This paper introduction was written based on the 'Research on the Development and Application of Lightweight Automotive Materials' published by 'IOP Publishing'.
1. Overview:
- Title: Research on the Development and Application of Lightweight Automotive Materials
- Author: Chengzhi Han
- Publication Year: 2020
- Publishing Journal/Academic Society: Journal of Physics: Conference Series
- Keywords: automotive materials, lightweight, energy saving, emission reduction
2. Abstracts or Introduction
Abstract-With the continuous improvement of people's living standards, mobility tools have also evolved from walking and cycling to today's private cars. The rapid increase in the number of private cars has caused China's energy consumption to increase. China does not have sufficient energy resources. In order to alleviate the pressure on energy, the energy conservation and emission reduction of automobiles must be paid attention to. There are many ways to save energy and reduce emissions of automobiles. One of them is to reduce the weight of the car. Once the weight of the car is reduced, the amount of energy consumed will be reduced, thereby achieving the goal of energy conservation. Based on this, this article focuses on the use of lightweight materials in current automotive materials, and introduces a variety of lightweight materials in detail to help cars reduce weight, reduce energy consumption, and achieve sustainable development in the automotive industry.
3. Research Background:
Background of the Research Topic:
Cars have become a necessary means of travel, and the increasing number of private cars reflects national economic improvement. However, this increase also leads to more serious pollution and energy shortage problems. "Automotive lightweighting is the development trend of the scientific development concept and the corresponding national call for energy conservation and environmental protection". This involves replacing traditional automotive materials with lighter materials to reduce vehicle weight and energy consumption. The development of automobiles depends on the "renewal and iteration of automotive materials", and applying lightweight automotive materials is key to achieving lightweight automobiles.
Status of Existing Research:
Common automotive materials are mainly glass, plastic, steel and aluminum alloys. Steel accounts for about 70% of the weight of automobiles, while aluminum alloy and other materials account for about 10%. To realize weight reduction, special materials must replace steel. Lightweight automotive materials are widely used, and their application can improve the scientific development of the automotive industry by ensuring vehicle performance.
Necessity of the Research:
The rapid increase in private cars in China has led to increased energy consumption, while China lacks sufficient energy resources. Energy conservation and emission reduction in automobiles are crucial. Reducing vehicle weight is an effective method for energy saving and emission reduction. This research focuses on the application of lightweight materials in automotive materials to address energy consumption and promote sustainable development in the automotive industry.
4. Research Purpose and Research Questions:
Research Purpose:
This article aims to focus on the use of lightweight materials in current automotive materials. It introduces various lightweight materials in detail to facilitate weight reduction in cars, reduce energy consumption, and achieve sustainable development in the automotive industry.
Key Research:
The key research area is the application of lightweight automotive materials to reduce vehicle weight, thereby reducing energy consumption and emissions. The paper investigates different types of lightweight materials and their applications in the automotive industry.
Research Hypotheses:
The paper implicitly hypothesizes that the application of lightweight automotive materials can significantly contribute to energy saving and emission reduction in the automotive industry, and is essential for sustainable development.
5. Research Methodology
Research Design:
This research appears to be a literature review and analysis paper. It summarizes and synthesizes existing knowledge on lightweight automotive materials and their applications.
Data Collection Method:
The paper gathers information from scientific statistics, customs data, and previous research papers and reports related to automotive materials and lightweighting technologies. References are cited to support the claims and information presented.
Analysis Method:
The paper uses qualitative analysis to discuss the practical significance of lightweight automotive materials, the need for energy saving, and the application of various lightweight materials. It compares different materials based on their weight reduction potential, application scenarios, and disadvantages.
Research Subjects and Scope:
The research focuses on lightweight automotive materials, including high strength steel, aluminum and aluminum alloy materials, magnesium alloy material, titanium alloy material, and plastics and composite materials. The scope is limited to the automotive industry and the context of energy conservation and sustainable development in China.
6. Main Research Results:
Key Research Results:
- Effective energy saving and emission reduction: Reducing vehicle weight by 10% can reduce fuel consumption by 6-8% and emission of polluting gases by about 4%. Lightweight automotive materials significantly reduce fuel consumption and emissions.
- Need to save energy: Research on automobile lightweighting is crucial for energy conservation due to China's reliance on imported petroleum and the need for sustainable energy development.
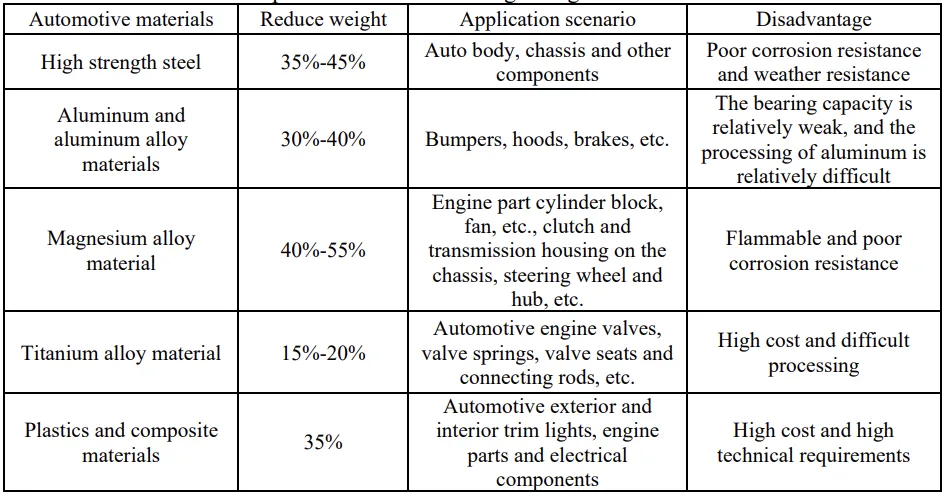
- Use of Lightweight Automotive Materials: The paper details the application, weight reduction potential, application scenarios, and disadvantages of various lightweight materials:
- High strength steel: 35%-45% weight reduction, used in auto body and chassis, disadvantage is poor corrosion resistance.
- Aluminum and aluminum alloy materials: 30%-40% weight reduction, used in bumpers, hoods, brakes, etc., disadvantages are weak bearing capacity and difficult processing.
- Magnesium alloy material: 40%-55% weight reduction, used in engine parts, chassis, steering wheel, etc., disadvantages are flammability and poor corrosion resistance.
- Titanium alloy material: 15%-20% weight reduction, used in engine valves, valve springs, etc., disadvantages are high cost and difficult processing.
- Plastics and composite materials: 35% weight reduction, used in automotive exterior and interior trim, engine parts, etc., disadvantages are high cost and high technical requirements.
Analysis of presented data:
Table 1 in the paper ("Comprehensive situation of lightweight automotive materials") summarizes the weight reduction, application scenarios, and disadvantages of different lightweight automotive materials. This data highlights the trade-offs between weight reduction potential, material properties, cost, and processing challenges for each material. The analysis emphasizes that selecting the appropriate lightweight material depends on the specific application and performance requirements.
7. Conclusion:
Summary of Key Findings:
The paper concludes that automobile materials are key to automotive development, and applying lightweight materials is essential for alleviating energy shortages in China. Lightweight materials are a scientific reform and innovation in the automotive industry. The paper introduces and analyzes high-strength steel, aluminum alloys, magnesium alloys, titanium alloys, and plastics/composites. Lightweight automotive materials are a top priority for future automotive manufacturing to promote China's sustainable development.
Academic Significance of the Study:
This study provides a handbook-level overview of lightweight automotive materials, consolidating information on various material types, their properties, and applications. It contributes to the academic understanding of material science in automotive engineering and highlights the importance of lightweighting for energy conservation and emission reduction.
Practical Implications:
The practical implication is to promote the application of lightweight automotive materials in the automotive industry. The information presented can guide automotive designers and manufacturers in selecting appropriate materials to reduce vehicle weight, improve fuel efficiency, and reduce environmental impact.
Limitations of the Study and Areas for Future Research:
The paper is a review and does not present original experimental data or in-depth quantitative analysis. Future research could focus on:
- Detailed life cycle assessments of different lightweight materials.
- Cost-benefit analyses of implementing lightweight materials in mass production.
- Development of new lightweight materials with improved properties and lower costs.
- Optimization of manufacturing processes for lightweight automotive components.
8. References:
[1] Zheng Hui, Zhao Xiya. Lightweight automobile and the application of aluminum alloy in modern automobile production [J]. Forging Technology, 2016 (02).
[2] Zhao Jun, Peng Qingfeng, Fang Yunzhou, Li Jinghua. Application analysis of lightweight and plastic glass in new energy vehicles [J]. Journal of Hefei University (Natural Science), 2018, 01:57-61+79
[3] Shi Shasha, Liu Jinli. Application of new materials in automotive lightweight technology [J]. Automotive Materials Use Technology, 2015 (7).
[4] Fan Youyu. Application status and research progress of lightweight automotive body materials [J]. Automotive Materials and Equipment Manufacturing, 2017 (6).
[5] Yue Haikuo. Overview of lightweight design methods for automotive structures [J]. Chinese High-tech Enterprise Discussion, 2017 (21)
[6] Shi Shasha, Liu Jinli. Application of new materials in automobile lightweight technology [J]. Automobile Use Technology, 2018 (7).
[7] FAN Youyu. Application status and research progress of lightweight automotive body materials [J]. High-end Equipment Manufacturing, 2018 (6).
[8] Yue Haikuo. Overview of lightweight design methods for automotive structures [J]. China High-tech Enterprises, 2018 (21).
9. Copyright:
- This material is "Chengzhi Han"'s paper: Based on "Research on the Development and Application of Lightweight Automotive Materials".
- Paper Source: doi:10.1088/1742-6596/1676/1/012085
This material was summarized based on the above paper, and unauthorized use for commercial purposes is prohibited.
Copyright © 2025 CASTMAN. All rights reserved.