This paper provides a valuable overview of the current state of magnesium alloy applications in the automotive industry.
- It synthesizes information from diverse sources to highlight the material's potential and the ongoing research and development efforts in this field.
- The review contributes to the academic understanding of lightweighting strategies and material selection in automotive engineering.
- Practical Implications:
- The findings encourage increased adoption of magnesium alloys in vehicle design and manufacturing to meet fuel economy and performance demands.
- The paper emphasizes the need for continued innovation in magnesium alloy technology, particularly in addressing challenges related to corrosion and mechanical properties.
- The discussion on manufacturing processes, especially die casting, provides practical insights for engineers and manufacturers working with magnesium alloys.
- Limitations of the Research:
- As a conference paper, the research is primarily a review and overview, lacking original experimental data or in-depth quantitative analysis.
- The scope is broad, covering various aspects of magnesium in automotive applications, which may limit the depth of analysis in specific areas.
7. Future Follow-up Research:
- Directions for Follow-up Research:
- Developing novel magnesium alloys with enhanced properties, including improved ductility, fatigue strength, creep resistance, and corrosion resistance, is crucial for expanding applications.
- Exploring and optimizing advanced manufacturing processes for magnesium components, such as hollow casting techniques and metal matrix composites, to further enhance performance and reduce costs.
- Further research is needed to develop accurate material models for magnesium fracture behavior under crash loading conditions to facilitate safer and more efficient component design.
- Areas Requiring Further Exploration:
- Surface finishing and corrosion protection technologies for magnesium alloys require continuous improvement to ensure long-term durability in automotive environments.
- Optimizing casting parameters, particularly for die casting processes, to minimize porosity and enhance the mechanical properties of magnesium components is essential for wider adoption.
- Investigating the long-term performance and durability of magnesium components in real-world automotive applications is necessary to validate their reliability and identify potential areas for improvement.
8. References:
- [1] Luo, A.A. (2013), Magnesium casting technology for structural applications, journal of magnesium and alloys 1.
- [2] Abbott, T.B. et al., Designing with Magnesium: Alloys, Properties, and casting process.
- [3] Dziubinska, A. (2016), The forming of magnesium alloy forgings for aircraft and automotive applications, Advances in Science and Technology Research Journal.
- [4] Musfirah, A.H. et al. (2012), Manesium and aluminium alloys in automotive industry, Journal of Applied Sciences Research, 8 (9), 4865-4875.
- [5] William J. (2016), Towards magnesium alloys for high-volume automotive applications, Scripta Materialia.
- [6] Wu R., et al. (2015), Recent progress in magnesium -lithium alloys, International Materials Reviews, Vol 60, No2.
- [7] Vorozhtsov, S., et al. (2016), Structure and Deformation Characteristics in Magnesium Alloy ZK51A Reinforced with AlN Nanoparticles, Prospects of Fundamental Sciences Development (PFSD), doi: 10.1063/1.4964542.
- [8] X.H., et al. (2012), Si3N4 Nanoparticle Addition to ConcentratedMagnesium Alloy AZ81: Enhanced Tensile Ductility and Compressive Strength Muralidharan Paramsothy,, Jimmy Chan, Richard Kwok, Manoj Gupta, International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Nanomaterials.
- [9] Bakhsheshi-Rad, H.R., et al. (2020), Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs)-Reinforced Magnesium-Based Matrix Composites: A Comprehensive Review, Somayeh Abazari,, Materials (MDPI).
- [10] Haghshenas, M. (2020), Magnesium nanocomposites reinforced with rare earth element nanoparticles: nanoindentation driven response, NANOCOMPOSITES Vol. 6, No. 1, 22–30.
- [11] Song, J., et al. (2020), Latest research advances on magnesium and magnesium alloys world wide, Jounal of Magnesium and Alloys, Vol 8.
9. Copyright:
- This material is Nima Khademian and Yaser Peimaei's paper: Based on Magnesium alloys and applications in automotive industry.
- Paper Source: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/354102981
This material was summarized based on the above paper, and unauthorized use for commercial purposes is prohibited.
Copyright © 2025 CASTMAN. All rights reserved.