The content of this introduction paper is based on the article 'Selection of Copper vs. Aluminum Rotors for Induction Motors' published by 'IEEE'.
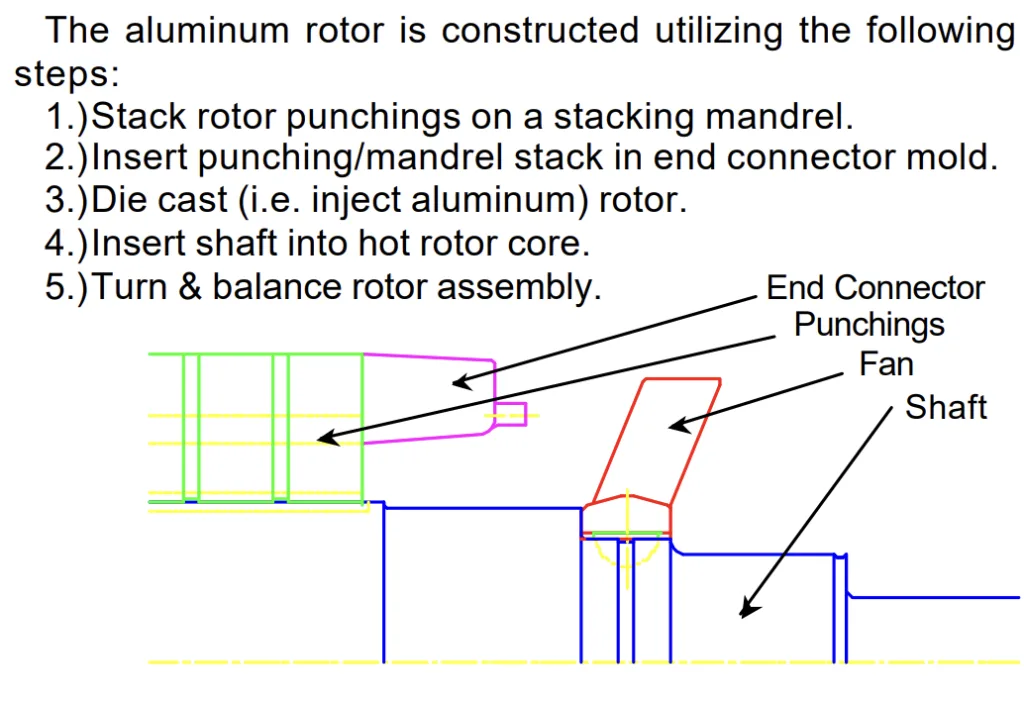
1. Overview:
- Title: Selection of Copper vs. Aluminum Rotors for Induction Motors
- Author: William R. Finley, Mark M. Hodowanec
- Year of publication: 2000
- Journal/academic society of publication: IEEE (Paper No. PCIC-00-XX)
- Keywords: Squirrel cage induction motors, rotor construction, aluminum die-cast rotor, copper bar rotor, motor performance, thermal sensitivity, rotor stresses.
2. Abstract:
On squirrel cage induction motors, there is an important choice between utilizing a lower cost die cast or fabricated aluminum rotor versus the more expensive copper bar rotor. Utilizing the wrong rotor construction for the application can either increase costs unnecessarily or lead to catastrophic failure. This paper will provide the background necessary to assist in making the proper choice. The fundamentals of rotor construction and basic information on how the induction motor works will be discussed. Additionally, the effects of various materials and types of rotor construction on motor performance will be analyzed.
3. Introduction:
Many critical processes rely on induction motors, where failure can be very costly. The selection of rotor construction (aluminum die-cast, fabricated aluminum, or copper bar) significantly impacts motor reliability and cost. The paper addresses the trade-offs between these rotor types, emphasizing that while copper bar rotors are often perceived as more reliable, aluminum die-cast rotors, due to advancements in technology, are viable in larger horsepower ratings than previously considered.
4. Summary of the study:
Background of the research topic:
The increasing demand for cost-effective and reliable induction motors necessitates a careful evaluation of rotor construction materials and methods.
Status of previous research:
Aluminum die-casting technology has advanced, allowing for reliable die-cast rotors in larger motor ratings.
Purpose of the study:
To provide the background necessary to assist in making the proper choice between utilizing a lower cost die cast or fabricated aluminum rotor versus the more expensive copper bar rotor.
Core study:
The effects of various materials and types of rotor construction on motor performance will be analyzed.
5. Research Methodology
Research Design:
The paper employs a descriptive approach, comparing and contrasting different rotor construction methods (aluminum die-cast, fabricated aluminum, and copper bar) and their impact on motor performance.
Data Collection and Analysis Methods:
The paper relies on established engineering principles, manufacturing practices, and empirical data to analyze rotor stresses, thermal behavior, and performance characteristics. Some comparative data is presented in tables.
Research Topics and Scope:
The paper covers the following topics:
- Rotor construction methods (ADC, AlBar, CuBar, CuDC).
- Achieving tight rotor bars.
- Rotor stresses (rotational and residual).
- Fundamentals of induction motor operation.
- Performance comparison of different rotor materials.
- Starting considerations and their impact on rotor design.
- Rotor bar repair.
- Adjustable Speed Drive (ASD) considerations.
- Rotor cost comparison.
6. Key Results:
Key Results:
- Aluminum die-cast (ADC) rotors are reliable and cost-effective, especially in smaller to medium horsepower ranges.
- Advancements in ADC technology allow for its use in larger motor ratings.
- Copper bar (CuBar) rotors offer higher thermal capacity and are better suited for high-inertia and frequent-start applications.
- Fabricated aluminum bar (AlBar) rotors offer a compromise between ADC and CuBar, with higher cost than ADC.
- Rotor stresses (rotational and residual) are present in all rotor types, but their impact varies depending on the material and construction method.
- Tight rotor bars are crucial for minimizing vibration and preventing premature failure, especially in CuBar rotors.
- Starting conditions (high current, thermal expansion) significantly impact rotor bar and end connector stresses.
- ASD applications have specific considerations regarding rotor bar heating and vibration.
- CuBar rotors generally result in a higher motor purchase price compared to ADC rotors.


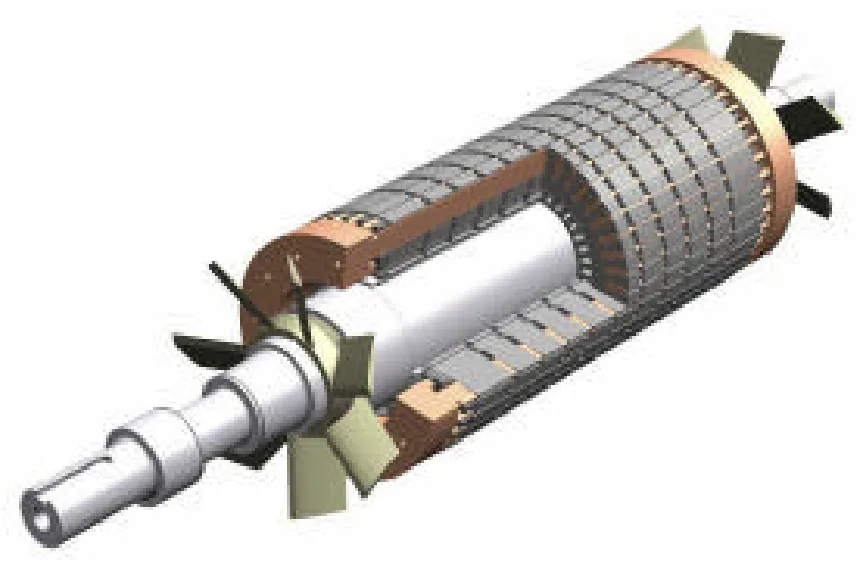

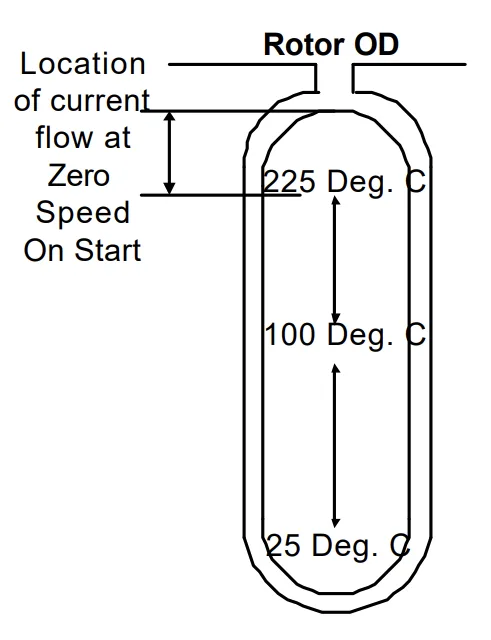
Figure Name List:
- FIG. 1 - ADC Rotor Cutaway View
- FIG. 2 - AlBar Rotor Cutaway View
- FIG. 3 - CuBar Rotor Cutaway View
- FIG. 4 - 3D CuBar Rotor Cutaway View
- Fig. 5 - Rotor Bar Swaging
- FIG. 6 - Shaped rotor bar
- FIG. 7 - Rotor Bar & Shim
- FIG. 8 - Cut away view of motor with rotor
- FIG. 9 - Typical Thermal Distribution for High Inertia Start on a Copper Bar Rotor
- FIG. 10 - Rotor Bar Thermal Bow Due to Heat Distribution
- FIG. 11 - FEA Model of Rotor Bar Bending during Startup
- FIG. 12 - Picture of Current Flowing in the Rotor Bar Tooth Tip in an ASD Application
- FIG. 13 - Cost Increase of CuBar vs. ADC
7. Conclusion:
It is impossible to pick 'the best' rotor construction for every situation. By understaning the manufacturing and design tradeoffs, it is possible to select the optimal rotor construction method (one that will yield the desired reliability at the lowest cost) for the particular application.
8. References:
- [1] API Standard 541 Third Edition, Form-Wound Squirrel Cage Motors 250 Horsepower and Larger Washington, D.C., 1995
- [2] NEMA Standards Publication No. MG 1-1993 Rosslyn, VA, 1996
- [3] Hodowanec, M.M., and Bezesky, D.M., "Field Motor Testing: Procedures which Limit Amount of Risk Involved, IEEE IAS PCIC Conference Records
- [4] Craggs, J.L., "Fabricated Aluminum Cage Construction in Large Induction Motors," IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, Vol. IA-12, No. 3, May/June 1976.
- [5] Hartung, E.C., "Fabricated Aluminum Rotor Construction for Induction Motors," IEEE IAS Pulp & Paper Conference Record, 1994.
- [6] Bredthauer, J., and Struck, N., "Starting of Large and Medium Voltage Motors Design, Protection and Safety Aspects," IEEE IAS PCIC Conference Record, 1994
- [7] Phillip E. Hayes, Barry M. Wood, Dennis G. Horn, "Mechanical Design of Induction Motors Applied on Adjustable Speed Drives," IEEE IAS PCIC Conference Record, 1997
- [8] Philip L. Alger " Induction Machines" Gordan and Breach Publishers First published 1965.
- [9] Austin H. Bonnett, "Root Cause of A.C. Motor Failure Analysis" IEEE IAS PCIC Conference Record, 1999
- [10] Metals Engineering, December 1992
9. Copyright:
- This material is a paper by "William R. Finley, Mark M. Hodowanec". Based on "Selection of Copper vs. Aluminum Rotors for Induction Motors".
- Source of the paper: [The paper does not provide a DOI URL.]
This material is summarized based on the above paper, and unauthorized use for commercial purposes is prohibited.
Copyright © 2025 CASTMAN. All rights reserved.