이 기술 요약은 Karani Kurtulus 외 저자가 Applied Thermal Engineering (2021)에 발표한 학술 논문 "An experimental investigation of the cooling and heating performance of a gravity die casting mold with conformal cooling channels"을 기반으로 합니다. 이 자료는 CASTMAN의 다이캐스팅 전문가들이 LLM AI(Gemini, ChatGPT, Grok 등)의 도움을 받아 분석하고 요약한 것입니다.
Keywords
- Primary Keyword: 컨포멀 쿨링 채널 (Conformal Cooling Channel)
- Secondary Keywords: 금형 냉각 (Mold Cooling), 다이캐스팅 사이클 타임 (Die Casting Cycle Time), 적층 제조 (Additive Manufacturing), 미세조직 (Microstructure), 열변형 (Thermal Distortion), 균일 냉각 (Uniform Cooling)
Executive Summary
- The Challenge: 기존의 직선형 냉각 채널을 사용하는 다이캐스팅 금형은 불균일한 냉각으로 인해 핫스팟, 제품 변형, 긴 사이클 타임 등의 고질적인 문제를 야기합니다.
- The Method: 연구팀은 전통적인 가공 방식으로 제작된 표준 냉각 금형과 적층 제조(DMLS) 기술로 제작된 컨포멀 냉각 채널 금형의 냉각 및 가열 성능을 수치 해석과 실제 실험을 통해 비교 분석했습니다.
- The Key Breakthrough: 컨포멀 쿨링 채널을 적용한 금형은 표준 금형 대비 사이클 타임을 28% 단축시켰으며, 더 균일한 금형 온도 분포를 통해 주조 부품의 미세조직을 현저히 개선했습니다.
- The Bottom Line: 컨포멀 쿨링 기술은 생산성을 극대화하고 최종 제품의 품질을 한 차원 높일 수 있는, 데이터로 검증된 혁신적인 금형 설계 솔루션입니다.
The Challenge: Why This Research Matters for HPDC Professionals
다이캐스팅 공정에서 금형의 냉각 성능은 생산 단가와 제품의 미세조직 품질을 결정하는 가장 중요한 요소 중 하나입니다. 수십 년간 엔지니어들은 전통적인 드릴링 가공으로 만들어진 직선형 냉각 채널의 한계와 싸워왔습니다. 이러한 방식은 푸셔 핀 홀이나 복잡한 형상의 코어 주변과 같이 냉각이 반드시 필요한 영역에 채널을 배치하기 어렵게 만듭니다.
그 결과, 금형 내부에 국부적인 '핫스팟(hot spots)'이 발생하여 불균일한 응고가 일어나고, 이는 수축, 뒤틀림과 같은 주조 결함으로 이어집니다 (Ref. [2]). 또한, 충분한 냉각을 위해 사이클 타임이 길어지면서 생산성이 저하되고 제조 원가가 상승하는 문제도 피할 수 없었습니다. 특히 박육화, 고강도화가 요구되는 최신 HPDC 부품에서 균일하고 효율적인 냉각은 품질 확보를 위한 핵심 과제입니다.
The Approach: Unpacking the Methodology
이러한 문제를 해결하기 위해 연구팀은 두 가지 유형의 금형을 설계하고 그 성능을 정밀하게 비교했습니다.
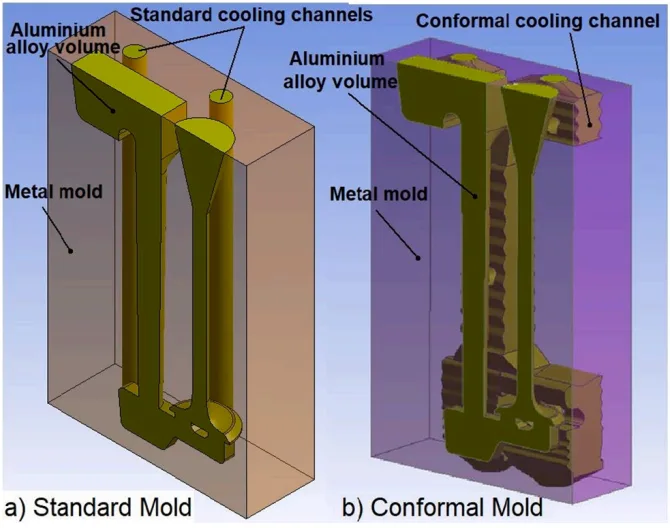
- 표준 냉각 금형 (Standard Mold): GGG-50 구상흑연주철을 전통적인 기계 가공으로 제작했으며, 직선형 원형 냉각 채널을 적용했습니다 (Figure 2).
- 컨포멀 냉각 금형 (Conformal Mold): 적층 제조 기술(DMLS, Direct Metal Laser Sintering)을 사용하여 Inconel-625 소재로 제작했습니다. 냉각 채널이 주조 제품(알루미늄 포펫 밸브)의 3차원 형상을 따라 흐르도록 설계되어 '컨포멀(Conformal, 형상 적응형)' 특성을 가집니다 (Figure 3, 4).
연구팀은 ANSYS-Fluent 소프트웨어를 이용한 유동 및 열전달 수치 해석과 함께, 금형 및 주조 부품의 여러 지점에 열전대(Thermocouple)를 설치한 물리적 실험(Figure 10)을 병행했습니다. 이를 통해 금형 가열 성능, 냉각 채널 내 압력 손실, 응고 과정에서의 열 유속, 사이클 타임 등 핵심 성능 지표들을 측정하고 비교 분석했습니다.
The Breakthrough: Key Findings & Data
실험과 분석을 통해 컨포멀 쿨링 채널의 압도적인 성능이 데이터로 입증되었습니다.
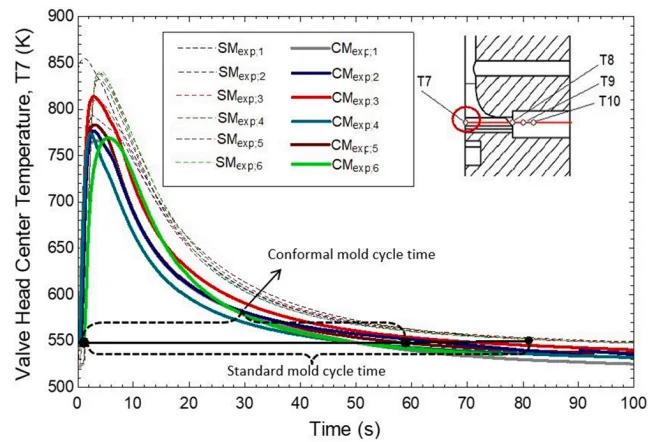
- Finding 1: 획기적인 사이클 타임 단축 (28% Reduction): 컨포멀 금형의 주조 사이클 타임은 평균 59초로, 표준 금형의 82초에 비해 28%나 단축되었습니다. 이는 동일한 시간 동안 더 많은 제품을 생산할 수 있음을 의미합니다 (Figure 21).
- Finding 2: 탁월한 열 관리 및 균일성: 컨포멀 금형은 표준 금형에 비해 훨씬 더 균일한 온도 분포를 보였습니다. 금형 가열 시, 표준 금형의 열전대 간 평균 온도 편차는 최대 22K에 달했지만, 컨포멀 금형은 6K에 불과했습니다 (Figure 15). 이는 제품의 열 응력과 변형을 최소화하는 데 결정적인 역할을 합니다. 특히 냉각이 중요했던 밸브 헤드 부위에서 더 높은 열 유속을 보이며 열을 신속하게 제거했습니다 (Figure 19).
- Finding 3: 미세조직 개선을 통한 품질 향상: 빠르고 균일한 냉각은 최종 제품의 미세조직을 더 작고 균일하게 만들었습니다. 컨포멀 금형으로 주조된 부품의 평균 입자 크기는 표준 금형 부품 대비 13.5% 더 작았습니다 (Figure 24). 또한, 더 넓은 결정립계 면적(Figure 23)은 더 미세한 조직이 형성되었음을 명확히 보여주며, 이는 곧 더 우수한 기계적 특성으로 이어질 수 있습니다.
- Finding 4: 실용적으로 허용 가능한 압력 손실: 컨포멀 채널은 구조가 복잡하여 유체 압력 손실이 12100 Pa로, 표준 채널(5250 Pa)보다 약 2배 높았습니다. 하지만 연구팀은 이 수치가 열교환기 설계 기준을 초과하지 않는, 실제 공정에서 충분히 수용 가능한 수준이라고 결론 내렸습니다.
Practical Implications for HPDC Products
이 연구 결과는 고압 다이캐스팅(HPDC) 현장에 다음과 같은 중요한 시사점을 제공합니다.
- For Process Engineers: Figure 21에서 확인된 28%의 사이클 타임 단축은 대량 생산 HPDC 라인에서 직접적인 생산성 향상과 단위당 제조원가 절감으로 이어집니다. 이는 수익성 개선을 위한 강력한 무기가 될 수 있습니다.
- For Quality Control: Figure 22와 Figure 24에서 나타난 균일하고 미세한 조직은 인장 강도, 항복 강도, 피로 수명 등 기계적 특성의 향상을 의미합니다. 이는 더 높은 신뢰성을 요구하는 자동차, 항공우주 부품의 품질을 보증하고 불량률을 낮추는 데 기여할 수 있습니다.
- For Die Design: 적층 제조(DMLS) 기술은 금형 설계의 패러다임을 바꿉니다. 기존 방식으로는 냉각 채널을 배치할 수 없었던 푸셔 핀이나 복잡한 코어 주변부에도 최적의 냉각 라인을 설계할 수 있습니다. 이를 통해 고질적인 핫스팟 문제를 근본적으로 해결하고 수축 및 변형과 같은 결함을 최소화하는 혁신적인 금형 설계가 가능해집니다.
Paper Details
An experimental investigation of the cooling and heating performance of a gravity die casting mold with conformal cooling channels
1. Overview:
- Title: An experimental investigation of the cooling and heating performance of a gravity die casting mold with conformal cooling channels
- Author: Karani Kurtulus, Ali Bolatturk, Ahmet Coskun, Barış Gürel
- Year of publication: 2021
- Journal/academic society of publication: Applied Thermal Engineering
- Keywords: Gravity die casting, Conformal cooling, Computational fluid dynamics, Additive manufacturing
2. Abstract:
In the gravity die casting process, cooling directly affects the unit cost and microstructure quality of casting products. In the conventional manufacturing methods, cooling channels in gravity casting molds are usually produced linearly in circular profiles. When cooling is not conformal, molding defects such as hot spots and distortions form in the products. This study investigated the effects of cooling channels on the casting steps and final properties of the products in standard and conformal cooling gravity die casting molds. Numerical analysis results were compared with the experimental data and then were verified. The pressure losses in cooling channels, the times for molds to reach the required temperature and the cycle times were all measured. The pressure losses in standard and conformal cooling channels were measured at 5250 Pa and 12100 Pa, respectively. In addition, a more homogeneous mold surface temperature distribution was achieved in the conformal cooling mold, as well as a 28% shorter cycle time. The average particle size of the parts cast with conformal molds was 13.5% smaller than those cast with standard molds. Finally, the mechanical properties of the parts cast with conformal cooling channel molds were found to be better than those cast with standard channel molds.
3. Introduction:
Today, gravity die casting is used for those parts with complex shapes and narrow dimensional tolerances manufactured in high volumes. The heat accumulated in the metal mold during casting is eliminated through cooling channels. Achievement of cooling rapidly and uniformly through the cooling channels is desirable. Because metal mold cooling directly affects the unit cost and microstructure quality of casting products manufactured in permanent molds. The cooling channels used in standard permanent molds are usually produced linearly in circular profiles using the conventional manufacturing methods. They cannot pass through some regions in the molds, such as pusher pin holes and runners. To determine the locations of the pusher pin holes in the mold, casting simulation software was used [1]. Cooling channels can be generated up to 5 mm from the mold cavity. Therefore, the cooling process is nonhomogeneous and insufficient in the molds produced using the conventional manufacturing methods. Significant problems are observed in molded products, such as increased production time which leads to increased product cost, casting defects and shrinkage [2]. To eliminate these problems, metal mold cooling channels should be produced in conformal cooling channel geometries. It is possible to manufacture metal molds with conformal cooling channel thanks to the additive manufacturing process, which has made considerable progress in recent years [3–5]. The disadvantages caused by pusher holes and shape factors can be eliminated using this method [6]. Moreover, channel design is possible up to 2 mm from the casting cavity.
4. Summary of the study:
Background of the research topic:
전통적인 직선형 냉각 채널은 금형 내 불균일한 냉각을 유발하여 핫스팟, 변형, 생산 시간 증가 등의 문제를 야기합니다.
Status of previous research:
플라스틱 사출 성형 분야에서는 컨포멀 쿨링에 대한 연구가 다수 존재하지만, 알루미늄 주조를 위한 그래비티 다이캐스팅 금형에 적층 제조를 적용하여 설계 및 생산한 연구는 드뭅니다.
Purpose of the study:
본 연구는 표준 냉각 채널과 컨포멀 냉각 채널을 가진 그래비티 다이캐스팅 금형이 주조 공정 단계와 최종 제품 특성에 미치는 영향을 실험적으로 규명하는 것을 목표로 합니다.
Core study:
표준 금형(GGG-50, 기계 가공)과 컨포멀 금형(Inconel-625, DMLS)을 제작하여 알루미늄(Al-6061) 포펫 밸브를 주조했습니다. 수치 해석(CFD)과 물리적 실험을 통해 금형 가열 성능, 압력 손실, 사이클 타임, 응고 거동, 최종 제품의 미세조직을 비교 분석했습니다.
5. Research Methodology
Research Design:
두 가지 금형(표준, 컨포멀)을 설계 및 제작하고, 동일한 조건에서 주조 실험을 수행하여 성능을 비교하는 실험적 연구 설계를 채택했습니다. 수치 해석 결과를 실험 데이터와 비교하여 검증했습니다.
Data Collection and Analysis Methods:
- 수치 해석: ANSYS-Fluent를 사용하여 금형 내 온도, 압력, 속도를 계산했습니다.
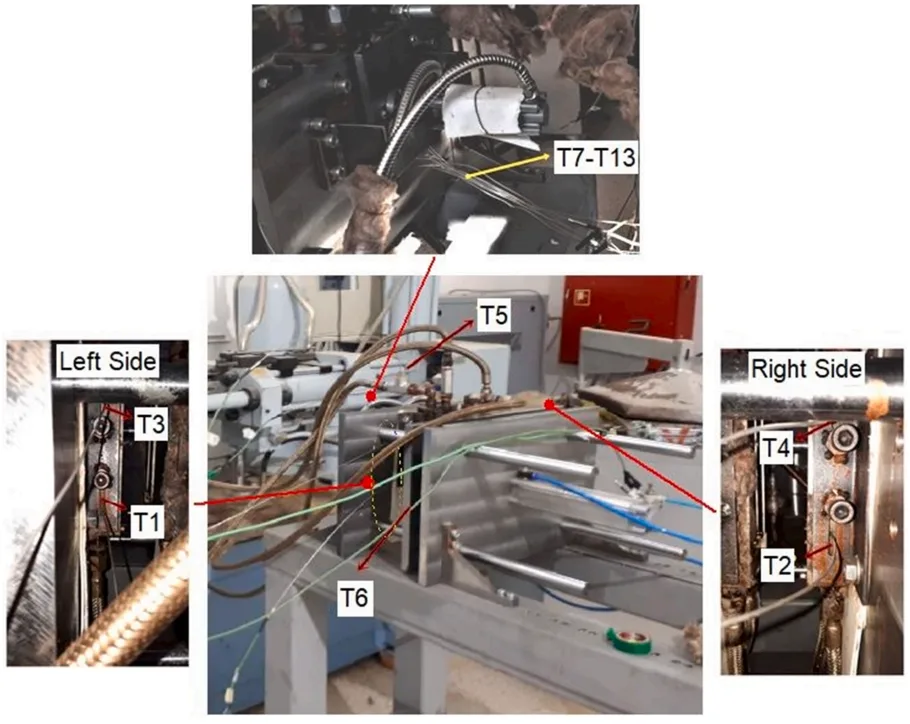
- 실험 데이터 수집: 압력 트랜스미터로 압력 손실을 측정하고, 13개의 K-타입 열전대를 금형과 주조부에 설치하여 온도 변화를 실시간으로 기록했습니다 (National Instrument-SCXI-1000 데이터 로거 사용).
- 미세조직 분석: 주조된 부품의 샘플을 채취하여 광학 현미경(Olympus BX51)으로 관찰하고, ImageJ 소프트웨어를 사용하여 입자 크기와 결정립계 면적을 분석했습니다.
Research Topics and Scope:
연구는 Al-6061 합금을 사용한 포펫 밸브의 그래비티 다이캐스팅에 국한됩니다. 표준 냉각 채널과 컨포멀 냉각 채널의 (1) 금형 가열 성능, (2) 압력 손실, (3) 응고 중 온도 분포 및 열 유속, (4) 사이클 타임, (5) 최종 제품의 미세조직에 미치는 영향을 비교하는 데 중점을 둡니다.
6. Key Results:
Key Results:
- 컨포멀 금형은 표준 금형 대비 28% 짧은 사이클 타임을 달성했습니다.
- 컨포멀 금형은 훨씬 더 균일한 금형 표면 온도 분포를 보였습니다.
- 컨포멀 금형으로 주조된 부품의 평균 입자 크기는 13.5% 더 작았으며, 이는 더 미세하고 균일한 미세조직을 의미합니다.
- 컨포멀 채널의 압력 손실(12100 Pa)은 표준 채널(5250 Pa)보다 높았지만, 실용적인 설계 기준을 충족했습니다.
- 컨포멀 금형은 열전도율이 낮은 소재(Inconel-625)로 제작되었음에도 불구하고, 우수한 설계 덕분에 더 빠르고 효율적인 냉각 성능을 보였습니다.
Figure Name List:
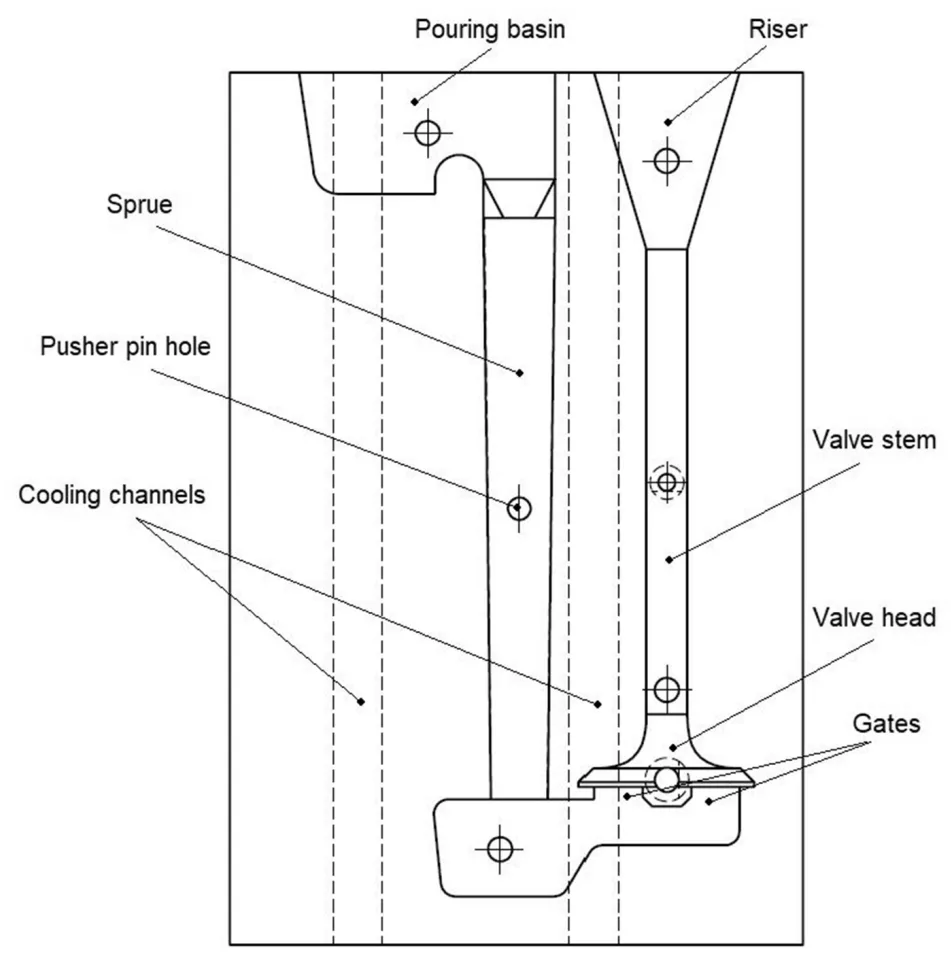
- Figure 1. Solid model and technical drawing of poppet valve.
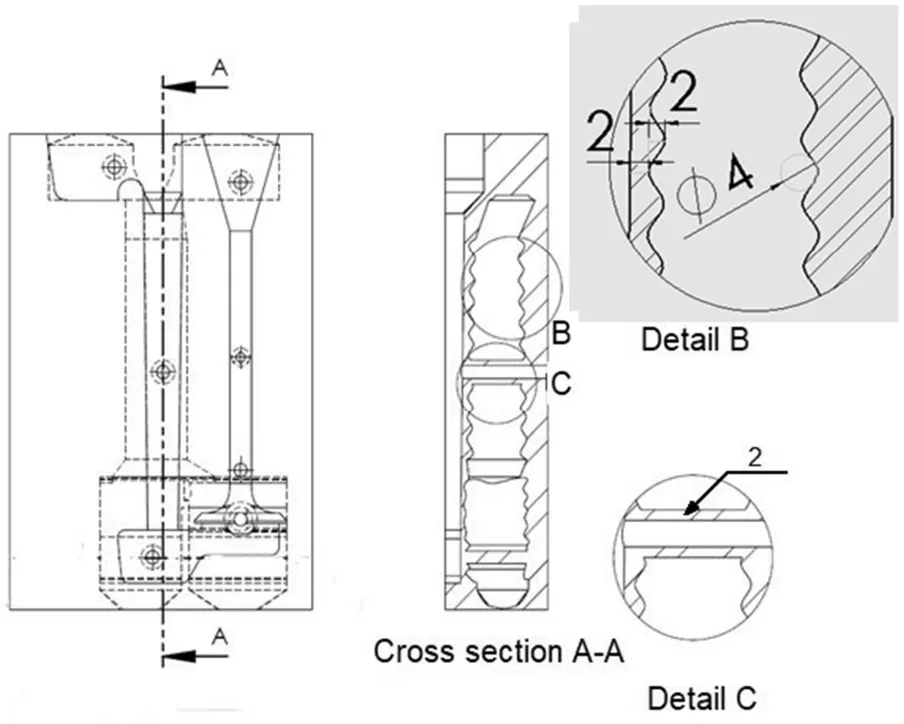
- Figure 2. Details of mold with standard cooling channel.
- Figure 3. Solid models of mold designs: a) standard b) conformal cooling channel.
- Figure 4. Details of mold with conformal cooling channel.
- Figure 5. Mold preheating numerical analysis models: a) standard mold b) conformal mold.
- Figure 6. Mesh structures used in analysis: a) standard mold b) conformal mold.
- Figure 7. Boundary conditions.
- Figure 8. Quadratic polynomials obtained at varying temperatures against time in the mold regulator.
- Figure 9. Scheme for the experimental setup.
- Figure 10. Thermocouple locations in the metal mold.
- Figure 11. Thermocouple placement in the experimental setup.
- Figure 12. Sampling zones for metallographic examinations.
- Figure 13. Comparison of simulated and measured metal mold temperatures of the standard mold.
- Figure 14. Comparison of the simulated and measured metal mold temperatures of the conformal mold.
- Figure 15. Comparison of the measured standard and conformal metal mold temperatures.
- Figure 16. Comparison of mold heating performances of standard and conformal cooling channel molds.
- Figure 17. Comparison of simulated metal mold temperatures for Inconel-625 and GGG-50 CM mold materials.
- Figure 18. Comparison of simulated metal mold average temperatures for different mold material and cooling channel types.
- Figure 19. Variation of the heat flux at the valve head and stem against time, a. standard mold, b.conformal mold.
- Figure 20. Comparison of the measured metal mold temperature differences for standard and conformal molds.
- Figure 21. Comparison of valve head center temperatures in the standard and conformal molds.
- Figure 22. Comparison of the optical micrographs of the casting parts for different sampling zones (A, B and C).
- Figure 23. Comparison of the grain boundary areas for the standard and conformal molded samples from different zones.
- Figure 24. Comparison of the average grain size for the standard and conformal molded samples from different zones.
7. Conclusion:
본 연구는 표준 및 컨포멀 냉각 채널 금형을 사용하여 제작된 제품의 주조 단계와 최종 특성에 대한 냉각 채널의 영향을 조사했습니다. 컨포멀 냉각 채널 금형은 표준 금형보다 압력 손실은 높았지만, 열교환기 설계 기준을 초과하지 않았습니다. 컨포멀 금형은 더 균일한 온도 분포를 보여 열응력이 적었으며, 사이클 타임이 28% 단축되었습니다. 또한, 컨포멀 금형으로 주조된 제품은 평균 입자 크기가 13.5% 더 작고 미세조직이 균일하여 기계적 특성이 더 우수할 것으로 예측됩니다. 결론적으로, 적층 제조를 통한 컨포멀 쿨링 금형은 더 높은 냉각/가열 성능을 통해 고품질의 부품을 생산하고, 짧은 사이클 타임으로 부품 단가를 낮출 수 있는 잠재력을 가지고 있음을 입증했습니다.
8. References:
- [1] S. Aravind, P. Ragupathi, G. Vignesh, Numerical and experimental approach to eliminate defects in al alloy pump-crank case processed through gravity die casting route, Materials Today. Proceedings, 2020, 1772–1777. softhttps://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.07.365.
- [2] F.H. Hsu, K. Wang, C.T. Huang, R.Y. Chang, Investigation on conformal cooling system design in injection molding, Adv. Prod. Eng. Manage. 8 (2) (2013) 107–115, https://doi.org/10.14743/apem2013.2.158.
- [3] J.G. Kovacs, F. Szabo, N.K. Kovacs, A. Suplicz, B. Zink, T. Tabi, H. Hargitai, Thermal simulations and measurements for rapid tool inserts in injection molding applications, Appl. Therm. Eng. 85 (2015) 44–51, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.03.075.
- [4] R. Holker, E. Tekkaya, Advancements in the manufacturing of dies for hot aluminum extrusion with conformal cooling channels, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 83 (2016) 1209–1220, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7647-4.
- [5] B.B. Kanbur, S. Suping, F. Duan, Design and optimization of conformal cooling channels for injection molding: a review, Int. J. Adv. Manufact. Technol. 106 (7) (2020) 3253–3271, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04697-9.
- [6] C. Tan, D. Wang, W. Ma, Y. Chen, S. Chen, Y. Yang, K. Zhou, Design and additive manufacturing of novel conformal cooling molds, Mater. Des. 196 (2020) 109–147, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2020.109147.
… (and all other references as listed in the paper)
Expert Q&A: Your Top Questions Answered
Q1: 컨포멀 쿨링의 가장 큰 이점은 무엇이며, 구체적인 데이터는 무엇인가요?
A1: 가장 큰 이점은 28%의 사이클 타임 단축입니다. 실험 결과, 표준 금형의 사이클 타임은 82초였지만 컨포멀 금형은 59초로 단축되었습니다 (Figure 21). 이는 HPDC 공정에서 생산성 향상과 제조원가 절감에 직접적으로 기여합니다.
Q2: 컨포멀 금형은 다른 재료(Inconel-625)로 만들어졌는데, 이것이 성능에 어떤 영향을 미쳤나요?
A2: Inconel-625는 표준 금형 재료인 GGG-50보다 열전도율이 낮습니다 (Table 5). 하지만 채널이 주조부 형상에 더 가깝고 표면적이 넓은 컨포멀 설계 덕분에 더 빠르고 균일한 냉각이 가능했습니다. 이는 재료의 한계를 혁신적인 설계로 극복할 수 있음을 보여주는 중요한 결과입니다 (Conclusion).
Q3: 압력 손실이 두 배 이상 높은데, 문제가 되지 않나요?
A3: 컨포멀 채널의 압력 손실은 12100 Pa로 표준 채널(5250 Pa)보다 높았지만, 논문에서는 이것이 균일한 냉각을 방해하지 않는 실제 공정에서 허용 가능한 수준이라고 명확히 밝혔습니다 (Section 3.1). 냉각 효율 향상이라는 더 큰 이점을 고려할 때 충분히 감수할 수 있는 수준입니다.
Q4: 이 기술(적층 제조)을 사용하면 금형 설계에서 어떤 새로운 가능성이 열리나요?
A4: 전통적인 가공 방식으로는 불가능했던 푸셔 핀 홀이나 복잡한 코어 주변과 같은 영역에도 냉각 채널을 자유롭게 배치할 수 있습니다 (Section 2.1.2). 이를 통해 핫스팟을 근본적으로 제거하고 수축 및 변형과 같은 고질적인 주조 결함을 획기적으로 줄일 수 있는 새로운 설계의 문이 열립니다.
Q5: 최종 제품의 품질에는 어떤 실질적인 변화가 있었나요?
A5: 컨포멀 금형으로 주조된 부품은 평균 입자 크기가 13.5% 더 작았고, 미세조직이 훨씬 더 균일했습니다 (Figure 24). 이는 인장 강도, 항복 강도, 피로 수명 등 기계적 특성 향상으로 이어져, 더욱 까다로운 성능을 요구하는 고부가가치 부품 생산에 유리합니다 (Conclusion).
Conclusion & Next Steps
이 연구는 컨포멀 쿨링 채널이 HPDC 공정의 핵심 과제인 생산성과 품질을 동시에 향상시킬 수 있는 강력하고 데이터 기반의 해결책임을 명확히 보여줍니다. 불균일한 냉각으로 인한 결함을 줄이고, 생산 사이클을 단축하며, 최종 부품의 기계적 성능을 극대화할 수 있는 검증된 로드맵을 제공합니다.
CASTMAN은 최신 산업 연구 결과를 적용하여 고객의 가장 어려운 다이캐스팅 문제를 해결하는 데 전념하고 있습니다. 본문에 논의된 이슈들이 귀사의 운영 목표와 관련이 있다면, 저희 엔지니어링 팀에 연락하여 이러한 첨단 원리를 귀사의 부품에 어떻게 적용할 수 있을지 논의해 보시기 바랍니다.
Copyright
- This material is a paper by "Karani Kurtulus, Ali Bolatturk, Ahmet Coskun, Barış Gürel". Based on "An experimental investigation of the cooling and heating performance of a gravity die casting mold with conformal cooling channels".
- Source of the paper: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2021.117105
This material is for informational purposes only. Unauthorized commercial use is prohibited. Copyright © 2025 CASTMAN. All rights reserved.