This article introduces the paper ['LEAN MANUFACTURING - PROCESS AUTOMATION AND ELIMINATION OF PRODUCTION LOSSES IN ROMANIAN AUTOMOTIVE INDUSTRY'] published by ['THE ANNALS OF "DUNAREA DE JOS" UNIVERSITY OF GALATI'].
1. Overview:
- Title: LEAN MANUFACTURING - PROCESS AUTOMATION AND ELIMINATION OF PRODUCTION LOSSES IN ROMANIAN AUTOMOTIVE INDUSTRY
- Author: Ovidiu AMBRUS
- Publication Year: 2017
- Publishing Journal/Academic Society: THE ANNALS OF "DUNAREA DE JOS" UNIVERSITY OF GALATI, FASCICLE IX. METALLURGY AND MATERIALS SCIENCE
- Keywords: lean manufactory, automotive industry, process automation
![Fig. 1. Lean Manufacturing pillars [1]](https://castman.co.kr/wp-content/uploads/image-732-png.webp)
2. Abstracts or Introduction
This paper addresses the paramount importance of Lean Manufacturing as a contemporary management methodology for manufacturing enterprises. Integrated with "six sigma" quality tools, Lean Manufacturing, adapted from the Toyota Production System by Womack and Jones in 1995, emphasizes fundamental operational capabilities. It encompasses flexible assembly cells, intricate operations, highly skilled personnel, superior product quality, a diverse range of interchangeable components, and consistently high quality, all while reducing costs through process optimization, international market reach, and global competitiveness [2]. TRW Automotive serves as a practical example of these principles in leather product preparation.
The paper introduces Lean manufacturing as a systematic approach to eradicate waste ("Muda") within manufacturing systems, also considering waste from overburden ("Muri") and uneven workloads ("Mura"). From a client-centric perspective, "value" is defined as any action or process customers are willing to pay for. Manufacturing at minimum costs is presented as a production philosophy aimed at shortening the lead time between order and delivery by eliminating losses. The adoption of LEAN principles is highlighted as a crucial survival strategy in today's cost-sensitive production landscape. The foundational pillars of Lean Manufacturing are illustrated in Figure 1.
3. Research Background:
Background of the Research Topic:
Lean manufacturing, or lean production, is defined as a systematic methodology focused on the elimination of waste ("Muda") within a manufacturing system. This extends to addressing waste generated by overburden ("Muri") and unevenness in workloads ("Mura"). From the viewpoint of the customer, "value" is any action or process deemed worth paying for. The core philosophy of minimizing manufacturing costs aims to reduce the order-to-delivery cycle time through loss elimination. The implementation of LEAN principles has evolved into a strategic imperative for survival in production environments where cost reduction is a market reality.
Status of Existing Research:
The methodology is rooted in the Toyota Production System and adapted for Western industries by Womack and Jones [2]. The paper references Taichi Ohno's classification of the seven production losses [3], indicating a foundation in established Lean Manufacturing theory. These losses include: Overproduction, Waiting, Transport, Processing, Inventory, Motion, and Corrections.
Necessity of the Research:
In a competitive market, continuous cost reduction is essential. The paper posits that companies must embrace Lean methodologies to remain competitive. Furthermore, it identifies limitations in human-driven process improvements, suggesting automation as a means to overcome these limitations and enhance efficiency and reliability beyond human capabilities. Automation is presented as a solution to achieve consistent results and address inherent variability associated with manual operations.
4. Research Purpose and Research Questions:
Research Purpose:
The primary research purpose is to investigate the implementation of automation within a Lean Manufacturing framework at TRW Automotive in Timisoara, Romania. The study aims to demonstrate how process automation can contribute to the elimination of production losses and enhance manufacturing efficiency within the automotive industry context.
Key Research:
The key research focus is a case study on the automation of the die casting process for steering wheels at TRW Automotive. This involves analyzing the transition from manual to automated process steps and evaluating the anticipated benefits in terms of productivity, quality, cost reduction, and safety.
Research Hypotheses:
The implicit research hypothesis is that the strategic implementation of automation technologies within a Lean Manufacturing framework will lead to significant improvements in key performance indicators, including:
- Increased productivity and output.
- Enhanced product quality through consistent process execution.
- Reduction in human operator time and associated labor costs.
- Improved operator safety, particularly in handling hazardous materials like magnesium.
5. Research Methodology
Research Design:
The research employs a case study design, focusing on the specific implementation of automation within the die casting process at TRW Automotive's Timisoara facility. This approach allows for an in-depth examination of the practical application of Lean Manufacturing principles and automation technologies in a real-world industrial setting.
Data Collection Method:
Data collection is based on the analysis of the existing manual and semi-automatic die casting processes at TRW Automotive, contrasted with the planned and implemented automated processes. This involves observing and documenting the process steps before and after automation, as well as collecting anticipated performance metrics.
Analysis Method:
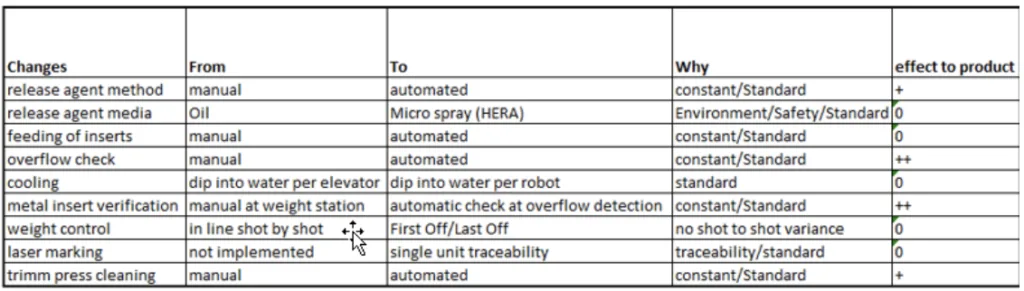
The analysis is primarily qualitative, involving a comparative assessment of the manual versus automated processes. The study evaluates the expected benefits of automation in the context of Lean Manufacturing principles, focusing on the elimination of the seven wastes. A table (Fig. 7) is presented to systematically analyze the changes and benefits resulting from automation implementation.
Research Subjects and Scope:
The research subject is the die casting operation at TRW Automotive in Timisoara, specifically focusing on the production of steering wheels. The scope is limited to the automation of specific process steps within this die casting operation and its impact on productivity, quality, cost, and safety.
6. Main Research Results:
Key Research Results:
The anticipated key research results, based on the prototype cell implementation, are:
- A projected 30% increase in productivity (output) for double cavity machines.
- An expected 10% improvement in product quality due to the elimination of human visual inspection variability and enhanced process consistency.
- A 40% reduction in human operator time, leading to decreased labor costs.
- A significant enhancement in human safety, particularly relevant in magnesium die casting, where uncontrolled ignition risks are mitigated through automation.
Analysis of presented data:
Figure 7, "Table of changes and benefits on product by the implementation of the automation process on die casting prototype cell," details the specific changes from manual to automated processes. Key changes include:
- Release agent method: Transition from manual to automated micro-spray (HERA), ensuring constant and standardized application.
- Release agent media: Shift from Oil to Micro spray (HERA) for environmental and safety improvements.
- Feeding of inserts: Automation of insert feeding for consistent and standardized process.
- Overflow check: Automated overflow detection for improved quality control.
- Cooling: Implementation of robot-controlled dip cooling, replacing manual elevator dip cooling for standardization.
- Metal insert verification: Automated verification at overflow detection, improving upon manual weight station checks.
- Weight control: Implementation of "First Off/Last Off" weight control to reduce shot-to-shot variance.
- Laser marking: Introduction of single unit traceability through automated laser marking.
- Trimm press cleaning: Automation of trimming press cleaning for consistent and standardized maintenance.
These changes are expected to yield benefits such as process standardization, enhanced environmental and safety conditions, improved quality control, reduced process variability, and enhanced product traceability.
Figure Name List:



- Fig. 1. Lean Manufacturing pillars [1]
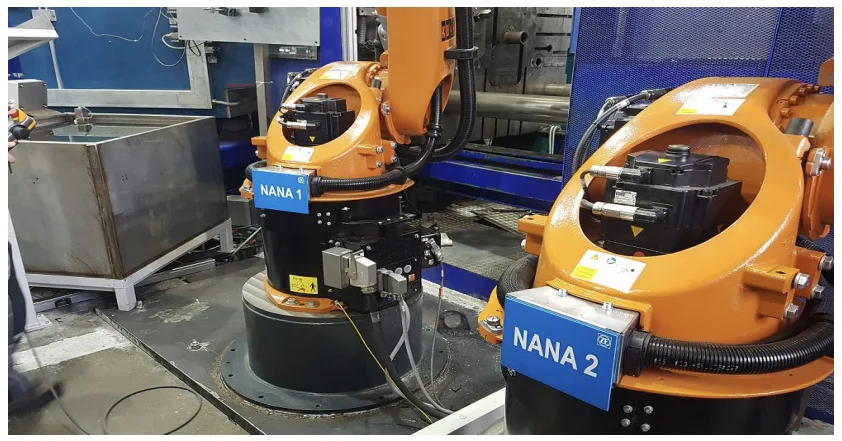
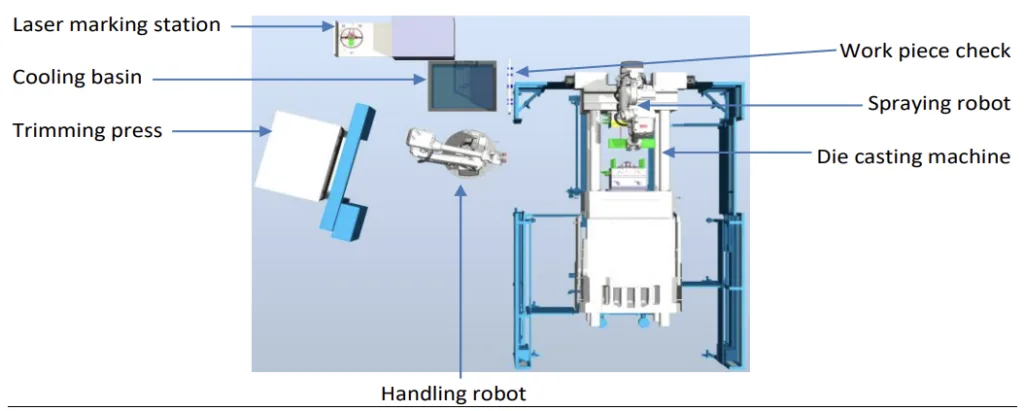
- Fig. 2. New process steps schematics - introduction of the first handling robot
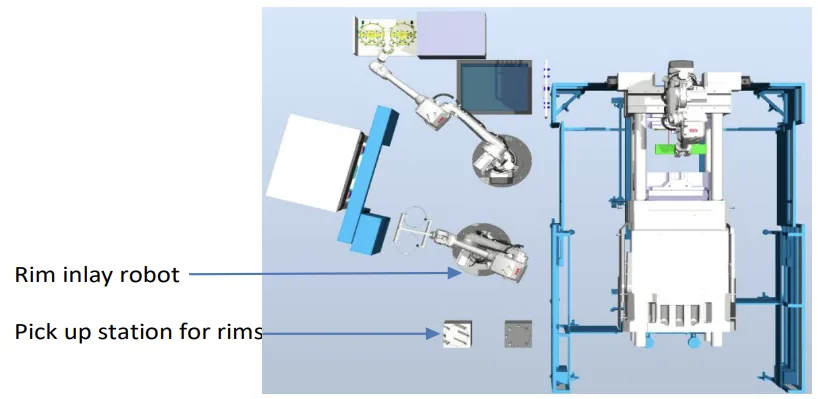
- Fig. 3. New process steps schematics- introduction of the second handling robot
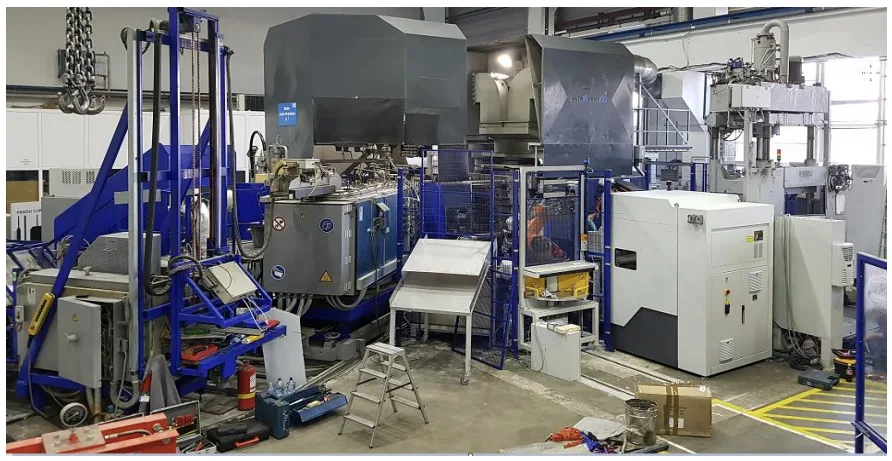
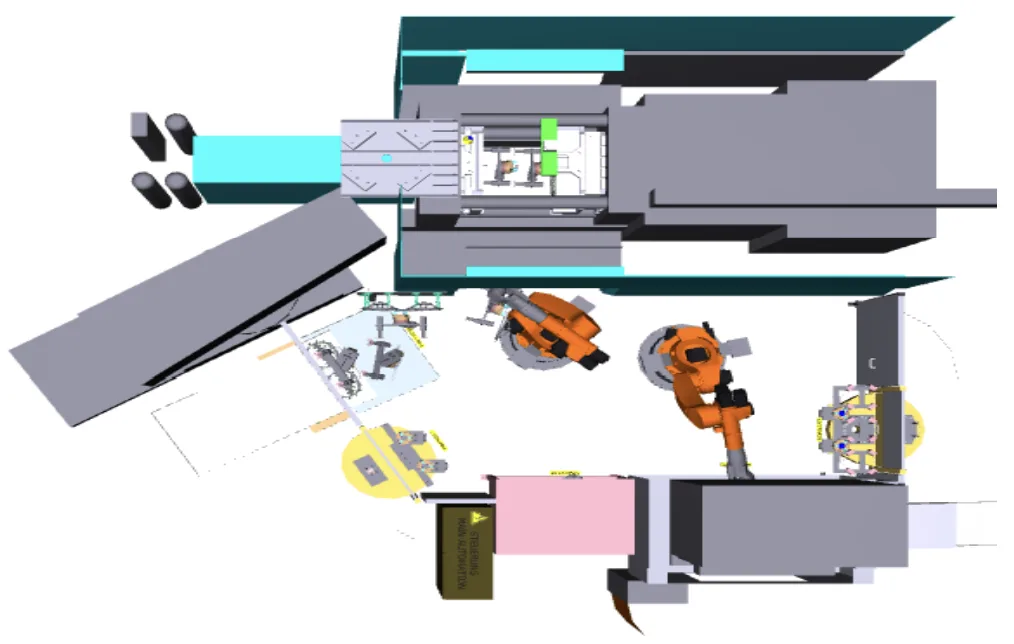
- Fig. 4. New layout of the die casting machine- after the implementation of automation
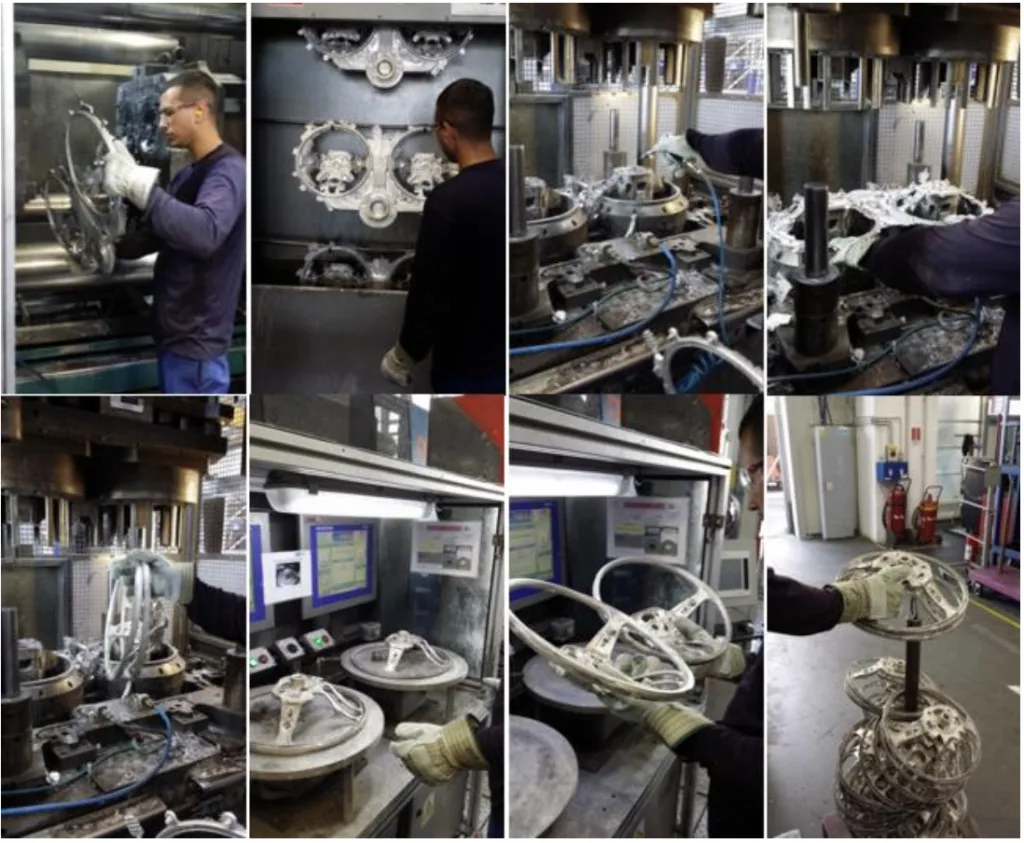
- Fig. 5. Activities related to the automation process implementation at first/prototype cell at TRW Automotive
- Fig. 6. Activities related to the automation process implementation at first/prototype cell at TRW Automotive
- Fig. 7. Table of changes and benefits on product by the implementation of the automation process on die casting prototype cell
7. Conclusion:
Summary of Key Findings:
The study concludes that the implementation of automation within a Lean Manufacturing framework at TRW Automotive is anticipated to be highly successful. Preliminary results from the prototype cell indicate significant potential for improvements in productivity, quality, operator time reduction, and safety. The automation initiative is expected to enhance production flexibility by enabling work brigades to synchronize their pace without extensive time studies for workload balancing.
Academic Significance of the Study:
This study provides a practical case example of successfully integrating Lean Manufacturing principles with advanced automation technologies within the automotive industry. It contributes to the body of knowledge on operational excellence by demonstrating the tangible benefits of this integrated approach in a real-world manufacturing environment.
Practical Implications:
The findings offer valuable insights for automotive manufacturers and other industries considering automation as a strategy to enhance their manufacturing processes. The case study at TRW Automotive serves as a model for implementing automation within a Lean framework to achieve operational improvements, reduce production losses, and enhance product quality.
Limitations of the Study and Areas for Future Research:
The study acknowledges that the results are preliminary and based on a prototype cell. The findings are not yet definitive for the entire production line. Future research should focus on evaluating the long-term impact and scalability of the automation implementation across the complete die casting production line at TRW Automotive. Further investigation into the broader applicability of these findings in other manufacturing contexts and industries is also recommended.
8. References:
- [1]. Allen J., Robinson C., Stewart D., Lean Manufacturing - a plant floor guide, Society.
- [2]. ***, Lean manufacturing - Methods for reducing costs, Pilot Project.
- [3]. Womack J. P., Jones D. T., Roos D., The Machine that Changed the World: How Lean Production Revolutionized the Global Car Wars, S. & Schuster, London, 1990.
- [4]. ***, Lean manufacturing - Methods for cost reduction, Pilot Project TRW Automotive.
9. Copyright:
- This material is "Ovidiu AMBRUS"'s paper: Based on "LEAN MANUFACTURING - PROCESS AUTOMATION AND ELIMINATION OF PRODUCTION LOSSES IN ROMANIAN AUTOMOTIVE INDUSTRY".
- Paper Source: [THE ANNALS OF "DUNAREA DE JOS" UNIVERSITY OF GALATI, FASCICLE IX. METALLURGY AND MATERIALS SCIENCE, Nº. 1 - 2017, ISSN 1453-083X]
This material was summarized based on the above paper, and unauthorized use for commercial purposes is prohibited.
Copyright © 2025 CASTMAN. All rights reserved.