This article introduces the paper ["Corrective and preventive actions of motor cycle cylinder component leak problem on casting process"] published by [ARPN Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences].
1. Overview:
- Title: Corrective and preventive actions of motor cycle cylinder component leak problem on casting process
- Author: Rahmat Nurcahyo and Fathur Rohman Fauzi
- Publication Year: January 2016
- Publishing Journal/Academic Society: ARPN Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences
- Keywords: PDCA, TQM, corrective action, die casting
2. Abstracts or Introduction
Defective product in industry is an undesirable quality product deviation in production process. In the casting process of motor cycle cylinder component, defective product problem is one of main problems with a rate of 4.47%. This research aims to reduce the problems with determined target at 3.6%. To analyze the problem and to develop corrective action, Plan Do Check Action (PDCA) methods with seven tools as quality assistance instrument is used. The analysis indicated that causes of the problem are undercut and porous on cylinder component. The corrective action related with material, machine and inspection were taken. The result of the corrective action shows a defective product rate at 3.17%. The preventive action was performed to diminish the potential causes of incompatible product for preventing recurrence in the future.
3. Research Background:
Background of the Research Topic:
Nowadays, motor cycle industry has placed as an immense industry and applies high standard on its product quality. Quality is defined as the combination of whole products and services characteristic from marketing, engineering, manufacture, to maintenance to fulfill customers' expectations (Feigenbaum, 1991), or totally features and characteristics of the product or services that can guarantee the satisfaction necessity given (ANSI/ASQC Standard (1978)). Total Quality Management (TQM) is a strategy and integration of management system to enhance customer's satisfaction (Crosby argued, Bhat dan Cozzolino, 1993). Adoption of quality management system is preferable as strategic decision organization based on ISO 9001: 2008. Design and implementation of quality management system in the organization are affected by organization environment, various necessities, main objectives, available product, applied process, organization size and structure.
Status of Existing Research:
Organization should continually improve the affectivity of quality management system by means of using quality policy, quality objectives, audit result, data analyses, corrective and preventive actions, and management considerations. Organization should give corrective actions to diminish the causes of incompatibility in order to prevent recurrence. Preventive action must precise to the preventions problems that might occurred. PDCA cycle is a method that is used to create continuous improvement and effectively used in the working process or program running. PDCA cycle possibly to do two types of improvement such ad temporary and permanent. Seven tools (seven quality assistance instruments) is a term from Japan and can't be separated from quality circle and continuous improvement. Seven tools are Pareto diagram, cause-effect diagram, check sheet, histogram, scatter diagram, flow chart, and run chart.
Necessity of the Research:
Defective product is an undesirable quality product deviation in production process and one of main problems in industry. A casting process of motor cycle cylinder component has defective product problems at 4.47% rate, which is above the company target of 3.6%. Therefore, corrective and preventive actions are necessary to reduce the defective product rate to meet the target.
4. Research Purpose and Research Questions:
Research Purpose:
The main objective of this research is to reduce the defective product percentage of cylinder component in die casting process, aiming to achieve the company target of 3.6%.
Key Research:
This research focuses on analyzing the causes of leak problems in motor cycle cylinder components produced by die casting and implementing corrective and preventive actions using PDCA methods and seven tools to reduce the defective product rate.
Research Hypotheses:
The paper does not explicitly state research hypotheses. However, it implicitly hypothesizes that by applying PDCA and seven tools, identifying the root causes of defects (undercut and porous), and implementing corrective and preventive actions, the defective product rate can be reduced from 4.47% to below the target of 3.6%.
5. Research Methodology
Research Design:
This research uses PDCA methods and theseven tools to analyze a defective problem of a casting process of motor cycle cylinder component leak problems. The research methodology steps are: Problem formulation, Determining research objectives, Literature review, Establishing research limitation, Data collection and calculation, Data analysis, Develop corrective action, Develop preventive action, Concluding research result.
Data Collection Method:
The preliminary data is the defective product of cylinder component data that occurred in Die Casting section of 10 months period, taken from a production process production system database. Data of defective process of Die Casting on the cylinder component from A production process Production System in 10 months on same year as the research is shown in Table-1.
Analysis Method:
Data tabulation was processed to determine the dominant type of defective cylinder component. Data analysis was performed by using PDCA methods and quality assistance instrument, seven tools to analyze the all causes factors of dominant type of defective product, in this case the leak problem of cylinder component. 5 why analysis is mentioned as part of the analysis process in PICA-PA description. Pareto diagram is used to determine the type of defective product that will prioritized in the corrective actions. Cause-effect diagram is used to comprehend the cause's factors of undercut and porous on the cylinder component.
Research Subjects and Scope:
The problem limitation of this research is only on cylinder component part, produced by Die Casting section, and the finishing methods is using the PDCA and quality assistance tools which are seven tools and corrective actions.
6. Main Research Results:
Key Research Results:
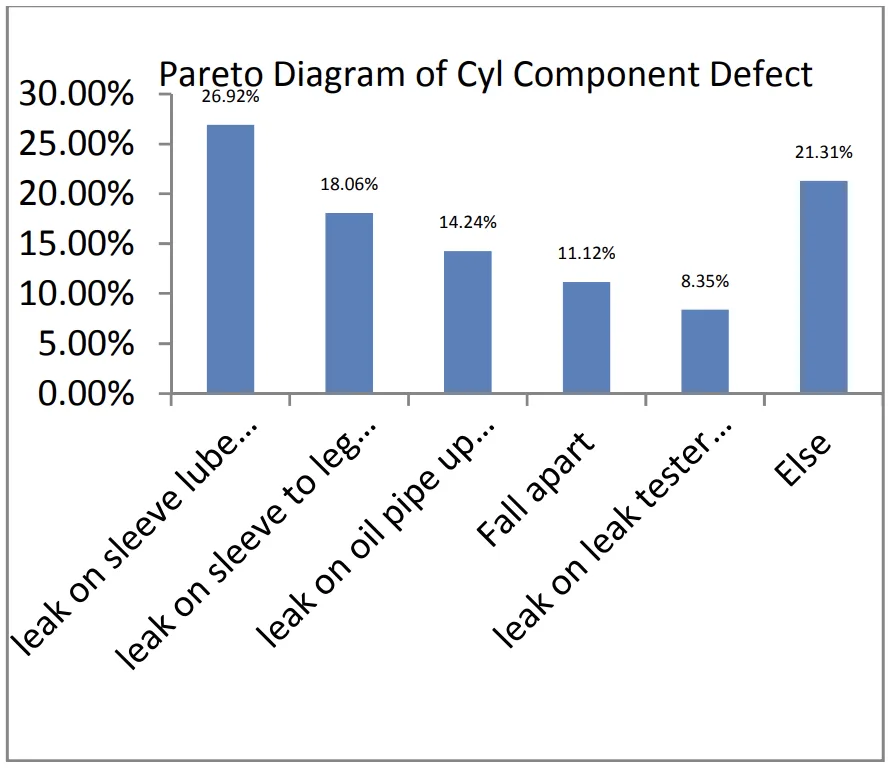
The preliminary data shows the defective product percentage of cylinder component in ten months at 4.47% rate, above the 3.6% target. Pareto diagram shows four defective categories at a total of 67.57% rate: leak on sleeve lube bolt stood (26,92%), leak on sleeve to leg shield (18,06%), leak on oil pipe up to leg shield (14,24%), and leak on leak tester machine (8,35%). The analysis indicated that causes of the problem are undercut and porous on cylinder component. Corrective action was performed to fix all factor that could initiate leak defective on cylinder component. Defective data is taken in five months after corrective actions, and the result shows achievement of total defective cylinder component for five months at 3.17%, which is below maximal limitation percentage defective product at 3.60%.
Analysis of presented data:
Table-1.Manufacturing defects cylinder component.
| Defect | Qty | % |
|---|---|---|
| leak on sleeve lube bolt stood | 7426 | 1.20 |
| leak on sleeve to leg shield | 4984 | 0.81 |
| leak on oil pipe up to leg shield | 3930 | 0.64 |
| part apart | 3068 | 0.50 |
| leak on leak tester machine | 2303 | 0.37 |
| else * | 5879 | 0.95 |
| Total | 27590 | 4.47 |
Figure-2. Pareto of cylinder component defect.
[Figure-2. Pareto of cylinder component defect. is presented here as described in the paper]
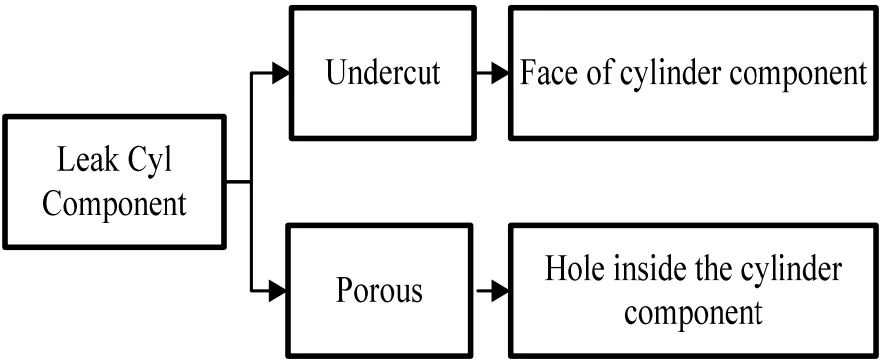
Figure-3. Analysis of primary causes of disability leaking cylinder components.
[Figure-3. Analysis of primary causes of disability leaking cylinder components. is presented here as described in the paper]
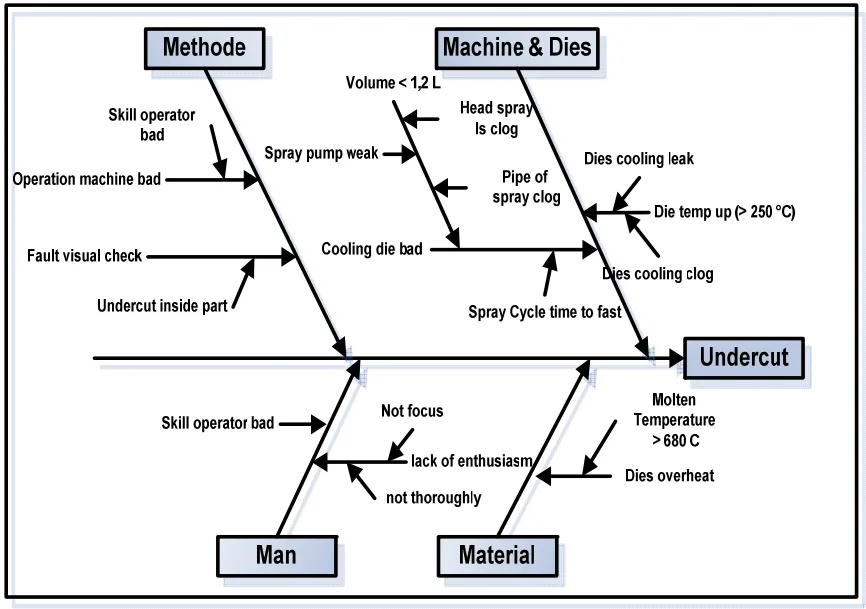
Figure-4. Cause and effect diagram undercut cylinder components.
[Figure-4. Cause and effect diagram undercut cylinder components. is presented here as described in the paper]
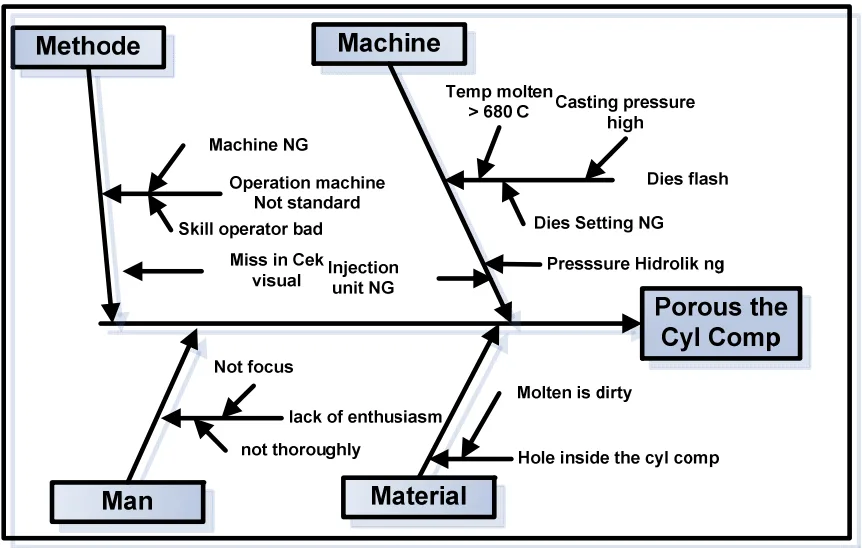
Figure-5. Cause and effect diagram component porous cylinder.
[Figure-5. Cause and effect diagram component porous cylinder. is presented here as described in the paper]
Table-2. Preventive action defective leaking cylinder component.
| Maintenance items | Period | PIC |
|---|---|---|
| Material | ||
| Control holding furnace temperature | 1 hour | Melting Operator |
| Cleaning holding furnace | 2 week | Melting operator |
| Replace holding furnace | 2 year | Process Engineering |
| Machine | ||
| Check nitrogen pressure | 1 month | Technician |
| Check hidrolik oil | Every start prod | Dies Casting operator |
| Replace hidrolik oil | 1 year | Process Engineering |
| Replace plunger tip | 7.000 shoot/NG | Technician |
| Replace plunger sleeve | 60.000 shoot/NG | Technician |
| Replace auto spray | 10.000 shoot | Technician |
| Cleaning auto spray | 10.000 shoot | Technician |
| Check spray pump | 1 month | Process Engineering |
| Dies | ||
| Maintain slide core dan dies pin | 3.000 shoot | Dies Maintenance |
| Maintain and replace dies | 10.000 shoot | Dies Maintenance |
| Operator | ||
| Upgrade skill competency | 6 month | Section head |
Table-3. Component defect data cylinders after repair.
| Defect | Qty | % |
|---|---|---|
| leak on sleeve to leg shield | 2,683 | 0.92 |
| leak on sleeve lube bolt stood | 1,288 | 0.44 |
| leak on oil pipe up to leg shield | 559 | 0.19 |
| part apart | 1,117 | 0.38 |
| leak on leak tester machine | 695 | 0.24 |
| else | 2,922 | 1.00 |
| Total | 9,264 | 3.17 |
Figure Name List:
- Figure-1. PDCA cycle in sustainable improvements.
- Figure-2. Pareto of cylinder component defect.
- Figure-3. Analysis of primary causes of disability leaking cylinder components.
- Figure-4. Cause and effect diagram undercut cylinder components.
- Figure-5. Cause and effect diagram component porous cylinder.
7. Conclusion:
Summary of Key Findings:
The research concluded that the corrective and preventive actions implemented using PDCA and seven quality tools were effective in reducing the defective rate of cylinder components from 4.47% to 3.17%, achieving the target of below 3.6%. The main causes of defects were identified as undercut and porous, stemming from issues related to material quality (dirty molten material, temperature), machine conditions (autospray unit, injection pressure, dies overhead), and operator skill.
Academic Significance of the Study:
This study demonstrates the practical application of PDCA and seven quality tools in a die casting process to systematically analyze and solve quality problems. It contributes to the body of knowledge on quality management in manufacturing, specifically in the context of die casting and motor cycle component production.
Practical Implications:
The findings provide a practical framework for die casting industries to improve their product quality and reduce defect rates. The specific corrective and preventive actions identified in the paper, such as maintaining molten metal temperature, optimizing spray unit performance, and regular die maintenance, can be directly implemented to address leak defects in cylinder components. The PICA-PA (Problem Identification Corrective Action and Preventive Action) approach outlined in the paper offers a structured method for problem-solving and documentation in production processes, aligning with ISO 9000 standards.
Limitations of the Study and Areas for Future Research:
The research acknowledges that some factors were not fully analyzed, including operator consistency, machine stability, and die design. Future research could delve deeper into these factors to further optimize the die casting process and minimize defects. Further investigation into advanced inspection methods for detecting leak defects could also be beneficial.
8. References:
- Baldwin R.M. Corrective/Preventive Actio (CAPA) Guide lines. http://www.rmbimedical.com/regulatoryAffairs/CAPAMai n.aspx.
- Bhat, V. And J Cozzolino. 1993. Total Quality: An Effective Management Tool. www.casact.org.pp. 101-123. Agustus 2005.
- Dahlgaard Jens J., Kanji, Gopal K and Kristensen Kai. 2002. Fundamentals of Total Quality Management. London and New York: Taylor and Francis Group.
- Feigenbaum, A.V.1991. Total Quality Control. New York: McGraw-Hill.
- ISO. 2008. Quality Management System Requirement (4th edition). Switzerland: Author.
- Montgomery, Douglas. 2005. Introduction to Statistical Quality Control. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley andSons, Inc.
- Nazlina. 2005. Studi Pengendalian Jumlah Cacat dengan Menggunakan Metode Poka Yoke di PT. Morawa Electric Transbuana. Jurnal Sistem Teknik Industri. 6(4).
- Pipan K. Kern., Pavletic D. and Sokovic M. 2010. Quality Improvement Methodologies – PDCA Cycle, RADAR Matrix, DMAIC and DFSS. Journal of Achievements in Materials and Manufacturing Engineering. 1: 476-483.
- Schneiderman Arthur M. 1998. Are There Limits to Total Quality Management. Journal of Strategy Management Competition. (11): 35-45.
- Sokovic M., Pavletic, D. and Krulcic D. 2006. Six Sigma Process Improvements in Automotive Parts Production. Journal of Achievements in Materials and Manufacturing Engineering. 19: 96-102.
9. Copyright:
- This material is "Rahmat Nurcahyo"'s paper: Based on "Corrective and preventive actions of motor cycle cylinder component leak problem on casting process".
- Paper Source: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/312062708
This material was created to introduce the above paper, and unauthorized use for commercial purposes is prohibited.
Copyright © 2025 CASTMAN. All rights reserved.