본 소개 논문의 내용은 "[Journal of the Faculty of Engineering and Architecture of Gazi University]"에서 발행한 논문 "[For different industrial applications: Outer rotor and low speed induction machine design]"를 기반으로 합니다.
1. 개요:
- 제목: 다양한 산업 응용 분야를 위한 외전형 저속 유도 전동기 설계 (For different industrial applications: Outer rotor and low speed induction machine design)
- 저자: 하칸 첼릭, 누만 사비트 체틴 (Hakan Çelik, Numan Sabit Çetin)
- 발행 연도: 2023년
- 발행 학술지/학회: 가지 대학교 공학 및 건축 학부 저널, 38:4 (2023) 2009-2023 (Journal of the Faculty of Engineering and Architecture of Gazi University, 38:4 (2023) 2009-2023)
- 키워드: 유도 전동기 (Induction machine), 외전형 로터 (Outer rotor), 설계 (Design), 최적화 (Optimization), 유한 요소법 (Finite element method)
2. 초록:
"오늘날, 새로운 기술 개발과 함께 비동기 전동기의 전통적인 사용 영역 외에도 전동기 및 발전기로서의 사용 영역이 점차 확대되고 있습니다. 최근 몇 년 동안 전기 자동차의 전동기/발전기, 풍력 터빈 및 소수력 발전과 같은 분야에서 유도 발전기의 사용이 확산되기 시작했습니다. 본 연구는 외전형 유도 전동기 응용 분야에 사용될 수 있고 선택적으로 직접 구동 발전기로도 사용될 수 있는 저속 및 고토크 외전형 유도 전동기를 설계하는 것을 목표로 합니다. 16극, 50Hz 주파수, 375rpm 동기 속도, 1kW 외전형 유도 전동기의 설계, 최적화 및 전자기 분석을 수행했으며, 본 연구의 분석을 위해 6가지의 서로 다른 모델을 개발했습니다. 고정자 설계에는 단일 슬롯 유형과 72개의 슬롯이 사용되었고, 회전자 설계에는 59개의 슬롯과 3가지의 서로 다른 슬롯 유형이 사용되었습니다. 농형 회전자에는 구리와 알루미늄 재료가 선호되었으며, 연구는 Ansys Maxwell 전자기 패키지 프로그램을 사용하여 수행되었습니다. 연구에서 Rmxprt-optimetrics 모듈을 사용하여 최고 효율을 얻기 위해 기계 기초 크기, 에어 갭 및 슬롯 치수를 최적화했습니다. 그 후 유한 요소법을 사용하여 전자기 분석을 수행했습니다. 기계의 전동기 작동 영역에 대해 수행된 분석 결과, IEC 60034-30-1에 따른 IE2 및 IE3 등급의 1.1kW 전력의 8극 내전형 비동기 전동기의 효율보다 높은 효율이 얻어졌습니다. 이 결과에 따르면 외전형, 저속 및 고토크 유도 전동기를 생산하여 전동기로 사용할 수 있음을 알 수 있었습니다."
3. 서론:
비동기 전동기, 즉 유도 전동기는 기술 발전으로 인해 인기가 높아지고 있으며, 전통적인 산업 용도 외에도 다양한 분야로 응용 범위가 확대되고 있습니다. 특히 전기 자동차 및 재생 에너지 시스템과 같은 분야에서 전동기 및 발전기로서의 역할이 증가하면서 효율적이고 적응 가능한 전동기 기술의 중요성이 강조되고 있습니다. 본 연구는 외전형 유도 전동기 (DRAMAK)에 초점을 맞추어 직접 구동 응용 분야 및 다양한 산업 환경에 적합한 저속, 고토크 전동기에 대한 증가하는 수요를 해결하고자 합니다. 기존의 내전형 비동기 전동기 (İRAMAK)가 널리 사용되고 있지만, 역사적으로 냉각 팬과 같은 응용 분야에 제한되었던 DRAMAK은 특히 전기 자동차 파워트레인 분야에서 주목받고 있습니다. 본 연구에서는 혁신적인 DRAMAK 설계를 제시하여 까다로운 산업 응용 분야에서 높은 효율과 성능을 발휘할 수 있는 잠재력을 강조합니다.
4. 연구 요약:
연구 주제 배경:
기술 발전으로 인해 비동기 전동기의 응용 분야가 확대됨에 따라 다양한 작동 요구 사항에 맞는 전동기 설계를 탐색하고 최적화해야 할 필요성이 커지고 있습니다. 전기 자동차 및 재생 에너지 시스템과 같은 분야에서 전동기 및 발전기에 대한 수요가 증가함에 따라 효율적이고 적응 가능한 전동기 기술의 중요성이 부각되고 있습니다.
기존 연구 현황:
DRAMAK에 대한 기존 연구는 주로 천장 선풍기와 같은 저성능 응용 분야를 위한 단상 전동기에 초점을 맞추었습니다. 이러한 설계는 종종 낮은 효율과 높은 슬립을 나타냅니다. 다양한 기술을 통해 성능 개선을 탐구한 연구가 있었지만, 산업 응용 분야 및 직접 구동 발전기 시스템에 적합한 고효율 3상 DRAMAK 설계에 대한 문헌은 부족합니다.
연구 목적:
본 연구는 3상, 저속, 고토크 및 고효율 외전형 유도 전동기를 설계하고 최적화하는 것을 목표로 합니다. 목표 응용 분야에는 전기 자동차용 전동기/발전기, 풍력 터빈 및 소수력 발전 응용 분야의 직접 구동 발전기, 팬 전동기 등이 포함됩니다.
핵심 연구:
본 연구의 핵심은 50Hz에서 작동하는 1kW, 16극 외전형 유도 전동기에 대한 분석적 설계, 최적화 및 2D 유한 요소 해석 (FEA)을 수행하는 것입니다. Ansys Maxwell 소프트웨어를 사용하여 6가지의 서로 다른 모델을 개발하고 분석했습니다. 본 연구에서는 IEC 60034-30-1 표준에 따른 고효율 달성에 초점을 맞춰 다양한 회전자 슬롯 유형 (원형, 드롭 케이지, 직사각형) 및 농형 재료 (구리 및 알루미늄)가 전동기 성능에 미치는 영향을 조사합니다.
5. 연구 방법론
연구 설계:
본 연구는 분석적 설계, 파라메트릭 최적화 및 유한 요소 해석을 포괄하는 다각적인 접근 방식을 채택합니다. 초기에는 분석적 설계 프레임워크를 구축한 다음 효율성을 극대화하기 위해 Ansys Maxwell 내의 RMxprt optimetrics 모듈을 사용하여 최적화를 수행했습니다. 그 후, 분석 모델을 검증하고 전자기 성능을 평가하기 위해 Ansys Maxwell을 사용하여 2D 유한 요소 해석 (FEA)을 수행했습니다. 포괄적인 시각화를 위해 2D 전동기 형상을 기반으로 3D 기계 설계를 구상했습니다. 6가지의 서로 다른 전동기 모델을 설계하여 회전자 슬롯 형상과 케이지 재료를 체계적으로 변경하여 각각의 영향을 평가했습니다.
데이터 수집 및 분석 방법:
데이터 수집 및 분석은 주로 Ansys Maxwell 소프트웨어 제품군을 사용하여 수행되었습니다. RMxprt optimetrics 모듈은 고정자 및 회전자 치수, 에어 갭 및 슬롯 파라미터의 최적화를 용이하게 했습니다. 전자기 분석은 2D FEA를 사용하여 전동기 작동 조건에서 전동기 동작을 시뮬레이션하기 위해 수행되었습니다. 효율, 토크, 역률 및 전류 특성과 같은 성능 지표를 시뮬레이션에서 추출하여 6가지 모델 간에 비교했습니다. 그런 다음 결과를 효율 등급 분류를 위해 IEC 60034-30-1 표준과 비교하여 평가했습니다.
연구 주제 및 범위:
본 연구는 1kW, 16극, 3상 외전형 유도 전동기의 설계 및 최적화에 특별히 초점을 맞추었습니다. 범위는 다음을 포함합니다.
- 세 가지 다른 회전자 슬롯 유형의 영향 조사: 원형 (Tip I), 드롭 케이지 (Tip II) 및 직사각형 (Tip III).
- 두 가지 다른 회전자 케이지 재료를 사용한 성능 분석: 구리 (Cu) 및 알루미늄 (Al).
- RMxprt optimetrics 모듈을 사용하여 최대 효율을 위한 전동기 파라미터 최적화.
- FEA를 사용한 2D 전자기 분석을 통한 분석 설계 검증.
- IEC 60034-30-1 표준 (IE2 및 IE3 효율 등급)에 따른 효율 등급 평가.
6. 주요 결과:
주요 결과:
분석 결과 설계된 6가지 모델에서 상당한 성능 변화가 나타났습니다. 주요 결과는 다음과 같습니다.
- 최고 효율: 드롭 케이지 슬롯 (Tip II)과 구리 케이지 재료를 특징으로 하는 M3 모델이 %η=78.38의 최고 효율을 달성했습니다.
- 최고 토크 및 최적 역률: 원형 슬롯 (Tip I)과 알루미늄 케이지 재료를 사용하는 M2 모델은 최고 토크 (Tm=27.36 Nm) 및 최적 역률 (Cosp=0.73)을 입증했습니다. 이 모델은 또한 최저 속도 (nr=348.99 rpm)와 높은 효율 %η=74.75를 나타냈습니다.
- 재료 및 슬롯 유형 영향: 회전자 케이지 재료 및 슬롯 유형의 선택은 전동기 성능, 특히 효율 및 토크 특성에 상당한 영향을 미칩니다. 일반적으로 구리는 더 높은 효율을 제공하는 반면, 원형 슬롯 구성은 분석된 모델에서 더 높은 토크에 기여했습니다.
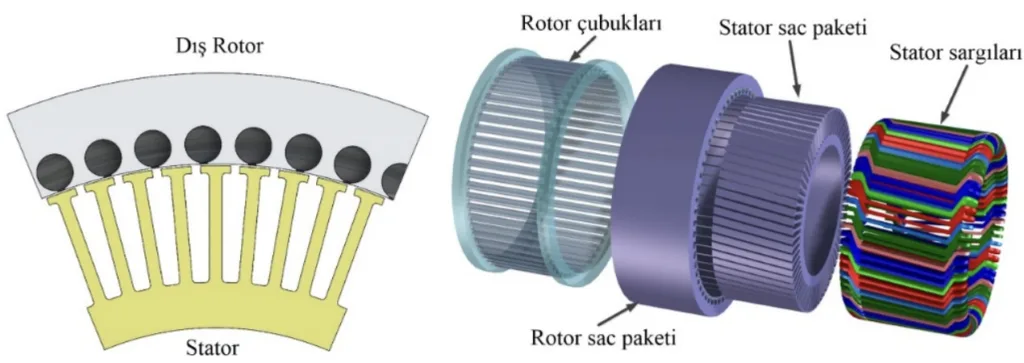
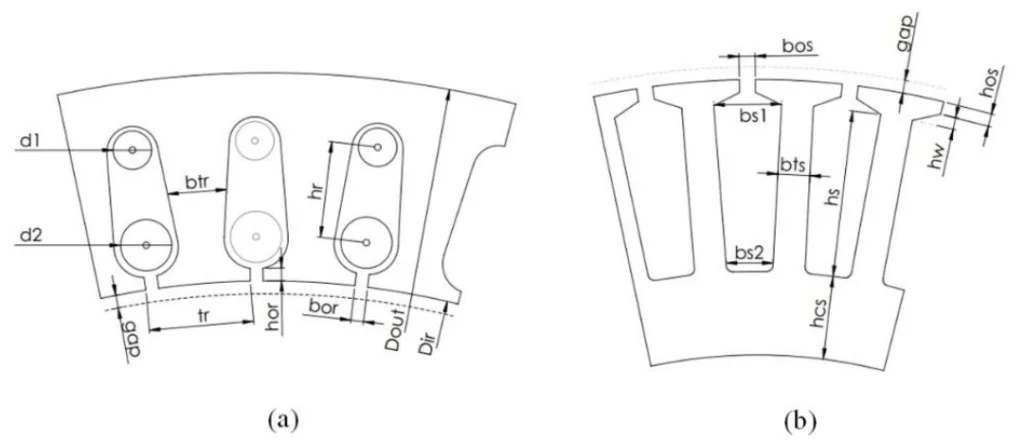
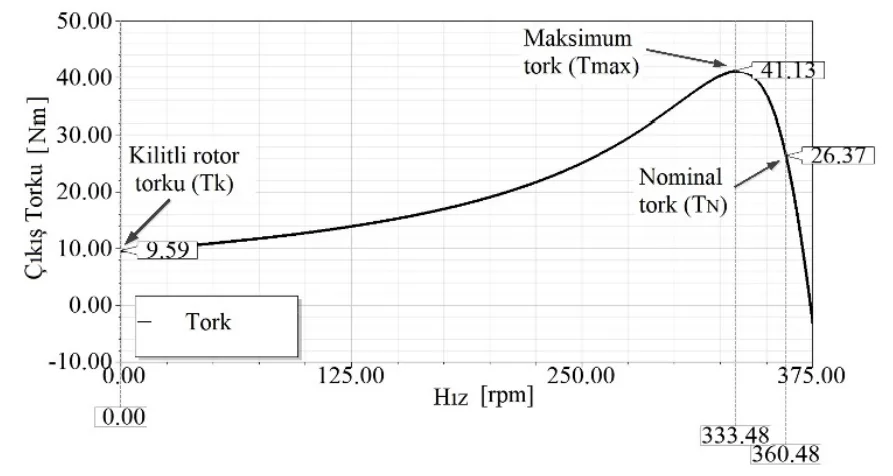
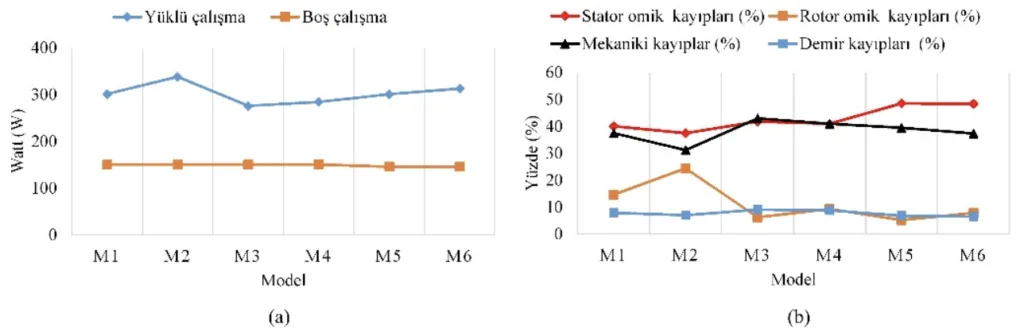
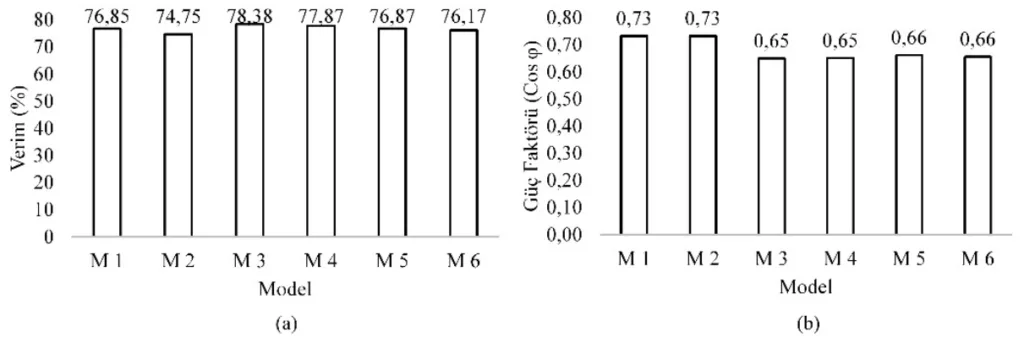
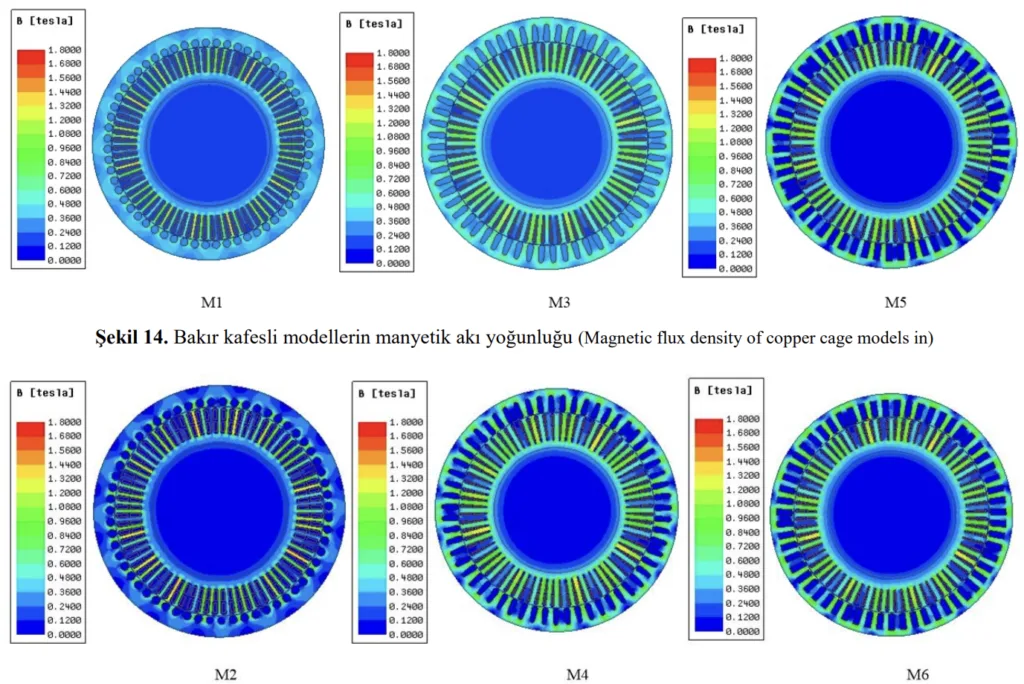
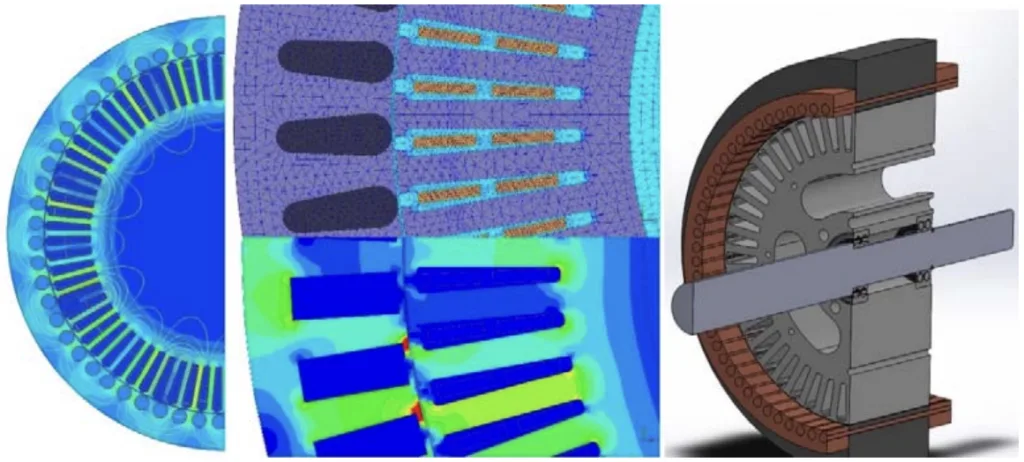
그림 목록:
- 그림 A. 외전형 유도 전동기 메시 작동 및 2D FEA (Outer rotor induction motor mesh operation and 2D FEA)
- 그림 5. M1 공극-효율 최적화 그래프 (M1 Air gap - efficiency optimization graph)
- 그림 7. 등가 회로 파라미터; a) R1 및 R2, b) X1 및 X2, c) Xm (Equivalent circuit parameters a) R1 and R2, b) X1 and X2, c) Xm )
- 그림 8. 상 전류 (Phase current)
- 그림 9. M1 토크-속도 곡선 (M1 torque-speed graphic)
- 그림 10. 토크 값 (Torque values)
- 그림 11. a) 총 손실, b) 상세 손실 비율 (a)Total losses, b) Detailed loss rates)
- 그림 12. a) 효율 b) 역률 (a-Efficiency, b-Power factor)
- 그림 13. M3 메시 처리 및 M5 자기장 분포 (M3 Mesh operation and M5 magnetics field disturibition)
- 그림 14. 구리 케이지 모델의 자기장 밀도 (Magnetic flux density of copper cage models in)
- 그림 15. 알루미늄 케이지 모델의 자기장 밀도 (Magnetic flux density of aluminium cage models)
- 그림 16. 토크-시간 곡선; a) M-M2, b) M3-M4, c) M5-M6, 전류-시간 곡선; d) M1-M2, e) M3-M4, f) M5-M6 (Torque-time graphic; a) M1-M2, b) M3-M4, c) M5-M6, Current-time graphic; d) M1-M2, e) M3-M4, f) M5-M6)
- 그림 17. 속도-시간 곡선 (Speed-time graphic)
7. 결론:
본 연구는 높은 극수를 가진 외전형 유도 전동기 (ORIM)에서 고효율을 달성할 수 있음을 입증합니다. 본 연구는 IEC 60034-30-1 표준에 따라 IE2 및 IE3 효율 등급의 8극 1.1kW 내전형 유도 전동기 (IRIM)의 효율 한계를 초과하는 효율로 16극 1kW ORIM을 제조할 수 있다는 참신함을 강조합니다. 연구 결과는 외전형, 저속 및 고토크 유도 전동기가 생산 및 실용적인 전동기 응용 분야에 적합하며, 첨단 산업 및 전기 자동차 구동 시스템을 위한 유망한 길을 제공함을 시사합니다.
8. 참고 문헌:
- [1] Bortoni, E. C., Bernardes Jr, J. V., da Silva, P. V., Faria, V. A., Vieira, P. A., Evaluation of manufacturers strategies to obtain high-efficient induction motors, Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments, 31, 221-227, 2019.
- [2] Kabul A., Ünsal A., Diagnosis of simultaneous broken rotor bars and static eccentricity faults of induction motors by analyzing stator current and vibration signals, Journal of the Faculty of Engineering and Architecture of Gazi University, 36 (4), 2011-2023, 2021.
- [3] Lenin N.C., Padmanaban S., Bhaskar M.S., Mitolo M., Hossain E., Ceiling fan drives-past, present and future, IEEE Access, 9, 44888-44904, 2021.
- [4] Holik P.J., Dorrell D.G., Popescu M., Performance improvement of an external-rotor split-phase induction motor for low-cost drive applications using external rotor can, IEEE Transactions on magnetics, 43 (6), 2549-2551 2007.
- [5] Shastri S., Sharma U., Singh B., Design of Fractional-slot concentrated winding consequent pole motor for ceiling fans, IEEE 5th Int. Conference on Computing Communication and Automation, New Delhi-India, 390-395, 30-31 October, 2020.
- [6] Mohammed K.G., Ramli A.Q., Analyzing the performance of completed designed outer rotor single phase induction motor, IEEE Student Conference on Research and Developement, Putrajaya-Malaysia, 238-242, 16-17 December, 2013.
- [7] Popescu M., Dorrell D.G. and Holik P., Improving the starting torque in external-rotor induction motors using an outer can, 3rd IET International Conference on Power Electronics, Machines and Drives, Dublin- Ireland, 531-535, 4-6 April, 2006.
- [8] György T., Biró K.A., Genetic algorithm based design optimization of a three-phase induction machine with external rotor, 2015 Intl Aegean Conference on Electrical Machines & Power Electronics (ACEMP), 2015 Intl Conference on Optimization of Electrical & Electronic Equipment (OPTIM) & 2015 Intl Symposium on Advanced Electromechanical Motion Systems (ELECTROMOTION), Side-Turkey, 462-467, 2-4 September 2015.
- [9] György T., Biró K.Á., Co-evolutionary optimization design of a three-phase induction machine with external rotor, XXII International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Lausanne-Switzerland, 1394-1398, 4-7 September, 2016.
- [10] György, T., Biró K.A., Loss analysis of a low power induction machine with external rotor, 6.th International Conference on Modern Power Systems MPS2015, Cluj Napoca-Romania, 117-122, 18-21 May 2015.
- [11] Virlan B., Benelghali S., Simion A., Livadaru L., Outbib R., Munteanu A., Induction motor with outer rotor and ring stator winding for multispeed applications, IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 28 (4), 999-1007, 2013.
- [12] Sundaram V. M., Toliyat H. A., A fractional slot concentrated winding (FSCW) configuration for outer rotor squirrel cage induction motors, IEEE International Electric Machines & Drives Conference (IEMDC), Coeur d'Alene- USA, 20-26, 10-13 May, 2015.
- [13] Dalal A., Kumar P., Design, prototyping, and testing of a dual-rotor motor for electric vehicle application, IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 65 (9), 7185-7192, 2018.
- [14] Cui S., Han S., Chan C.C., Overview of multi-machine drive systems for electric and hybrid electric vehicles, IEEE Conference and Expo Transportation Electrification Asia-Pacific (ITEC Asia-Pacific), Beijing-China, 1-6, 31 August - 3 September, 2014.
- [15] Wang W., Chen X., Wang J., Motor/generator applications in electrified vehicle chassis-A Survey, IEEE Trans. Transactions on Transportation Electrification, 5 (3), 584-601, 2019.
- [16] Cha A.H.R., Jeong B.T.W., Im C.D.Y., Shin D.K.J., Seo E.Y.J., Design of outer rotor type induction motor having high power density for in-wheel system, 15th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Sapporo-Japan, 1-4, 21-24 October, 2012.
- [17] Popescu M., Riviere N., Volpe G., Villani M., Fabri G., Leonardo L.D., A copper rotor induction motor solution for electrical vehicles traction system, IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, Baltimore MD-USA, 3924-3930, September 29-October 3, 2019.
- [18] Livadaru L., Munteanu A., Simion A., Cantemir C., Design and finite element analysis of high-density torque induction motor for traction applications, 9th International Symposium on Advanced Topics in Electrical Engineering (ATEE), Bucharest-Romania, 211-214, 7-9 May, 2015.
- [19] Munteanu A., Livadaru L., Simion A., Vîrlan B., Single-tooth winding induction motor with external rotor for electric vehicle applications, International Conference and Exposition on Electrical and Power Engineering (EPE), Iasi-Romania, 209-212, October 20-22, 2016.
- [20] Hwang M.H., Lee H.S., Yang S.H., Cha H.R., Park S.J., Electromagnetic field analysis and design of an efficient outer rotor inductor in the low-speed section for driving electric vehicles, Energies, 12 (24), 4615, 2019.
- [21] Matthew H., Jensen B.B., Induction generators for direct-drive wind turbines, IEEE International Electric Machines & Drives Conference (IEMDC), Niagara Falls Ontario-Canada, 1125-1130, 14-17 May, 2011.
- [22] Mellah, H., Hemsas K.E., Design and analysis of an external-rotor internal-stator doubly fed induction generator for small wind turbine application by fem, International Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, 2 (1), 1-11, 2013.
- [23] Hamdi, E. S., Design of small electrical machines, John Wiley & Sons, New York, A.B.D., 1994.
- [24] Dorrell D. G., The challenges of meeting IE4 efficiency standards for induction and other machines, IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Busan-Korea (South), 213-218, 26 Feb.-1 March, 2014.
- [25] Kimball J. W., Amrhein M., IEEE Machine design considerations for the future energy challenge, Proceedings Electrical Insulation Conference and Electrical Manufacturing Expo, Indianapolis-USA, 448-453, 24-26 October, 2005.
- [26] Popescu M., Analysis and modelling of single-phase induction motor with external rotor for domestic applications, In Conference Record of the 2000 IEEE Industry Applications Conference, Thirty-Fifth IAS Annual Meeting and World Conference on Industrial Applications of Electrical Energy, Rome Italy, 1-463-470, 8-12 October, 2000.
- [27] Boldea, I., Induction machines handbook, CRC press Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton, A.B.D., 2010.
- [28] Demir U., Aküner M.C., Design and optimization of in-wheel asynchronous motor for electric vehicle, Journal of the Faculty of Engineering and Architecture of Gazi University, 33 (4), 1517-1530, 2018.
- [29] Purwanto W., Risfendra, Putra D S., Effect of stator slot geometry on high speed spindle motor performance, 2018 International Conference on Information and Communications Technology (ICOIACT), Yogyakarta- Indonesia, 561-565, 6-7 March, 2018.
- [30] Lipo T.A., Introduction to AC machine design, John Wiley & Sons, New Jersey, A.B.D, 2017.
- [31] Gundogdu T., Zhu Z. Q., Mipo J. C., Farah P., Influence of air-gap length on rotor bar current waveform of squirrel-cage induction motor. 19th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS) IEEE, Chiba-Japan, 1-6, 13-16 November, 2016.
- [32] Joksimović G., Kajević A., Mezzarobba M., Tessarolo, A., Optimal rotor bars number in four pole cage induction motor with 36 stator slots-part II: results, International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM) IEEE, Gothenburg-Sweden, 1, 509-514. 23-26 August, 2020.
- [33] Babypriya B., Gomathi, S., Numerical analysis on impact of choice of number of rotor slots on performance of three phase induction motor, Materials Today: Proceedings (Article in press), 1-7, 2020.
- [34] Chapman, S., Electric machinery fundamentals, McGraw-Hill Education, New York, A.B.D, 2005.
- [35] Araz H. K., Yılmaz M., Design procedure and implementation of a high-efficiency PMSM with reduced magnet-mass and torque-ripple for electric vehicles, Journal of the Faculty of Engineering and Architecture of Gazi University, 35 (2), 1089-1109, 2020.
9. 저작권:
- This material is a paper by "Hakan Çelik, Numan Sabit Çetin". Based on "For different industrial applications: Outer rotor and low speed induction machine design".
- Source of the paper: https://doi.org/10.17341/gazimmfd.937127
본 자료는 위 논문을 요약한 것으로, 상업적 목적으로 무단 사용하는 것을 금지합니다.
Copyright © 2025 CASTMAN. All rights reserved.