This article introduces the paper ['ANALIZE DIE CASTING PROCESS AND STRUCTURE OF MOLDING FOR INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE VEHICLE'] published by ['International Journal Science and Technology'].
1. Overview:
- Title: ANALIZE DIE CASTING PROCESS AND STRUCTURE OF MOLDING FOR INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE VEHICLE
- Author: Muhammad Yusuf Nurfani, Abdulrahman Agung Ramadhan
- Publication Year: 2023
- Publishing Journal/Academic Society: International Journal Science and Technology (IJST)
- Keywords: Die Casting, Molding, Internal Combustion Engine

2. Abstracts or Introduction
Abstract:
Die casting is part of manufacturing process for making metal product, especially internal combustion engine of vehicle. Molding is component for making product from metallurgy process or polymer process. Basically, all part of molding process will be using 3 conditions of process. First is solid raw material for process production, second is melting process of raw material for making product using molding and third is solid for part of finish product after process molding process. In this research will analyze of molding process and structure of engine for internal combustion engine vehicle. Mold casting will be using specification for SUV capacity 2.7L. basic raw material is silica sand, resin, bentonite, and sea coal. The result show that after process mixing optimal pressure from machine to molding is 109675,8 N. and spot test check result show that, after process die casting no any crack founding by 10 specimens of engine of vehicle.
Keyword: Die Casting, Molding, Internal Combustion Engine.
Introduction:
Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) is part of component of vehicle. Process of development of engine one of them is die casting. Die casting is manufacturing process on automotive industry for development. Basically, durability of engines be affected by design, structure, and production process when development. [1]. Die Casting Die Design and Process Optimization of Aluminum Alloy Gearbox Shell, the result show that Aiming at the leakage problem of the gearbox shell in the bench and road test after assembly, the cause was found through numerical simulation and industrial CT analysis, and the problem was solved by adding high-pressure point cooling at the corresponding position of the leakage, and the correctness of the optimization was verified [2]. Design and Analysis of Pressure Die Casting Die for Automobile Component, the result show that the reduced all machining and can make the process the optimum choice for small volume production as well [3]. Effect of refractory aggregate shape on the porosity of A356 alloy castings in lost foam casting, the result show that Defects at specific locations of the castings were analyzed and statistically counted through optical microscopy. In conclusion, the combination of expanded graphite and bauxite clinker yields the best quality castings in A356 LFC. [4]. The Application of the Direct Water-Cooling Process on the Lost-Foam Casting Technique to Improve Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of A356 Alloy, the result show that the highest obtained mechanical values were found around to be approximately 195 ± 3.5 MPa ultimate tensile strength, 4.45 ± 0.78% elongation, and 84 ± 1.77 HB in hardness.
3. Research Background:
Background of the Research Topic:
The paper addresses the application of die casting in the automotive industry, specifically for the production of Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) components. Die casting is highlighted as a crucial manufacturing process for engine development due to its efficiency in producing metal parts. The durability of engines is inherently linked to their design, structural integrity, and the manufacturing process employed during their development.
Status of Existing Research:
The introduction references prior studies to contextualize the current research.
- [1] Mingyu, Huang, Qian Zhou, Shihua Li “Die Casting Die Design and Process Optimization of Aluminum Alloy Gearbox Shell” investigated the leakage problem in gearbox shells using numerical simulation and industrial CT analysis, resolving it with high-pressure point cooling optimization.
- [2] Y Abdulfatah, T.M Shafii, K.K Dubey, Prof U.K Gupta "Design and Analysis of Pressure Die Casting Die for Automobile Component" demonstrated that pressure die casting can reduce machining requirements and is suitable for small volume production of automobile components.
- [3] Chi Sun, Zhanyi Cho, Guojun Liu, “Effect of refractory aggregate shape on the porosity of A356 alloy castings in lost Foam Casting" explored the impact of refractory aggregate shape on porosity in A356 alloy castings within lost foam casting, concluding that a combination of expanded graphite and bauxite clinker yields optimal casting quality.
- [4] Ibrahim Tutuk, Serhat Acar, Kerem Altug Guler, “The Application of the Direct Water-Cooling Process on the Lost-Foam Casting Technique to Improve Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of A356 Alloy" examined the application of direct water-cooling in lost-foam casting to enhance the microstructural and mechanical properties of A356 alloy, achieving improved mechanical values.
Necessity of the Research:
This research is necessitated by the ongoing need to optimize manufacturing processes for critical automotive components like ICEs. Analyzing the die casting process and the resulting structure of engine moldings is crucial for ensuring the quality and reliability of these components. The study focuses on achieving optimal pressure settings and verifying the structural integrity of die-cast engine blocks, addressing fundamental aspects of die casting for engine manufacturing.
4. Research Purpose and Research Questions:
Research Purpose:
The primary research purpose is to analyze the die casting process and the structure of the molding produced for an internal combustion engine vehicle. Specifically, the study aims to develop a mold for a 2.7L SUV capacity engine and to determine the optimal pressure for the die casting process using specified materials.
Key Research:
The key research focuses on:
- Determining the optimal pressure for die casting using a hydraulic press to create engine molds without defects.
- Analyzing the material composition of the mold and the aluminum ingot (HSN 7061) used for die casting.
- Evaluating the structural integrity of the die-cast engine blocks using Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) with ARDROX 9814 penetrant.
Research Hypotheses:
While not explicitly stated as hypotheses, the research implicitly tests the feasibility of producing defect-free engine blocks for a 2.7L ICE using die casting with HSN 7061 aluminum alloy and a mold made of silica sand, bentonite, sea coal, and resin, under optimized pressure conditions. The expected outcome is to demonstrate that by controlling the die casting process parameters, particularly pressure, and employing appropriate materials, it is possible to manufacture engine blocks without cracks or structural flaws.
5. Research Methodology
Research Design:
The research employs an experimental design focused on die casting an engine block and subsequently evaluating its structural integrity. The process involves material preparation, mold creation, die casting using a hydraulic press, cooling, finishing, and non-destructive testing.
Data Collection Method:
Data collection methods include:
- Process Parameter Monitoring: Recording and controlling the pressure of the hydraulic press during the die casting process.
- Visual Inspection: Conducting visual checks of the die-cast engine blocks to identify macroscopic defects such as cracks, flashes, and flow marks.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Utilizing ARDROX 9814 penetrant testing and X-ray inspection to detect surface and internal cracks or structural failures in the cast parts.
Analysis Method:
The analysis methods used are:
- Pressure Calculation: Calculating the required pressure for the hydraulic press based on the mold dimensions and desired pressure per unit area, using the formula P = F/A.
- Qualitative Defect Analysis: Assessing the presence or absence of defects through visual inspection and NDT results. The NDT results are recorded as "Passed" or "Failed" based on crack detection.
Research Subjects and Scope:
- Materials:
- Die casting material: Aluminum Ingot HSN 7061 (composition detailed in Table 2).
- Molding material: Silica sand, bentonite, sea coal, and resin (composition detailed in Table 1).
- Engine Type: 2.7L SUV capacity Internal Combustion Engine.
- Equipment: TRFD-2000T hydraulic press.
- Scope: The study is limited to the die casting process and structural analysis of a single-cavity mold for the specified engine block, focusing on pressure optimization and defect detection.
6. Main Research Results:
Key Research Results:
- Optimal Pressure: The calculated optimal pressure for the hydraulic press was determined to be 109675.8 N.
- Successful Mold Creation: Mold processing using silica sand, bentonite, and sea coal was successfully completed using the hydraulic press at the calculated pressure without any defects.
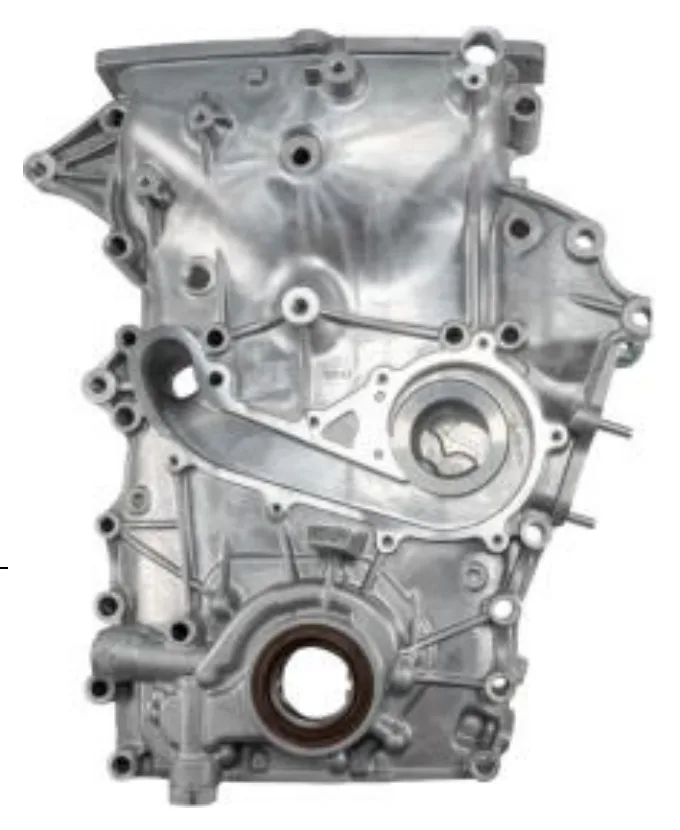
- Defect-Free Die Casting: Die casting using Aluminum Ingots HSN 7061 at a temperature ≥ 400°C resulted in engine blocks without visual defects such as cracks, flashes, or flow marks.
- NDT Confirmation: Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) using ARDROX 9814 on 10 specimen engine blocks showed no cracks or structural issues after the die casting process (Table 4).
Analysis of presented data:
- Material Composition (Table 1 & 2): Table 1 details the material composition of the mold, including Silica Sand (3 Ton), Bentonite (20 Kg), Sea Coal (8.2 Kg), and Water (35 L). Table 2 specifies the composition of Aluminum Ingots HSN 7061, with Aluminum ranging from 80-95% and other elements like Silicon, Zinc, Iron, Manganese, and Magnesium in smaller percentages (0.1-2%).
- Hydraulic Press Specification (Table 3): Table 3 outlines the specifications of the Wodda TRFD-2000T hydraulic press used, including a 400 mm slide stroke, working speed of 8-15 mm/s, and 35-ton ejecting force.
- NDT Results (Table 4): Table 4 presents the NDT results for 10 samples, all of which "Passed" the crack test, indicating no crack issues were detected after the inspection process.
- Figures: Figure 1 illustrates the research methods flowchart. Figure 2 shows the material of molding (Silica Sand, Bentonite, Sea Coal). Figure 3 displays Aluminum Ingots. Figure 4 shows the Hydraulic Press. Figure 5 depicts the Mold Process and Die Casting. Figure 6 presents the Internal Combustion Engine Block 2.7L. Figure 7 shows the NDT Process Measurement. Figure 8 illustrates the Structure of Engine 2.7L.
Figure Name List:
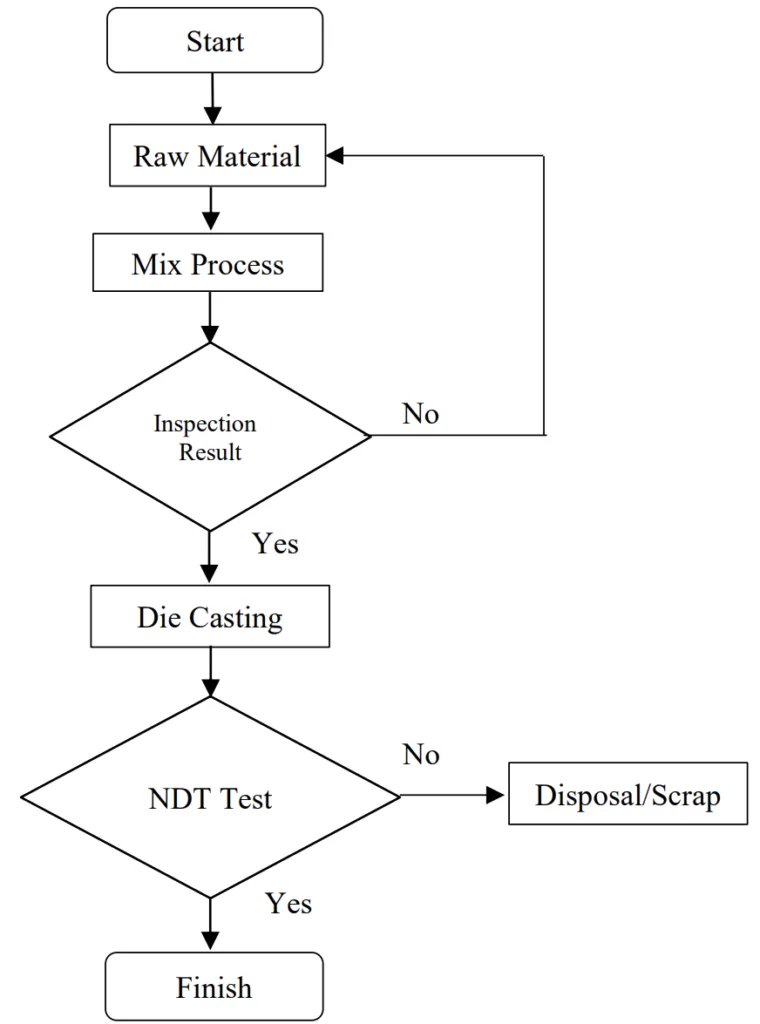






- Figure 1. Research Methods
- Figure 2. Material of Molding (Silica Sand, Bentonite, Sea Coal)
- Figure 3 Aluminum Ingots
- Figure 4. Hydraulic Press
- Figure 5. Mold Process and Die Casting
- Figure 6. Internal Combustion Engine Block 2.7L
- Figure 7. NDT Process Measurement
- Figure 8. Structure of Engine 2.7L
7. Conclusion:
Summary of Key Findings:
The study successfully demonstrated the feasibility of producing 2.7L internal combustion engine blocks using die casting with Aluminum Ingots HSN 7061 and a single-cavity mold. The optimized pressure of 109675.8 N in the hydraulic press facilitated defect-free mold creation and subsequent die casting. Both visual inspection and Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) confirmed the absence of cracks and structural issues in the produced engine blocks, indicating a high level of casting quality.
Academic Significance of the Study:
This research contributes to the field of die casting technology by providing empirical validation for the application of die casting in manufacturing complex engine components. It offers specific parameters for pressure optimization and material selection (HSN 7061 aluminum alloy and specified mold materials) that can be referenced for similar die casting applications in automotive manufacturing.
Practical Implications:
The findings have practical implications for mass production of durable engine blocks using die casting. The study indicates that by adhering to the determined pressure settings and material specifications, manufacturers can achieve consistent quality and minimize defects in die-cast engine components, enhancing production efficiency and product reliability. The use of aluminum alloy also contributes to lighter engine weights, beneficial for vehicle performance and fuel efficiency.
Limitations of the Study and Areas for Future Research:
The study is limited to a single engine block design (2.7L ICE) and a specific set of materials and equipment. Future research could explore:
- The scalability of these findings to different engine sizes and designs.
- The long-term durability and performance testing of the die-cast engine blocks under operational conditions.
- Optimization of other die casting parameters beyond pressure, such as temperature control, injection speed, and cooling rates, to further enhance casting quality and efficiency.
- Comparative studies with other aluminum alloys and mold materials to identify potentially superior combinations for die casting engine blocks.
8. References:
[1] Mingyu, Huang, Qian Zhou, Shihua Li “Die Casting Die Design and Process Optimization of Aluminum Alloy Gearbox Shell”, MDPI Journal, Vol. 14, 4 June Page 1-12, 2021
[2] Y Abdulfatah, T.M Shafii, K.K Dubey, Prof U.K Gupta "Design and Analysis of Pressure Die Casting Die for Automobile Component", Global Journal Researches in Engineering a Mechanical and Mechainc Engineering, Vol. 16, 10 November Page 01-07, 2016.
[3] Chi Sun, Zhanyi Cho, Guojun Liu, “Effect of refractory aggregate shape on the porosity of A356 alloy castings in lost Foam Casting", Springer, Vol 6, 17 November, Page 1-9, 2023.
[4] Ibrahim Tutuk, Serhat Acar, Kerem Altug Guler, “The Application of the Direct Water-Cooling Process on the Lost-Foam Casting Technique to Improve Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of A356 Alloy" Springer, Vol 1, 06 January, Page 1-12s, 2023.
[5] Alexandra Chesa " Die Casting Technology – Present and future in Automotive Applications", Institute of Automotive Engineering, June. Page 1-141, 2019
9. Copyright:
- This material is "Muhammad Yusuf Nurfani and Abdulrahman Agung Ramadhan"'s paper: Based on "ANALIZE DIE CASTING PROCESS AND STRUCTURE OF MOLDING FOR INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE VEHICLE".
- Paper Source: https://doi.org/10.56127/ijst.v2i3.1102
This material was summarized based on the above paper, and unauthorized use for commercial purposes is prohibited.
Copyright © 2025 CASTMAN. All rights reserved.