YuanLia, JinxiangLiua, QiangZhangb, WeiqingHuanga
a School of Mechanical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
b Liaoshen Industries Group Co. Ltd, Shenyang 110045, China
Abstract
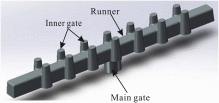
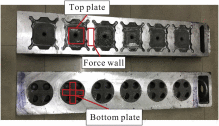
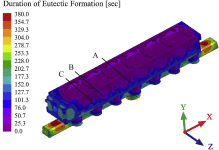
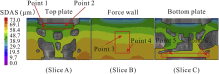
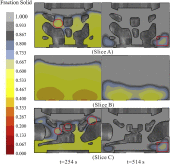
Due to the complex structure of the large cylinder head, it is prone to produce uncontrolled casting defects and uneven microstructure distribution. In order to predict the porosity defects and secondary dendrite arm spacing (SDAS) in the as-cast cylinder head, the low pressure casting process of aluminum alloy cylinder head was simulated. Moreover, to verify the accuracy of the simulation results, microscopic observations were performed, in which the simulation results are reasonably matching with that of experiment results. Both simulation and experiment results demonstrate that porosity defects mainly exist in thick walls as well as thick-thin wall junctions. In addition, the top plate presents the finest microstructure, while the microstructure of the force wall is the coarsest. Additionally, the correlation of casting parameters with porosity defects and microstructure was discussed, suggesting that increasing the cooling rate could partially reduce porosity defects. Furthermore, the finding that decreasing the cooling rate can reduce the SDAS of the casting, resulting in a dense microstructure, was drawn. Besides, it has been concluded that regular shapes and thin walls are advantageous for both reducing porosity defects and obtaining uniform microstructures. This provides an effective approach for predicting the casting defects and microstructure of large complex structural castings through numerical simulation. In addition, a quantitative understanding of the casting parameters, complex structure-microstructure relationship for cast aluminum alloys will allow better determination of process parameters based on microstructure and properties requirements of complex components.
Korea Abstract
대형 실린더 헤드의 복잡한 구조로 인해 제어되지 않은 주조 결함과 고르지 않은 미세 구조 분포가 발생하기 쉽습니다. 주조 된 실린더 헤드의 다공성 결함과 2 차 덴드라이트 암 간격 (SDAS)을 예측하기 위해 알루미늄 합금 실린더 헤드의 저압 주조 공정을 시뮬레이션했습니다.
또한 시뮬레이션 결과의 정확성을 확인하기 위해 미세한 관찰을 수행하여 시뮬레이션 결과가 실험 결과와 합리적으로 일치합니다. 시뮬레이션과 실험 결과 모두 다공성 결함이 주로 두꺼운 벽과 두꺼운 벽 접합부에 존재 함을 보여줍니다. 또한 상판은 가장 미세한 미세 구조를 나타내며 힘 벽의 미세 구조는 가장 거칠다.
또한, 주조 매개 변수와 다공성 결함 및 미세 구조의 상관 관계가 논의되어 냉각 속도를 높이면 다공성 결함을 부분적으로 줄일 수 있음을 시사합니다. 또한 냉각 속도를 줄이면 주물의 SDAS를 줄일 수있어 조밀 한 미세 구조를 만들 수 있다는 발견이 도출되었습니다.
또한, 일정한 모양과 얇은 벽이 다공성 결함을 줄이고 균일 한 미세 구조를 얻는 데 모두 유리하다는 결론을 내 렸습니다. 이는 수치 시뮬레이션을 통해 대형 복합 구조 주조의 주조 결함 및 미세 구조를 예측하는 효과적인 접근 방식을 제공합니다.
또한 주조 매개 변수, 주조 알루미늄 합금의 복잡한 구조-미세 구조 관계에 대한 정량적 이해를 통해 복잡한 구성 요소의 미세 구조 및 특성 요구 사항을 기반으로 공정 매개 변수를 더 잘 결정할 수 있습니다.
Keywords
Aluminum alloy cylinder head, Low pressure casting, Porosity defects, Secondary dendrite arm spacing, Microstructure