Ashwin D; Ashok S; Manglesh Dixit; Vinila Chavan
Abstract
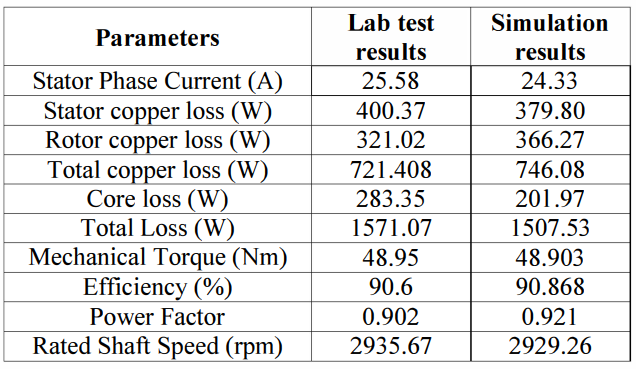
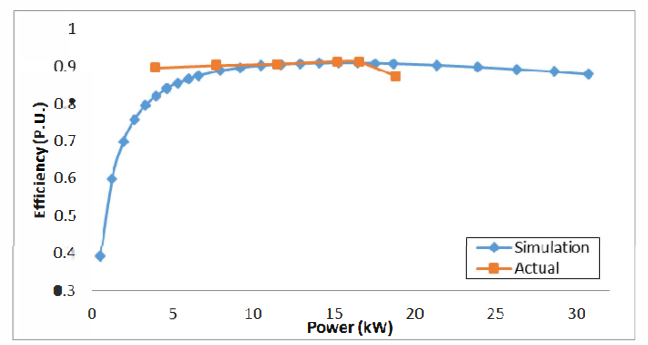
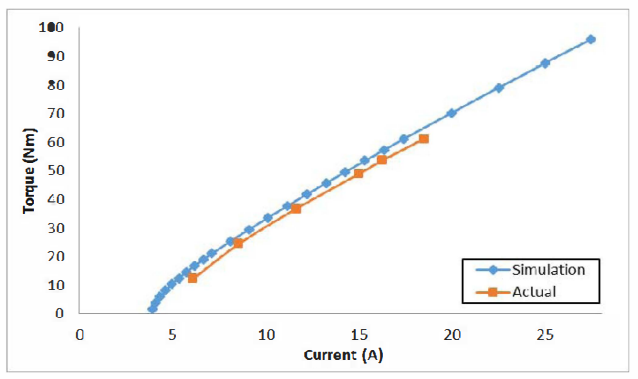
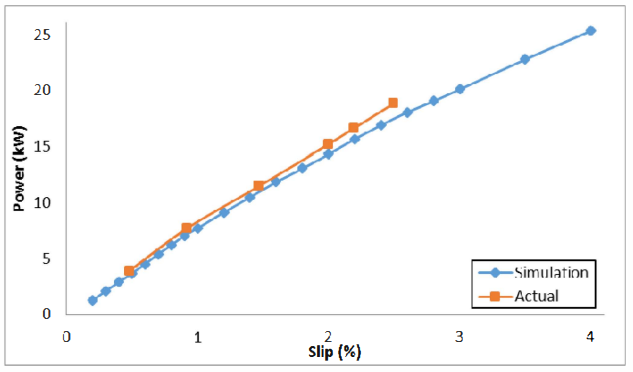
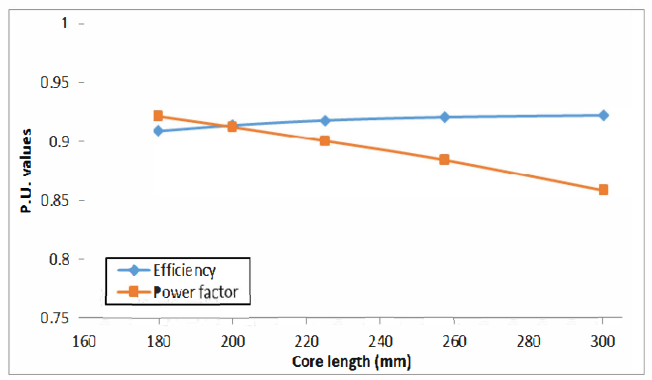
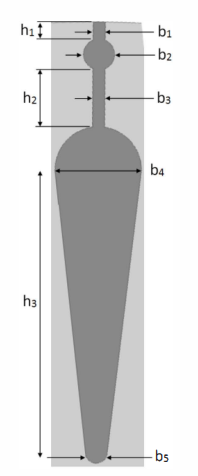
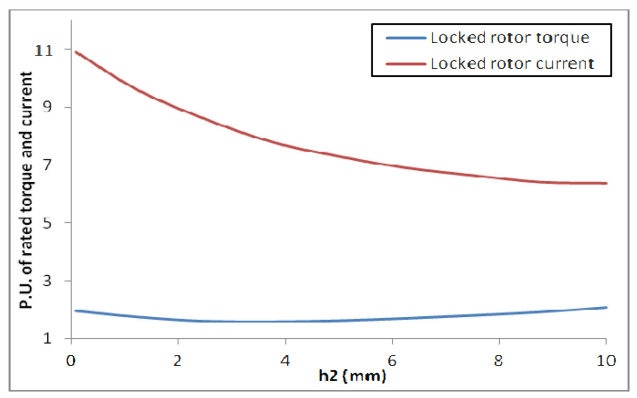
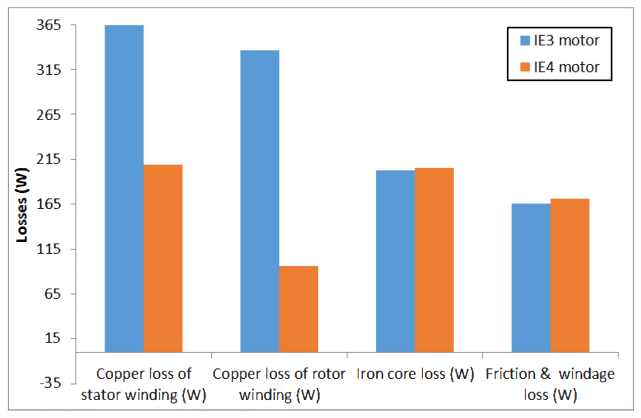
This paper describes the design and simulation of 15 kW, 2 pole, 50 Hz, three phase induction motor to achieve IE4 efficiency level as defined by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). For achieving higher efficiency, the motor is designed, optimized and simulated with copper die-cast rotor and low loss electrical steel. The simulation method is first validated by comparing with the test results of standard IE3 motor. The same simulated model was taken as reference to design the IE4 motor. This design solution having IE4 efficiency is achieved without changing the stator geometry and frame size.
이 논문은 IEC(International Electrotechnical Commission)에서 정의한 IE4 효율 수준을 달성하기 위한 15kW, 2극, 50Hz, 3상 유도 전동기의 설계 및 시뮬레이션에 대해 설명합니다. 더 높은 효율을 달성하기 위해 모터는 구리 다이캐스트 로터와 저손실 전기강으로 설계, 최적화 및 시뮬레이션되었습니다. 시뮬레이션 방법은 먼저 표준 IE3 모터의 테스트 결과와 비교하여 검증됩니다. 동일한 시뮬레이션 모델이 IE4 모터를 설계하기 위한 참조로 사용되었습니다. IE4 효율성을 갖는 이 설계 솔루션은 고정자 형상 및 프레임 크기를 변경하지 않고 달성됩니다.
I. INTRODUCTION
With the rising costs of energy and the substantial concerns about global C02 emissions, achieving the highest possible motor system efficiency has become a critical priority. Subsequently, stringent energy efficiency standards are being implemented by several countries to introduce energy efficient motors for energy savings. The International Electrotechnical Commission (1EC) provides guidelines for efficiency classes. The IEC has recently published the new standard IEC 60034- 30-1 which includes the 1E4 Super Premium efficiency class [6]. Accordingly, motor manufacturers are geared-up to enhance the efficiency using newer designs, technology, improved materials and processes. In this paper, an optimized design for a 15 kW, 2 Pole IE4 induction motor is presented. It was designed in such a way that it utilizes the same frame as the standard 1E3 motor, in order to reduce unnecessary production costs.
에너지 비용 상승과 전 세계 CO2 배출에 대한 실질적인 우려로 인해 가능한 최고의 모터 시스템 효율성을 달성하는 것이 중요한 우선 순위가 되었습니다. 그 후, 에너지 절약을 위한 에너지 효율적인 모터를 도입하기 위해 여러 국가에서 엄격한 에너지 효율 표준을 시행하고 있습니다. 1EC(International Electrotechnical Commission)는 효율성 등급에 대한 지침을 제공합니다. IEC는 최근 1E4 Super Premium 효율 등급을 포함하는 새로운 표준 IEC 60034-30-1을 발표했습니다[6]. 따라서 모터 제조업체는 더 새로운 디자인, 기술, 개선된 재료 및 프로세스를 사용하여 효율성을 향상시킬 준비를 하고 있습니다. 이 논문에서는 15kW, 2극 IE4 유도 전동기에 최적화된 설계를 제시합니다. 불필요한 생산비를 줄이기 위해 표준 1E3 모터와 동일한 프레임을 사용하도록 설계되었습니다.
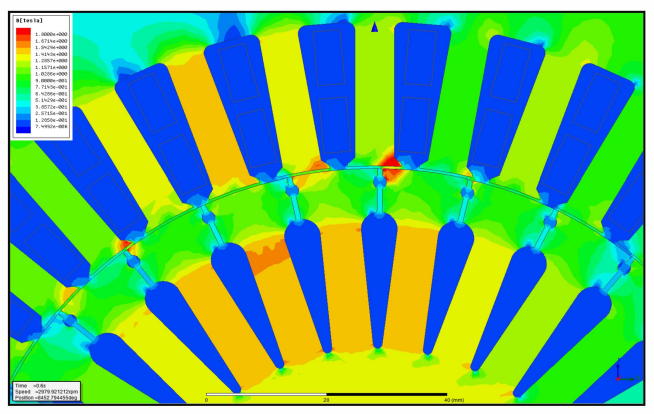
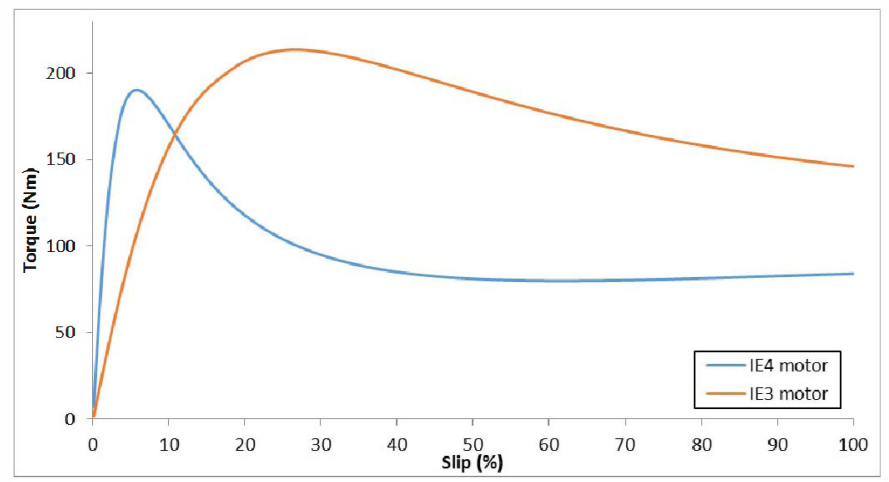
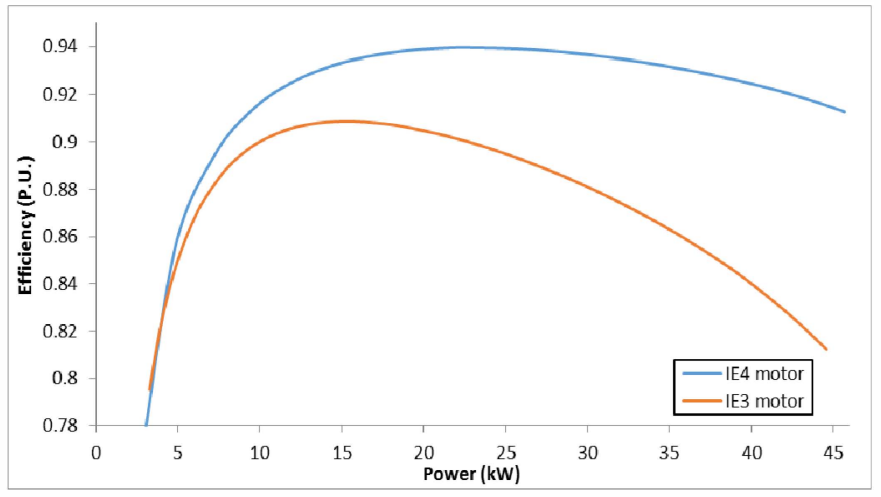
REFERENCES
[1] Alberti, Luigi, et al. "Core axial lengthening as effective solution to improve the induction motor efficiency classes." Industry Applications, IEEE Transactions on 50.1 (2014): 218-225.
[2] Kim, Kwangsoo, Seung-Bin Lim, and .Tu Lee. "Design of rotor slot of single phase induction motor with copper die-cast rotor cage for high efficiency. "Telecommunications Energy Conference, 2009. INTELEC 2009. 31 st International. IEEE, 2009.
[3] Boglietti, Aldo, et al. "Induction motor design methodology based on rotor diameter progressive growth." Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), 2011 IEEE. IEEE,2011.
[4] Boglietti, Aldo, et a!. "No tooling cost process for induction motors energy efficiency improvements." Industry Applications, IEEE Transactions on 41.3 (2005): 808-816.
[5] Parasiliti, Francesco, and Marco Villani. "Design of high efficiency induction motors with die-casting copper rotors." Energy Efficiency in Motor Driven Systems. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2003. 144-151.
[6] Rotating Electrical Machines-Part 30-1: Efficiency Classes of Line Operated AC Motors, Int. Std. lEC/EN 60034-30-1.
[7] Rotating Electrical Machines-Part 2-1: Standard Methods for Determining Losses and Efficiency From Tests (Excluding Machines for Traction Vehicles), Int. Std. lEC/EN 60034-2-1, 2007.
[8] Torres, Andre G. "A generalized Epstein test method for the computation of core losses in induction motors." IECON 02 [Industrial Electronics Society, IEEE 2002 28th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society]. Vol. 2 . 2002.
[9] Machines-Part, Rotating Electrical. "12: Starting Performance of Single-Speed Three-Phase Cage Induction Motors." IEC Standard (2002):60034-12.