This article introduces the paper "Computer aided design of Gating systems for die casting dies" presented at ResearchGate
1. Overview:
- Title: Computer aided design of Gating systems for die casting dies
- Author: P.N.Rao, R.Thukral, S.Saxena, K.L.Rajpal
- Publication Year: January 1989 (Conference Paper)
- Publishing Journal/Academic Society: ResearchGate (Conference Paper)
- Keywords: Die casting, Gating system, CAD/CAM, Fluid flow analysis, Runner system, Machine parameters, P-Q² diagram, Gate design
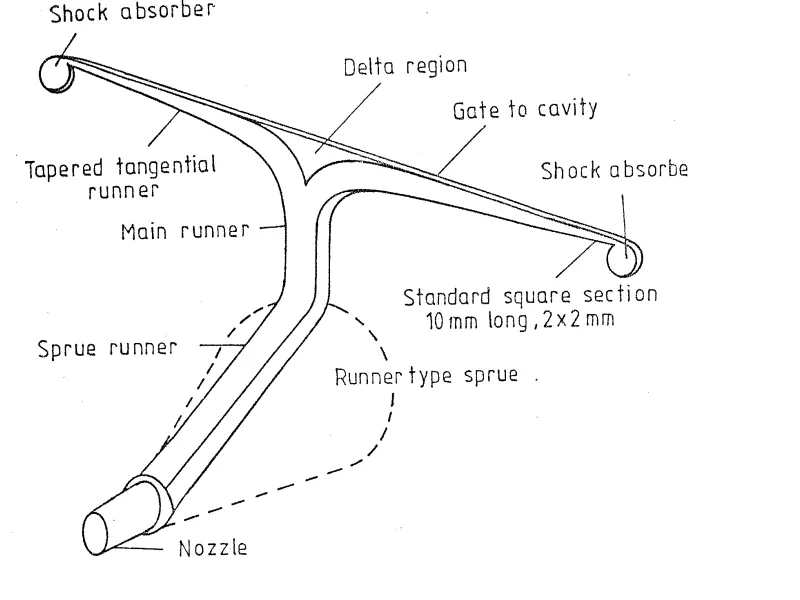
2. Research Background:
- Social/Academic Context of the Research Topic: Pressure diecasting is one of the most important manufacturing processes used in the industry. In recent years, rapid developments in CAD/CAM technology have shown potential for significant reductions in overall production costs and improved casting quality in die casting die design and production. However, traditional gating design methods often lack a basis in scientific or engineering principles.
- Limitations of Existing Research: Existing die casting gating system designs rely heavily on empirical methods, lacking systematic design methodologies grounded in scientific and engineering principles.
- Necessity of the Research: There is a need to develop a systematic design procedure utilizing the potential of CAD/CAM technology for more effective die casting die design. Specifically, the development of CAD software incorporating fluid flow analysis to quantitatively assess design condition variations and offer diverse gating system options is required.
3. Research Purpose and Research Questions:
- Research Purpose: To develop a software package for designing gating systems for die casting dies using CAD/CAM methods. Specifically, the aim is to perform fluid flow analysis within the runner and design detailed runner systems based on gate area and flow patterns.
- Key Research Questions:
- How can CAD/CAM methods be effectively utilized for die casting gating system design?
- How can fluid flow within the runner be analyzed to quantitatively assess design condition variations?
- How can detailed runner systems be designed based on gate area and flow patterns?
- Research Hypotheses: CAD/CAM-based gating system design can lead to improved casting quality and reduced production costs. Fluid flow analysis and P-Q² diagrams are effective tools for gating system design.
4. Research Methodology
- Research Design: CAD software package development. This software integrates modules for die casting gating system design.
- Data Collection Method: Rather than traditional data collection, the focus is on developing algorithms and implementing software based on existing knowledge and principles of the die casting process. Machine parameters (P1, P2) are determined using experimental data.
- Analysis Method: Fluid flow analysis, P-Q² diagram analysis, and algorithm development for runner design. P-Q² diagrams are utilized to analyze the relationship between the metal flow system and die casting machine characteristics.
- Research Subjects and Scope: Gating systems for pressure die casting dies, specifically focusing on runner design and machine parameter considerations.
5. Main Research Results:
- Key Research Results: Developed a software package for CAD of die casting gating systems. This package includes modules for casting parameters, machine parameters, P-Q² subprogram, and runner design. It supports tapered tangential runner, fan feed gate, and main runner system designs.
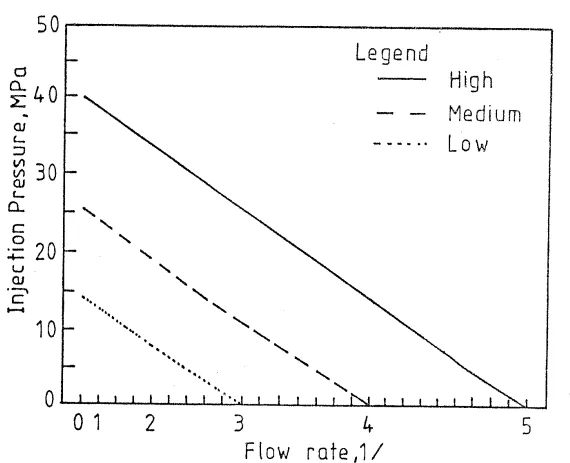
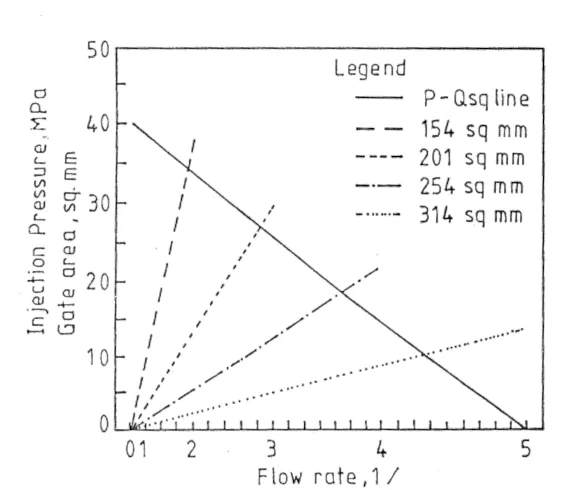
- Statistical/Qualitative Analysis Results: Traditional statistical/qualitative analysis results are not presented. The software package's functionality and design options demonstrate the research results. Figures 1, 2, and 3 are presented to illustrate concepts such as P-Q² diagrams and runner system schematics.
- Data Interpretation: P-Q² diagrams are used to analyze the relationship between metal flow and machine characteristics. Design rules for gate thickness and length are provided based on designer experience.
- Figure Name List:
- Fig. 1 EFFECT OF VARYING INJECTION PRESSURE
- Fig. 2 EFFECT OF CHANGES IN GATE AREA
- Fig. 3 SCHEMATIC OF RUNNER SYSTEM FOR HOT CHAMBER DIACASTING MACHINE
6. Conclusion and Discussion:
- Summary of Main Results: Developed a software package that designs gating and runner systems for die casting dies by optimizing gate velocity and cavity fill time based on casting and machine parameters.
- Academic Significance of the Research: Presents a case study of applying CAD/CAM technology to die casting gating system design. Introduced a systematic design methodology utilizing P-Q² diagrams and fluid flow analysis.
- Practical Implications: Provides mold designers with a tool to improve gating system design, potentially enhancing casting quality and reducing production costs. The software can generate detailed geometries for NC machining.
- Limitations of the Research: This paper was published in 1989, so there are differences compared to current computing power and CAD/CAM technology levels. The paper focuses on design methodology and software structure, and does not present extensive validation or experimental results.
7. Future Follow-up Research:
- Directions for Follow-up Research: While the paper itself does not explicitly suggest future research directions, based on the context, the following research is possible:
- Validation of the software package through experimental die casting trials.
- Integration with the latest CAD/CAM systems.
- Further development of runner design options and optimization algorithms.
- Integration of more advanced simulation technologies for flow and solidification simulation.
8. References:
- [1] Upton, B: Pressure Diecasting Part -1,Mct-als, Machines, and Furnaces, Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1982
- [2] Allsop, D.F. and Kennedy, D. : Pressure Die-casting Part 2, The Technology of Casting, Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1982.
- [3] Cope, M.A: Zinc Pressure Diecasting – the metal flow system, Australian Zinc Diecasting Association, Melbourne, 1979.
- [4] ZDA: Zinc Die Casting, Die Design Aid, Zinc Development Association, London
- [5] Andresen, W.T.: Metlflow Computer Aids for Diecasting, Diecasting Engineer, 1986
- [6] Cocks, Derek, L.: Diecasting of Fan Feeds for Pressure Diecasting, Diecasting Engineer, July-August, 1981
- [7] Siauw, T.H. and Tartaglia, S.: Sirorun 1: A Software Package for the Design and Manufacture of Runners Used in Pressure Diecastings, Second South Pacific Diecasting Congress, Sydney, 1983
9. Copyright:
- This material is "[Nageswara Rao Posinasetti, R.Thukral, S.Saxena, K.L.Rajpal]"'s paper: Based on "[Computer aided design of Gating systems for die casting dies]".
- Paper Source: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/260639166
This material was summarized based on the above paper, and unauthorized use for commercial purposes is prohibited.
Copyright © 2025 CASTMAN. All rights reserved.