This introduction paper is based on the paper "A Review of Bobbin Tool Friction Stir Welding (FSW) Process" published by "IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering".
![Fig. 1: Representation of the main parameters and nomenclature of FSW joints [2]](https://castman.co.kr/wp-content/uploads/image-2647.webp)
1. Overview:
- Title: A Review of Bobbin Tool Friction Stir Welding (FSW) Process
- Author: Sameer S. Chaudhary, Kaushal H. Bhavsar
- Year of publication: 2016
- Journal/academic society of publication: IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering
- Keywords: Friction stirs welding (FSW); bobbin tool; aluminums alloy; mechanical properties
2. Abstract:
Over the last twenty years Friction Stir Welding (FSW) has proven to be a very promising new joining technique. Especially high strength aluminium alloys can be welded with large advantages as compared to conventional fusion welding processes. Friction stir welding (FSW) of aluminium components using both fixed and variable gap bobbin tools has been demonstrated by several researchers, and reportedly these procedures were relatively easy to develop. Bobbin welds do not have an initial phase where the welding tool probe is plunged axially into the work piece as is done in conventional FSW. The objective of current paper is to examine and summarize information for change in mechanical properties for bobbin tool friction stir welding (FSW) for joining materials.
3. Introduction:
Friction stir welding (FSW) process was invented by Wayne Thomas et al. and patented by The Welding Institute (TWI) on 6th December 1991. This patent has since become one of the most widely referenced documents in welding and joining technology. The FSW process has become one major milestone in the welding technology history, especially in the joining of lightweight metallic structures. FSW has matured to the point where it is used in applications such as commercial and military aircraft where welding has never before been allowed.
4. Summary of the study:
Background of the research topic:
FSW is a process for joining workpieces in the solid-phase, using an intermediate non-consumable tool, with a suitably profiled shoulder and probe, made of material that is harder than the workpiece material being welded. The rotating tool is plunged into the weld joint and forced to traverse along the joint line, heating the abutting components by interfacial and internal friction.
Status of previous research:
The ever growing list of FSW users includes Boeing, Airbus, Eclipse, BEA, Lockheed Martin, NASA, US Navy, Mitsubishi, and Kawasaki, Fokker as well as other industrial concerns throughout the world in transport structural applications. Friction stir welding has been applied to many lightweight metals and alloys, for example aluminium, copper and zinc, magnesium, and titanium, with excellent results once the operational parameters have been optimized.
Purpose of the study:
The objective of current paper is to examine and summarize information for change in mechanical properties for bobbin tool friction stir welding (FSW) for joining materials. The findings presented, friction stir welding (FSW) with bobbin tool and parameter involved in it understand.
Core study:
The study focuses on bobbin tool technology which differs from conventional FSW tools. The bobbin techniques provide a fixed gap between two shoulders, while the adaptive technique enables adjustment of the gap between the shoulders during the welding operation. The self-reacting principle of the bobbin technique means that the normal down force required by conventional FSW is reduced/eliminated.
5. Research Methodology
Research Design:
This is a comprehensive literature review examining various research findings on bobbin tool friction stir welding technology and its applications in aluminum alloy welding.
Data Collection and Analysis Methods:
The study collected and analyzed data from multiple research papers and experimental studies conducted by various researchers including Pedro Vilaça et al. (2011), Wayne Thomas et al. (2010), Eládio Amaro Camacho Andrade et al.(2010), Huijie Zhang et al. (2014), and J. Hilgert et al.(2010).
Research Topics and Scope:
The research scope covers bobbin tool configurations, mechanical properties analysis, hardness distribution, tensile strength evaluation, and comparison with conventional FSW processes for aluminum alloy welding applications.
6. Key Results:
Key Results:
- The fixed gap bobbin technique shows promise for welding 25 mm thick aluminium plate without the need for an axial down force
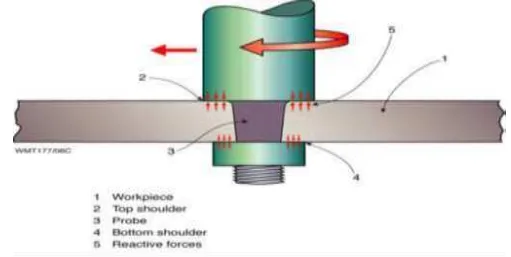
- For bobbin tool, two shoulders provide sufficient heat generation from both sides of the workpiece and the containment of reactive forces within the tool itself means that compressive deformation (Squashing) of the probe does not occur
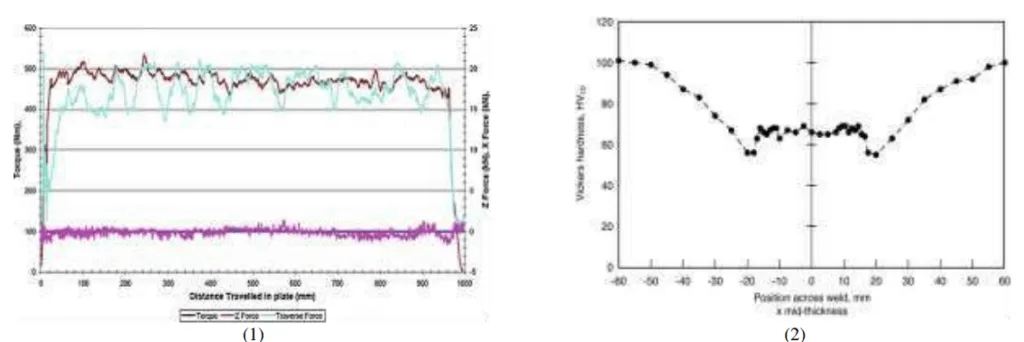
- The minimum hardness is located in the HAZ near the interface between the TMAZ and the HAZ
- The tensile strength of bobbin tool FSW joint is firstly increased with the increase of welding speed, and then shows a sharp decrease at a high welding speed of 150 mm/min due to the occurrence of void defects
- A maximum strength efficiency of 75% is achieved in bobbin tool FSW joints
- The hardness distributions are nearly the same in the three layers of the joint, indicating a homogeneity of mechanical properties in thickness direction of joints of the bobbin tool FSW
Figure Name List:
- Fig. 1: Representation of the main parameters and nomenclature of FSW joints
- Fig. 2: Bobbin tool showing self-contained reactive forces
- Fig. 3: (1) Instrumentation chart (2) Hardness survey mid-thickness in 25mm thick 6082-T6 aluminium weld
7. Conclusion:
- The minimum hardness is located in the heat affected zone (HAZ) near the interface between the Thermomechanical affected zone (TMAZ) and the heat affected zone (HAZ)
- The fixed gap bobbin technique shows promise for welding 25 mm thick aluminium plate without the need for an axial down force
- For bobbin tool, two shoulders provide sufficient heat generation from both sides of the workpiece and the containment of reactive forces within the tool itself means that compressive deformation (Squashing) of the probe does not occur
- The tensile strength of bobbin tool FSW joint is firstly increased with the increase of welding speed, and then shows a sharp decrease at a high welding speed due to the occurrence of void defects. A maximum strength efficiency of 75% is achieved in this study
8. References:
[1] Thomas, W.M., Nicholas, E.D., Needham, J.C., Murch, M.G, Temple-Smith, P., Dawes, C.J.Improvements relating to friction stir welding. US Patent No. 5,460,317 (1991). [2] Pedro Vilaça and Wayne Thomas: Friction Stir Welding Technology. DOI: 10.1007/8611_2011_56(10 April 2011) [3] Thomas, WM; Nicholas, ED; Needham, JC; Murch, MG;Temple-Smith, P;Dawes, CJ.Friction-stir butt welding, GB Patent No. 9125978.8, International patent application No. PCT/GB92/02203, (1991). [4] Eládio Amaro Camacho Andrade, Instituto Superior Técnico, Lisboa, Portugal. Development of the Bobbin-Tool for Friction Stir Welding Characterization and analysis of aluminum alloy processed AA 6061-T4 (2010). [5] Huijie Zhang ⇑, Min Wang, Xiao Zhang, Guangxin Yang. Microstructural characteristics and mechanical properties of bobbin tool friction stir welded 2A14-T6 aluminum alloy (2014). [6] J. Hilgert*,1, L.L. Huetsch1, J.F. dos Santos1 and N. Huber1. Material Flow around a Bobbin Tool for Friction Stir Welding 2010.
9. Copyright:
- This material is a paper by "Sameer S. Chaudhary, Kaushal H. Bhavsar". Based on "A Review of Bobbin Tool Friction Stir Welding (FSW) Process".
- Source of the paper: IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering | Volume 2 | Issue 10 | April 2016
- This material is summarized based on the above paper, and unauthorized use for commercial purposes is prohibited.
- Copyright © 2025 CASTMAN. All rights reserved.
Paper Summarize:
This comprehensive review examines bobbin tool friction stir welding (FSW) technology as an advanced joining technique for aluminum alloys. The study demonstrates that bobbin tool FSW offers significant advantages over conventional FSW, including elimination of axial down force requirements and improved mechanical properties. The research confirms that bobbin tool technology achieves maximum strength efficiency of 75% with optimal welding parameters and provides homogeneous mechanical properties throughout the joint thickness.
Key questions and answers about the research:
Q1. What is the main advantage of bobbin tool FSW compared to conventional FSW?
A1. According to "A Review of Bobbin Tool Friction Stir Welding (FSW) Process", the main advantage is that bobbin tool FSW eliminates the need for axial down force because the reactive forces within the weld are contained between the bobbin shoulders, and two shoulders provide sufficient heat generation from both sides of the workpiece.
Q2. What is the maximum strength efficiency achieved in bobbin tool FSW joints?
A2. Based on the research findings in "A Review of Bobbin Tool Friction Stir Welding (FSW) Process", a maximum strength efficiency of 75% is achieved in bobbin tool FSW joints, as reported in the Key Results section.
Q3. Where is the minimum hardness located in bobbin tool FSW joints?
A3. According to the Conclusion section of "A Review of Bobbin Tool Friction Stir Welding (FSW) Process", the minimum hardness is located in the heat affected zone (HAZ) near the interface between the Thermomechanical affected zone (TMAZ) and the heat affected zone (HAZ).
Q4. What happens to tensile strength at high welding speeds in bobbin tool FSW?
A4. As stated in "A Review of Bobbin Tool Friction Stir Welding (FSW) Process", the tensile strength of bobbin tool FSW joint firstly increases with the increase of welding speed, but then shows a sharp decrease at a high welding speed of 150 mm/min due to the occurrence of void defects.
Q5. What thickness of aluminum plate can be welded using the fixed gap bobbin technique?
A5. According to the research findings in "A Review of Bobbin Tool Friction Stir Welding (FSW) Process", the fixed gap bobbin technique shows promise for welding 25 mm thick aluminium plate without the need for an axial down force.
Q6. How does the hardness distribution vary across the thickness direction in bobbin tool FSW joints?
A6. Based on the Key Results section of "A Review of Bobbin Tool Friction Stir Welding (FSW) Process", the hardness distributions are nearly the same in the three layers of the joint, indicating a homogeneity of mechanical properties in thickness direction of joints of the bobbin tool FSW.