This article introduces the paper "Development of a semi-automated die casting die design system" presented at the Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part B: Journal of Engineering Manufacture.
1. Overview:
- Title: Development of a semi-automated die casting die design system
- Author: J.Y.H. Fuh, S.H. Wu and K.S. Lee
- Publication Year: 2002
- Publishing Journal/Academic Society: Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part B: Journal of Engineering Manufacture
- Keywords: die-casting, die-base, feature-based, CAD, die, gating, runner
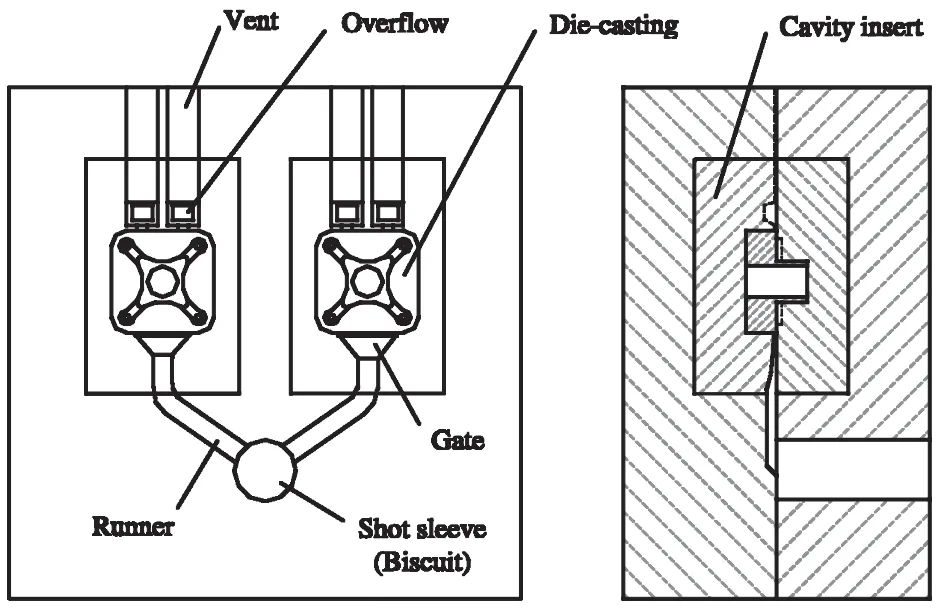
2. Research Background:
- Social/Academic Context of the Research Topic:
The die casting industry faces increasing pressure to reduce lead times and costs in die design and manufacturing. While Computer-Aided Design (CAD) systems are widely adopted to enhance design efficiency and quality, they generally lack specific functionalities tailored for die casting die design. This necessitates the development of specialized CAD tools for this industry. - Limitations of Existing Research:
Conventional CAD systems offer geometric modeling and drafting capabilities but do not provide the domain-specific knowledge and modules required for efficient die casting die design. Although "add-on" software applications exist for injection mold design, similar solutions for die casting die design have been lacking. Previous research efforts in die casting die design have often focused on isolated aspects such as feeder systems or casting designs, rather than a comprehensive die design system. - Necessity of the Research:
To address the market demand for faster turnaround and cost reduction, and to overcome the limitations of general-purpose CAD systems, there is a clear need for a dedicated computer-aided system for die casting die design. Such a system should improve design efficiency, enhance design quality, and incorporate specialized knowledge for die casting processes.
3. Research Purpose and Research Questions:
- Research Purpose:
The primary purpose of this research is to develop a prototype of a semi-automated die casting die design system. This system is structured as specific add-on applications to a commercial CAD platform, aiming to provide functionalities specifically for die casting die design. - Key Research Questions:
The research seeks to address the following key questions:- How can functional modules be developed as add-on applications on a commercial CAD system to support various stages of die casting die design?
- Which modules are essential for a semi-automated system, including data initialization, cavity layout, gating system design, die-base design, parting design, and standard component design?
- How can the system development be focused on critical aspects of die casting die design, particularly gating, runner, and die-base design?
- Research Hypotheses:
While not explicitly stated as hypotheses, the research operates under the implicit assumption that a modular, add-on system, incorporating feature-based design and process knowledge, can significantly improve the efficiency and effectiveness of die casting die design compared to using generic CAD systems or manual methods.
4. Research Methodology
- Research Design:
The research employs a prototype system development approach. A modular system named "DieWizard" is designed as an add-on to a commercial CAD platform. This system is structured into functional modules, each addressing a specific aspect of the die casting die design process. - Data Collection Method:
The research does not involve traditional data collection from experiments or surveys. Instead, it focuses on the development and integration of existing die casting knowledge, design principles, and computational techniques into the software system. Process data and material data are incorporated through databases within the system. - Analysis Method:
The system integrates the P-Q² technique for gating system design and employs feature-based parametric design for creating and managing gating features and die-base components. Algorithms are developed and implemented for tasks such as cavity number determination, cavity layout, and automatic die-base generation. - Research Subjects and Scope:
The scope of the research is limited to the development of key modules for die casting die design, including:- Data initialization
- Cavity layout
- Gating system design (gate, runner, overflow, shot sleeve)
- Die-base design
- Parting design
- Standard component design
The primary focus of the development is placed on the gating system, runner, and die-base design modules. The system is implemented within a commercial CAD environment.
5. Main Research Results:
- Key Research Results:
The research successfully developed a prototype semi-automated die casting die design system, DieWizard. This system comprises functional modules for various stages of die design, including data initialization, layout design, gating design, die-base design, and parting design. Key achievements include:- Development of a modular system architecture for die casting die design as an add-on to commercial CAD.
- Implementation of modules for data initialization, cavity layout, gating system design, die-base design, and parting design.
- Creation of a gating feature library and a die-base library to facilitate automated design generation.
- Integration of the P-Q² technique and feature-based parametric design for gating system design.
- Algorithms for determining cavity number and automating die-base selection.
- Statistical/Qualitative Analysis Results:
The paper does not present statistical or qualitative analysis results in the traditional sense. The effectiveness of the system is demonstrated through an illustrative example of designing a die casting die for a cover plate. - Data Interpretation:
The developed DieWizard system demonstrates the feasibility of semi-automating die casting die design. By integrating domain-specific knowledge, feature-based design, and process analysis techniques, the system aims to streamline the design process, reduce design time, and improve the consistency and quality of die designs. - Figure Name List:
- Fig. 1 A die casting die assembly
- Fig. 2 The die casting die design process
- Fig. 3 The gating system of a die casting die
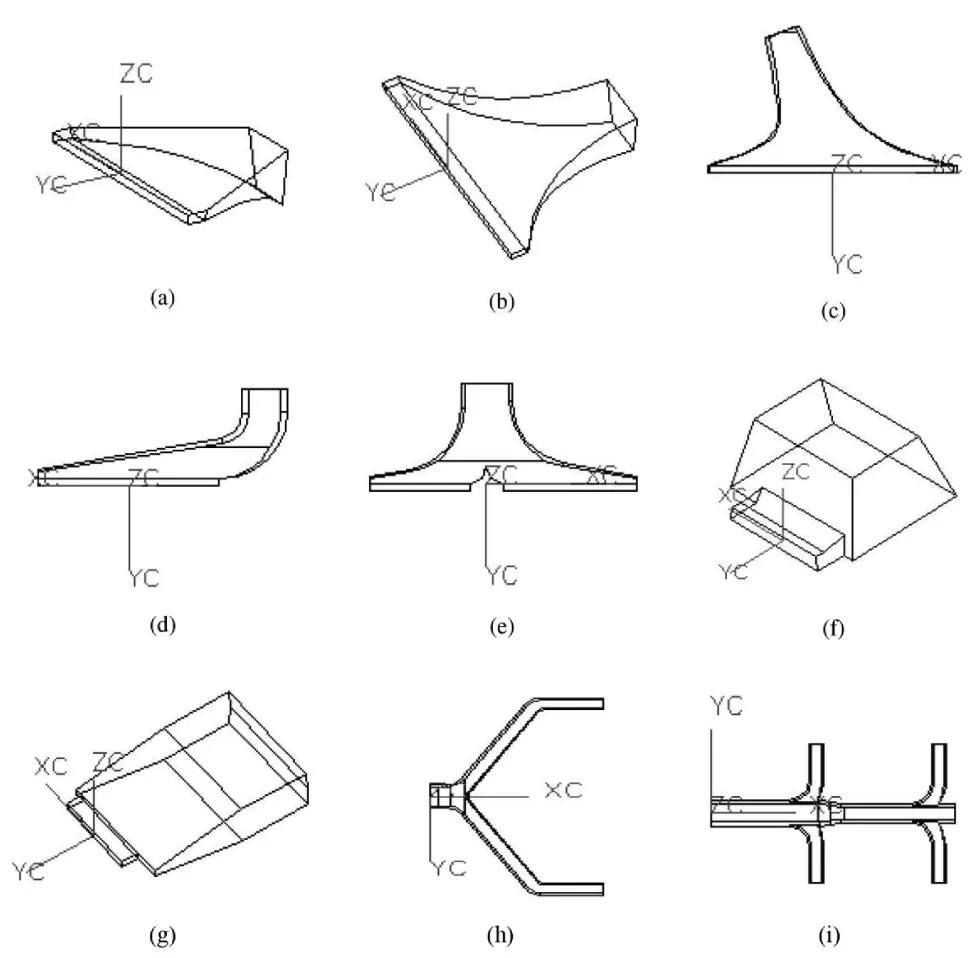
- Fig. 4 The gating features
- Fig. 5 The process of gating feature creation and retrieval
- Fig. 6 The system architecture of Die Wizard
- Fig. 7 Interfaces of: (a) cavity layout and (b) filling analysis
- Fig. 8 Interfaces of: (a) gate design and (b) runner design
- Fig. 9 Interfaces of: (a) sleeve/sprue and (b) die-base design
- Fig. 10 The three-dimensional part model and its related process data
- Fig. 11 The cavity layout created from a four-cavity pattern
- Fig. 12 The filling analysis result
- Fig. 13 Design of the gate, overflow and runner
- Fig. 14 The designed die base and die casting die assembly
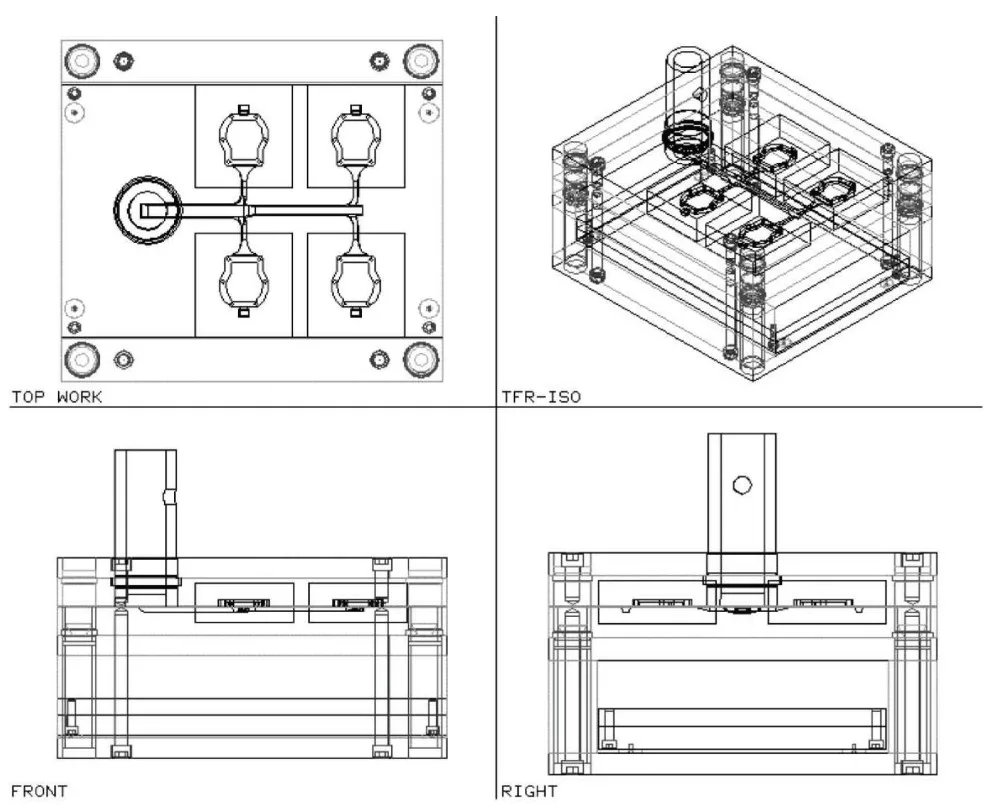
6. Conclusion and Discussion:
- Summary of Main Results:
The paper concludes that the developed prototype system, DieWizard, successfully demonstrates a semi-automated approach to die casting die design. The system, built as an add-on to a commercial CAD platform, incorporates specific modules for data initialization, layout, gating, and die-base design. Feature-based parametric design is effectively applied to the gating system, enabling automatic generation of gating components, cavity layouts, and die-bases based on user-defined features and parameters. - Academic Significance of the Research:
This research contributes to the field by demonstrating a practical approach to integrating die casting design functionalities within existing CAD software. It highlights the application of feature-based parametric design and the P-Q² technique in automating critical aspects of die casting die design. The modular system architecture provides a framework for further development and expansion. - Practical Implications:
The DieWizard system offers significant practical benefits for die casting die designers. It has the potential to reduce design time, shorten modification cycles, and improve overall design efficiency. By automating repetitive tasks and incorporating expert knowledge, the system can assist designers in creating consistent and optimized die designs, ultimately contributing to reduced lead times and manufacturing costs in the die casting industry. - Limitations of the Research:
The authors acknowledge that DieWizard is a prototype system and does not yet encompass all aspects of a complete die casting die design process. Functionalities such as cooling system design, ejection system design, and moving core system design are identified as areas not fully addressed in this research. The primary focus was on gating and die-base design, leaving other important die components for future development.
7. Future Follow-up Research:
- Directions for Follow-up Research:
Future research should focus on expanding the capabilities of DieWizard to encompass a more comprehensive range of die casting die design functionalities. Specifically, the integration of modules for:- Cooling system design
- Ejection system design
- Moving core system design
- Standard component design (beyond die-base)
- Areas Requiring Further Exploration:
Further exploration is needed to develop a truly complete die casting die design system. This includes refining existing modules, adding new functionalities, and potentially incorporating simulation and optimization tools to further enhance the system's capabilities and practical utility in industrial settings.
8. References:
[1] NADCA, North American Die Casting Association, 2000; http://www.diecasting.org/.
[2] Lee, K. S., Fuh, J. Y. H., Zhang, Y. F., Nee, A. Y. C. and Li, Z. IMOLD: an intelligent plastic injection mould design and assembly system. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Die and Mould Technology, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 1997, pp. 30–37.
[3] IMOLDWorks, Manusoft Plastics Pte Ltd, Singapore, 2001; http://www.manusoftcorp.com.sg.
[4] Mehalawi, M. E. and Miller, R. A. Towards computer-assisted configuration of diecasting dies. Die-Casting Engineer, January-February 2000, 41–46.
[5] CASTFLOWTM and CASTHERMTM software, Castec Australia Pte Ltd, 2000.
[6] MAGMA User Manual, MAGMA Software, Germany, 2001; http://www.magmasoft.com/.
[7] Zhang, H. G., Webster, P. D. and Dean, T. A. Computer aided design of feeders for castings. Proc. Instn Mech. Engrs, Part B, Journal of Engineering Manufacture, 1994, 208(B4), 279-287.
[8] Sirilertworakul, N., Webster, P. D. and Dean, T. A. A software package for the design and production of castings. The Foundryman 86, 1993, Part 9, 365-369.
[9] Huang, Y. S., Webster, P. D. and Dean, T. A. CADcast, design and production software for castings. In Proceedings of 99th Casting Congress, Kansas City, 1995.
[10] Dean, T. A. A knowledge based package for design and low cost manufacture of tooling for casting. In Proceedings of CIRP International Symposium on Advances in Design and Manufacture in the Global Manufacturing Era, Hong Kong, 1997, pp. 427-432.
[11] Huang, Y. S., Webster, P. D. and Dean, T. A. Software for the rapid production of patterns for castings. Proc. Instn Mech. Engrs, Part B, Journal of Engineering Manufacture, 1997, 211(B6), 425-434.
[12] Tu, J. S., Foran, R. K., Hines, A. M. and Aimone, P. R. Integrated procedure for modeling investment castings. J. Metals, 1995, 47(10), 64-68.
[13] Allsop, D. F. and Kennedy, D. Pressure Die Casting Part 2: The Technology of the Casting and the Die, 1983 (Pergamon Press, Oxford and New York).
[14] Herman, E. A. Designing Die Casting Die, 1996 (North American Die Casting Association).
[15] Herman, E. A. Gating Die Casting Die, 1996 (North American Die Casting Association).
[16] Unigraphics, Assemblies User Manual, Unigraphics Solution Company, Maryland Heights, Missouri, 1997.
[17] Feng, B. Y., Han, T. R., Yin, Z. H. and Jiang, W. S. Die casting die design. In A Concise Handbook for Mould Design and Manufacture, 1996 (Shanghai Technological Press, PR China).
9. Copyright:
*This material is J.Y.H. Fuh, S.H. Wu and K.S. Lee's paper: Based on Development of a semi-automated die casting die design system.
*Paper Source: https://doi.org/10.1243/095440502321016323
This material was summarized based on the above paper, and unauthorized use for commercial purposes is prohibited.
Copyright © 2025 CASTMAN. All rights reserved.