YongfaZhangabc FuhuiShenb JiangZhengcd SebastianMünstermannb TianjiaoLic WeijianHanef ShiyaoHuangef
Highlights
•The microstructure and ductile fracture characteristics of the aluminum alloy (Aural-2) produced by high-pressure die casting have been thoroughly characterized via experimental and numerical approaches.
•Stochastic ductile fracture property observed over a wide range of stress states of the studied material could be captured by the proposed classic ductile damage model in combination with the probabilistic function.
•Simulation results of 3D synthetic finite element models indicate that the global failure strain and the local crack propagation path can be precisely predicted using the calibrated probabilistic damage mechanics model.
Abstract
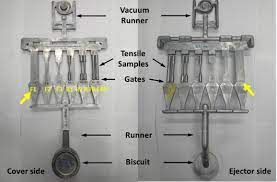
The microstructure and ductile fracture characteristics of the aluminum alloy (Aural-2) produced by high-pressure die casting have been characterized via experimental and numerical approaches. The stochastic distribution of casting defects (i.e., initial porosity), which is measured by X-ray tomography, leads to a pronounced scatter in the ductile fracture properties of the alloy. Numerical investigations on the ductile fracture behavior have revealed a considerable stress triaxiality dependence of fracture initiation strain, whereas the Lode angle parameter has only marginal effects on the ductile fracture behavior in this material. A probabilistic damage mechanics model is put forward to depict the apparent stochastic ductile fracture behavior over a wide range of stress states. Detailed calibration and validation of model parameters are elaborated in comparison with experimental results. As a further application of the calibrated probabilistic damage mechanics model, the deformation and fracture behavior of heterogeneous structures containing defects has been simulated. Simulation results have confirmed that the variation of initial porosity in different specimens is one of the dominating factors attributed to the observed scatter of failure strain. When the calibrated fracture criteria are applied to simulate the deformation of synthetic porosity-containing finite element models, both the global failure strain and the local crack propagation path can be precisely predicted.
고압 다이캐스팅으로 생산된 알루미늄 합금(Aural-2)의 미세구조 및 연성 파괴 특성은 실험적 및 수치적 접근을 통해 특성화되었습니다. X-선 단층 촬영으로 측정되는 주조 결함(즉, 초기 다공성)의 확률론적 분포는 합금의 연성 파괴 특성에 뚜렷한 분산을 초래합니다. 연성 파괴 거동에 대한 수치적 조사는 파괴 개시 변형률의 상당한 응력 삼축 의존성을 나타내는 반면, Lode 각도 매개변수는 이 재료의 연성 파괴 거동에 미미한 영향을 미칩니다. 광범위한 응력 상태에서 명백한 확률적 연성 파괴 거동을 묘사하기 위해 확률론적 손상 역학 모델이 제시되었습니다. 모델 매개변수의 상세한 보정 및 검증은 실험 결과와 비교하여 정교화됩니다. 보정된 확률적 손상 역학 모델의 추가 적용으로 결함을 포함하는 이종 구조의 변형 및 파괴 거동이 시뮬레이션되었습니다. 시뮬레이션 결과는 다양한 시편에서 초기 다공성의 변화가 관찰된 파손 변형률 분산에 기인한 지배적인 요인 중 하나임을 확인했습니다. 보정된 파괴 기준을 적용하여 합성 다공성 함유 유한 요소 모델의 변형을 시뮬레이션하면 전체 파괴 변형률과 국부 균열 전파 경로를 모두 정확하게 예측할 수 있습니다.
Keywords
Aluminum casting, Ductile fracture, Probability, Porosity, Stress states