1. Overview:
- Title: Die Casting of Lightweight Thin Fin Heat Sink Using Al-25%Si
- Authors: Toshio Haga and Hiroshi Fuse
- Year of Publication: 2024
- Journal/Conference: Metals (MDPI)
2. Research Background:
The demand for lightweight and cost-effective heat sinks is increasing. Die casting is a common and economical method for producing complex-shaped heat sinks. To reduce weight, a typical approach involves thinning the fins and base of the heat sink. Previous research explored alternative casting methods like semisolid casting, high-density casting, and high-vacuum die casting to achieve thinner fins. However, these methods often require specialized and expensive equipment, increasing production costs. Composite materials offer lightweight solutions with good thermal conductivity, but their complex processing, high material cost, and recyclability challenges limit their widespread adoption. This study aims to leverage the superior fluidity of Al-25%Si aluminum alloy to overcome the limitations of traditional die casting when producing thin fins and bases, utilizing a conventional die casting machine for cost-effectiveness.
3. Research Objectives and Questions:
- Research Objective: To investigate the feasibility and characteristics of producing lightweight thin-fin heat sinks using Al-25%Si aluminum alloy with a conventional die casting machine. The study aims to assess the heat dissipation performance and weight reduction achieved compared to traditional aluminum alloys and commercial heat sinks.
- Key Research Questions:
- How does the fluidity of Al-25%Si compare to that of conventional aluminum die casting alloys (e.g., ADC12)?
- What are the effects of fin thickness, fin height, number of fins, and base thickness on heat dissipation and weight reduction in Al-25%Si heat sinks?
- How does the heat dissipation performance and weight of the Al-25%Si heat sink compare to a commercial heat sink?
- Research Hypothesis: The superior fluidity of Al-25%Si allows for the creation of thinner fins and bases in a conventional die casting process, leading to a lighter weight heat sink without compromising heat dissipation performance.
4. Research Methodology:
- Research Design: Experimental design. The study used a 500 kN cold chamber die casting machine to produce a series of Al-25%Si heat sinks with varying parameters (fin thickness, fin height, number of fins, base thickness). A control group using ADC12 was also included for comparison.
- Data Collection Methods: Heat dissipation was measured using a micro-ceramic heater with a thermal interface material. Flow length was assessed using spiral dies. Microstructure analysis was performed using optical microscopy. Weight measurements were conducted.
- Analytical Methods: ANOVA and other statistical methods were used to analyze the data. Optical microscopy was employed for microstructural characterization.
- Research Subjects and Scope: The study focused on Al-25%Si and ADC12 aluminum alloys, comparing the properties of heat sinks with varying design parameters. A commercial heat sink was used as a benchmark for comparison.
5. Main Research Results:
- Key Findings: Al-25%Si exhibited significantly higher fluidity than ADC12. Thin fins (0.5 mm thickness, 0.5° draft angle) were successfully cast using Al-25%Si and a conventional die casting machine. Fin thickness did not significantly affect heat dissipation, but it did affect weight. Increasing fin height, number of fins, and base thickness improved heat dissipation, but the effect of fin height was most significant, particularly under constant weight conditions. Porosity and microstructural non-uniformity had minimal effects on heat dissipation. The Al-25%Si heat sinks demonstrated comparable heat dissipation performance but significantly lower weight (up to 68% reduction) compared to the commercial heat sink.
- Statistical/Qualitative Analysis Results: Detailed statistical analysis supporting these findings is present in the full paper. Qualitative observations from optical microscopy provided insight into the microstructural characteristics of the cast Al-25%Si.
- Data Interpretation: The superior fluidity of Al-25%Si enabled the creation of lightweight, high-performance heat sinks with thin fins. The results suggest that optimizing fin height is crucial for efficient heat dissipation in lightweight designs.
- Figure List and Description: The figures in the full paper would visually represent the data on fluidity comparison, heat dissipation performance under varying parameters, microstructural analysis, and comparison with the commercial heat sink.
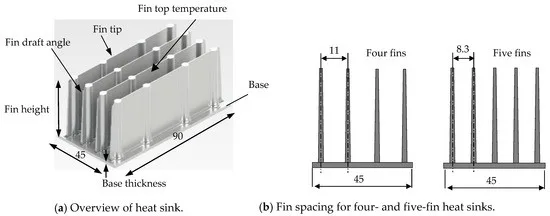
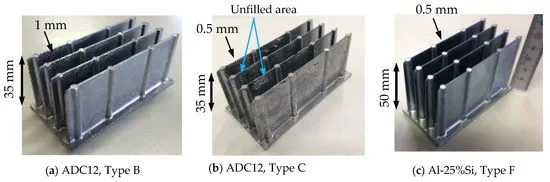
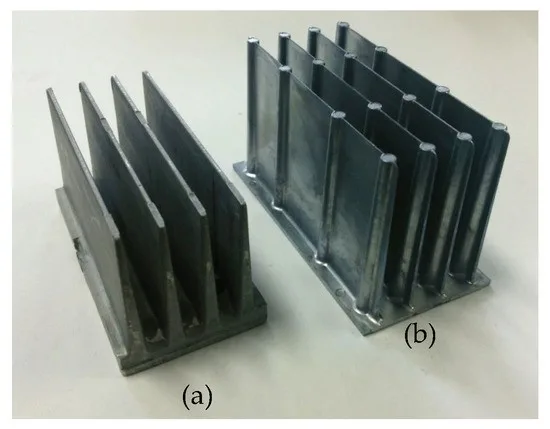
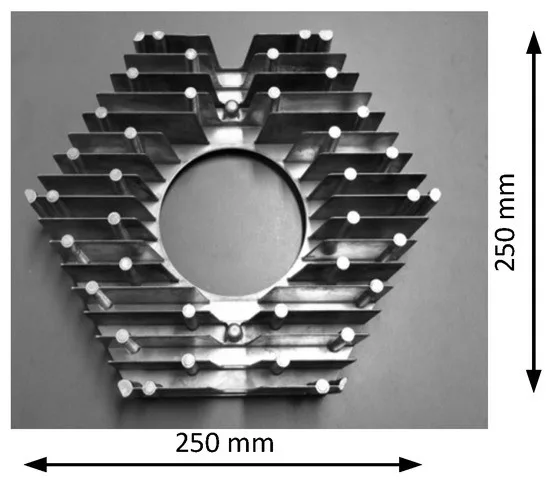
6. Conclusion and Discussion:
The study successfully demonstrated the feasibility of producing lightweight, high-performance heat sinks using Al-25%Si and a conventional die casting process. The superior fluidity of Al-25%Si allowed for the creation of significantly thinner fins than typically achievable with traditional die casting alloys. Optimization of fin height was identified as a key factor for maximizing heat dissipation under weight constraints. The Al-25%Si heat sinks demonstrated comparable heat dissipation performance to a commercial heat sink while achieving significant weight reduction. The findings highlight the potential for Al-25%Si in cost-effective manufacturing of lightweight heat sinks for various applications, particularly in automotive and high-ceiling LED lighting. Further research could focus on the impact of porosity, microstructural uniformity, and exploring other Al-Si alloys.
7. Suggestions for Future Research:
- Further investigation into the influence of porosity and microstructural variations on heat dissipation performance.
- Comparative studies of different Al-Si alloys to optimize alloy composition for thin-fin heat sink manufacturing.
- Experimental validation of heat sink performance under real-world operating conditions.
- Cost-benefit analysis comparing Al-25%Si with other materials for heat sink applications.
References
- Car LED Lamp Heat Sink. Available online: https://www.nikkeikinholdings.co.jp/car/detail/a0180.html (accessed on 29 March 2024).
- Car LED Lamp Heat Sink. Available online: http://www.nanshin-grp.co.jp/car_product/ (accessed on 29 March 2024).
- High-Ceiling LED Lamp Heat Sink. Available online: http://ja.perfumecaps.com (accessed on 29 March 2024).
- Şevik, S.; Őzdilli, Ő.; Akbulut, F. Numerical investigation of the effect of different heat sink fin structures on the thermal performance of automotive LED headlights. Int. J. Automot. Sci. Technol. 2022, 6, 17–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafford, J.; Walsh, E.; Egn, V.; Walsh, P.; Muzychka, Y.S. A novel Approach to Low Profile Heat Sink Design. J. Heat Transf. 2010, 132, 091401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.J.; Kim, D.K.; Oh, H.H. Comparison of Fluid Flow and Thermal Characteristics of Plate-Fin and Pin-Fin Heat Sinks Subject to Parallel Flow. Heat Transf. Eng. 2008, 29, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallikarjuna, V.; Rajesh, K.; Ramesh, K.; Reddy, B.R.B. Modeling and Optimization of shape of a Heat Sink Fins on Motherboard. J. Comput. Math. Sci. 2015, 65, 228–251. [Google Scholar]
- Kappranos, P. Current State of Semi-Solid Net-Shape Die Casting. Metals 2019, 9, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- See, A.; Caporale, L. High Density Die Casting (HDDC): New frontiers in the manufacturing of heat sinks. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2014, 525, 012020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jou, R.Y. Thermal analysis of LED Heat Sinks by High-Vacuum Die Casting (HVDC). Adv. Sci. Lett. 2012, 8, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Sun, M.; Guo, H.; Zie, Z.; Du, S. Enhancement effect of a diamond network on the flow boiling heat transfer characteristics of a diamond/Cu heat Sink. Energies 2023, 16, 7228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiorano, L.P.; Castillo, R.; Molina, J.M. Al/Gf composite foams with SiC-engineered interfaces for the next generation of active heat dissipation materials. Compos. Part A 2023, 166, 107367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Ali, H.M.; Rehman, T.; Arsalanloo, A.; Niyas, H. Composite pin-fin for effective hotspot reduction. Heat Trans. 2024, 53, 1816–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ding, L.; Li, J.; Fang, Y.; Li, G.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, L. Progress in preparation of silicon carbide particulate copper composites. Shandong Chem. Ind. 2021, 50, 65–67. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, C.; Xie, Y.; Pan, Z.; Ren, S.; Qu, X. Preparation and research process of high thermal conductivity metal matrix composites. Powder Metall. Technol. 2022, 40, 40–52. [Google Scholar]
- Coia, P.; Dharmasiri, B.; Stojcevski, F.; Hayne, D.J.; Austria, E., Jr.; Akhavan, B.; Razal, J.M.; Usman, K.A.S.; Stanfield, M.K.; Henderson, L.C. Scalable electrochemical grafting of anthraquinone for fabrication of multifunctional carbon fibers. L. JMST 2024, 200, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.K. Mechanical behaviors of Al6063/TiB2 composites fabricated by stir casting process. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 82, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zasadzińska, M.; Strzępek, P.; Mamala, A.; Noga, P. Reinforcement of aluminium-matrix composites with glass fibre by metallurgical synthesis. Materials 2020, 13, 5441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haga, T.; Imamura, S.; Fuse, H. Fluidity Investigation of Pure Al and Al-Si Alloys. Materials 2022, 14, 5372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- JIS H 5032: 2006(E); Aluminum Alloy Die Castings. Japanese Industrial Standards: Tokyo, Japan, 2006.
- Keller, K.P. Cast heatsink Design Advantages. ITherm’98. In Proceedings of the Sixth Intersociety Conference on Thermal and Thermomechanical Phenomena in Electronic Systems (Cat. No.98CH36208), Seattle, WA, USA, 27–30 May 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Z.; Lau, E.; Botting, C.; Bahrami, M. Naturally cooled heat sinks for battery chargers. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 14, 118911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, H.S.; Lee, J.J.; Lai, C.Y. Thermal Analysis and Optimum Fin Length of a Heat Sink. Heat Transf. Eng. 2003, 24, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goshayeshi, H.R.; Ampofo, F. Heat Transfer by Natural Convection from a Vertical and Horizontal Surfaces Using Vertical Fins. Int. J. Energy Power Eng. 2009, 1, 85–89. Available online: http://www.scirp.org/journal/epe (accessed on 2 November 2022). [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Ishikawa, A.; Hashimoto, R.; Kanematsu, H.; Utsumi, Y. Effect of Heat Sink Structure on Cooling Performance of LED Bulb. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Design Engineering and Science, ICDES, Pilsen, Czech Republic, 31 August–3 September 2014; pp. 171–174. [Google Scholar]
- Shengxiong, C.; Daqing, Z. Heat Analysis and Optimal Design of Heat Sink of LED Fish Aggregation Lamp. Sens. Mater. 2018, 30, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, R.; Wang, C.C. A novel heat dissipation fi design applicable for natural convection augmentation. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer. 2014, 59, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, Y.; Kurkute, V.; Deshmukh, S.M.; Pathan, K.A.; Attar, A.R. The influence of Plate Fin Heat Sink Orientation under Natural Convection on Thermal Performance: An Experimental and Numerical Study. J. Adv. Res. Fluid Mech. Therm. Sci. 2024, 114, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasangika, A.H.D.K.; Nasif, M.S.; Pao, W.; Al-Waked, R. Effect of fin spacing on the vibration-assisted thermal performance of hat sink. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1281, 012059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, P.; Radhakrishnan, S.; Mahalingam, A.; Vellaiyan, S. Heat dissipation effects of different nanocoated Lateral Fins an Experimental investigation. Therm. Sci. 2024, 28, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, V.; Kamkari, B.; Zandimaghm, M.; Hewitt, N. Transient Thermal Behavior of a passive heat sink integrated with phase change material: A numerical simulation. Int. J. Thermofluids 2023, 20, 100454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, J.; Yang, H.; Feng, B.; Zhang, Q.; Song, X. Study on performance of the thermoelectric cooling device with novel subchannel Finned Heat Sink. Energies 2022, 15, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, S.; Hyeon, S.; Lee, K.S. Guide vane for thermal enhancement of a LED heat sink. Energies 2022, 15, 2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, N.; Siddiqi, M.U.R.; Tahir, M. Thermal analysis of proposed heat sink design under natural convection for the thermal management of electronics. Therm. Sci. 2022, 26, 1487–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekpu, M.; Ogbodo, E.A.; Ngobigha, F.; Njoku, J.E. Thermal Effect of Cylindrical Heat Sink on Heat Management in LED Applications. Energies 2022, 15, 7583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradikazerouni, A.; Afrand, M.; Alsarraf, J.; Wongwises, S.; Asadi, A.; Nguyen, T.K. Investigation of a Computer CPU Heat Sink under Laminar Forced Convection Using a Structural Stability Method. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 134, 1218–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wengang, H.; Lulu, W.; Zongmin, Z.; Yanhua, L.; Mingxin, L. Research on simulation and experimental of thermal performance of LED array heat sink. Procedia Eng. 2017, 205, 2084–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muneeshwaran, M.; Tsai, M.K.; Wang, C.C. Heat transfer augmentation of natural convection heat sink through notched fin design. Mass Trans. 2023, 142, 106676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, A.; Alabdullatif, M.I.; Jabbal, M.; Yan, Y. Towards the thermal management of electronic devices: A parametric investigation of finned heat sink filled with OCM. Mass Trans. 2021, 129, 105643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, M.B.B.; Hatami, M. Optimimization of Fins Arrangements for the square Light Emitting Diode (LED) cooling through nanofluid-filled microchannel. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payandeh, M.; Belov, I.; Jarfors, A.E.; Wessén, M. Effect of Material Inhomogeneity on Thermal Performance of a Rheocast Aluminum Heatsink for Electronics Cooling. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2016, 25, 2116–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, M.M.A.; Hassan, S.F.; Saheb, N.; Patel, F. Metal Matrix Composite in Heat Sink Application: Reinforcement, Processing, and Properties. Materials 2021, 14, 6257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Die Casting Machine. Available online: https://hishinuma.jp/menu/2013/09/hc50f.html (accessed on 22 April 2022).
- Temperature Controller. Available online: https://hishinuma.jp/menu/cat/cat132/cat1/ (accessed on 22 April 2022).
- Zhang, Z.; Collins, M.; Lau, E.; Botting, C.; Bahrami, M. The Role of Anodization in Naturally Cooled Heat Sinks for Power Electronic Devices. J. Heat Transf. 2020, 142, 05290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Copyright and Source Material:
This summary is based on the partial OCR text of the paper "Die Casting of Lightweight Thin Fin Heat Sink Using Al-25%Si" by Toshio Haga and Hiroshi Fuse.
Unauthorized commercial use is prohibited.
Copyright © 2025 CASTMAN. All rights reserved.