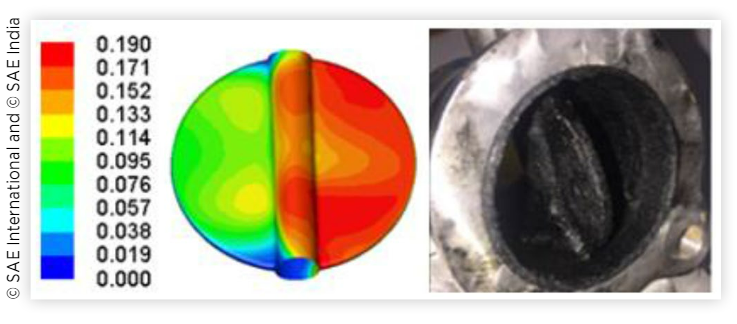
CFD 시뮬레이션을 사용하여 플라스틱 덕트의 열 핫스팟 및 스로틀 밸브의 그을음 침착을 최소화하기 위한 EGR 믹서 최적화
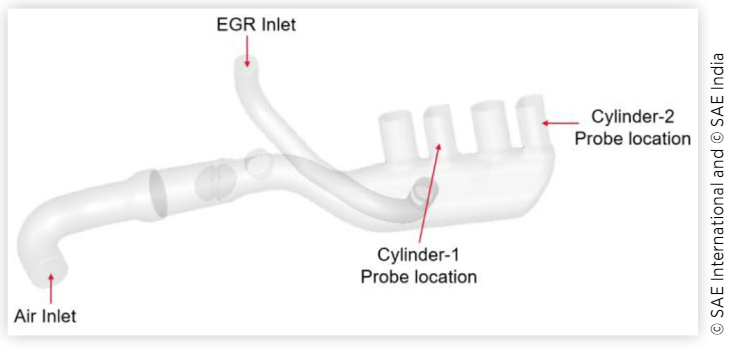
In recent time, with inception of BS VI emission regulation with more focus on fuel economy and emission, many engine parts which were conventionally made from metal are getting replaced with plastic components for reducing weight to attain better fuel economy. EGR is commonly used technique to reduce emissions in diesel engine along with after treatment devices. EGR reduces peak combustion temperature inside the combustion chamber thereby reducing NOx. EGR is bypassed from the exhaust manifold, cooled down in EGR cooler and mixed with intake air at upstream of the intake manifold. Throttle valve is used for controlling the charged air flow to cylinders for different vehicle operating conditions. With compact engine layout EGR mixer are often located near to throttle valve thereby increasing the possibility of soot deposition on throttle valve. Once these soot & hydrocarbons cool down they can transform into sticky amorphous carbon, which obstruct the functioning of throttle valve thereby leads to not meeting the required emission levels. At the same time, hot EGR impinging on plastic intake ducts can melt the plastic surface. Mixer module is provided to create turbulence for better mixing of EGR & fresh air. While most of the literature work done in past is based on EGR distribution analysis, this paper focuses on minimizing the thermal hotspot and chances of soot deposition on throttle valve along with cylinder-to-cylinder EGR distribution. It was challenging to design an EGR mixer with given constraints which could meet all the above requirements. The boundary conditions for the highly pulsating flow are used from transient 1-D simulation. CFD simulations are performed for different EGR mixers to evaluate & reduce temperature on the plastic duct, soot deposition and increase EGR mixing quality. For the final model, hot spot location, soot deposition and cylinder-to-cylinder distribution were optimized.
최근에는 연비와 배기가스에 더 중점을 둔 BS VI 배기가스 규제가 시작되면서 기존의 금속으로 만들어진 많은 엔진 부품이 더 나은 연비를 달성하기 위해 무게를 줄이기 위해 플라스틱 부품으로 교체되고 있습니다. EGR은 후처리 장치와 함께 디젤 엔진의 배기 가스를 줄이기 위해 일반적으로 사용되는 기술입니다. EGR은 연소실 내부의 피크 연소 온도를 낮추어 NOx를 감소시킵니다. EGR은 배기 매니폴드에서 우회되고 EGR 쿨러에서 냉각되고 흡기 매니폴드의 상류에서 흡기 공기와 혼합됩니다. 스로틀 밸브는 다양한 차량 작동 조건에서 실린더로의 충전 공기 흐름을 제어하는 데 사용됩니다. 컴팩트한 엔진 레이아웃으로 EGR 믹서는 종종 스로틀 밸브 근처에 위치하여 스로틀 밸브에 그을음이 침착될 가능성을 높입니다. 이러한 그을음 및 탄화수소가 냉각되면 끈적한 비정질 탄소로 변형되어 스로틀 밸브의 기능을 방해하여 필요한 배출 수준을 충족하지 못하게 됩니다. 동시에 플라스틱 흡입 덕트에 닿는 뜨거운 EGR은 플라스틱 표면을 녹일 수 있습니다. 믹서 모듈은 EGR과 신선한 공기의 더 나은 혼합을 위해 난류를 생성하기 위해 제공됩니다. 과거에 수행된 대부분의 문헌 작업은 EGR 분포 분석을 기반으로 하지만 이 문서에서는 실린더 대 실린더 EGR 분포와 함께 스로틀 밸브의 열 핫스팟 및 그을음 침착 가능성을 최소화하는 데 중점을 둡니다. 위의 모든 요구 사항을 충족할 수 있는 주어진 제약 조건으로 EGR 믹서를 설계하는 것은 어려운 일이었습니다. 높은 맥동 흐름에 대한 경계 조건은 과도 1차원 시뮬레이션에서 사용됩니다. 다양한 EGR 믹서에 대해 CFD 시뮬레이션이 수행되어 플라스틱 덕트의 온도, 그을음 퇴적 및 EGR 혼합 품질을 평가 및 감소시킵니다. 최종 모델의 경우 핫스팟 위치, 그을음 침착 및 실린더 간 분포가 최적화되었습니다.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4271/2019-26-0286
Citation: Agrawal, A., Raju, K., Santra, T., Gopinathan, N. et al., "Optimization of EGR Mixer to Minimize Thermal Hot Spot on Plastic Duct & Soot Deposition on Throttle Valve Using CFD Simulation," SAE Technical Paper 2019-26-0286, 2019, https://doi.org/10.4271/2019-26-0286.
Download Citation
Author(s): Ayush Agrawal, Kumar Raju, Tanmay Santra, Nagarajan Gopinathan, Joy Varghese, Sataya Brata Ghadei
Affiliated: Mahindra & Mahindra, Ltd., Mahindra Research Valley
Pages: 6
Event: Symposium on International Automotive Technology 2019
ISSN: 0148-7191e-ISSN: 2688-3627

References
- Maiboom , A. , Tauzia , X. , and Hétet , J.-F. Influence of EGR Unequal Distribution from Cylinder to Cylinder on NOx-PM Trade-Off of a HSDI Automotive Diesel Engine Applied Thermal Engineering 29 10 2043 2050 2009
- Heywood , J. Internal Combustion Engine Fundamentals New York McGraw Hill 1988
- Husberg , T. , Gjirja , S. , Denbratt , I. , and Engström , J. Visualization of EGR Influence on Diesel Combustion With Long Ignition Delay in a Heavy-duty Engine SAE Technical Paper 2004-01-2947 2004 10.4271/2004-01-2947
- Balázs , K. , Marcell , K. , and Huba , N.
- Partridge , W. , Lewis , S. , Ruth , M. , Muntean , G. et al. Resolving EGR Distribution and Mixing SAE Technical Paper 2002-01-2882 2002 10.4271/2002-01-2882
- Dimitriou , P. , Burke , R. , Copeland , C. et al. Study on the Effects of EGR Supply Configuration on Cylinder-to-Cylinder Dispersion and Engine Performance Using 1D-3D Co-Simulation SAE Technical Paper 2015-32-0816 2015
Cited By
- Karthikeyan N. Krishnan, Padmavathi Ramadandi, Vinodini Bhargava, Karthik Chandana, "EGR Flow Control Strategy for a Smaller Capacity Diesel Engine Using a Phase Shifting Chamber", SAE Technical Paper Series 1 , 2020SAE MOBILUS
- Karthikeyan N. Krishnan, Padmavathi Ramadandi, Vikramraj M, Sakthivel Elumalai, "Simulation Based Approach to Improve the Engine Oil Warmup Behavior Using Exhaust Gas During NEDC Cycle", SAE Technical Paper Series 1 , 2021SAE MOBILUS