1. 개요:
- 제목: Multi-component topology optimization for die casting (MTO-D) (다이캐스팅을 위한 다성분 위상 최적화 (MTO-D))
- 저자: Hao Zhou, Junyuan Zhang, Yuqing Zhou, Kazuhiro Saitou
- 발행 연도: 2019년
- 출판 저널/학회: Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization (구조 및 다분야 최적화)
- 키워드: Multi-component topology optimization (다성분 위상 최적화), Manufacturability (제조 가능성), Die cast components (다이캐스팅 부품), Parting lines (분할선)
2. 연구 배경:
- 연구 주제의 사회적/학문적 맥락:
- 위상 최적화는 구조 최적화를 위한 효과적인 계산 설계 도구로 널리 연구되고 산업 응용 분야에 채택되었습니다.
- 위상 최적화는 혁신적인 설계 솔루션을 생성하여 성능 향상과 비용 절감을 가능하게 합니다.
- 기존 위상 최적화는 주로 단일 부품 구조 설계에 사용되지만, 대부분의 엔지니어링 구조물은 단순한 형상의 다중 부품 조립체로 구성됩니다.
- 복잡한 형상은 단일 부품으로 경제적으로 제조하기 어렵거나 불가능할 수 있습니다.
- 따라서 복잡한 형상을 더 단순한 부품 형상으로 분할하는 것은 구조적 성능과 제조 비용 개선 사이의 절충점을 신중하게 고려하여 결정해야 합니다.
- 기존 연구의 한계:
- 기존 다성분 조립체 위상 최적화 연구는 부품 경계를 미리 정의된 입력 또는 부품 임베딩의 부산물로 취급했습니다.
- 이러한 접근 방식은 구조적 성능과 제조 비용의 균형을 고려한 결과로서의 부품 경계를 최적화하는 데는 미흡했습니다.
- 기존 연구는 주로 비기울기 최적화 알고리즘을 사용하여 계산 효율성이 낮았습니다.
- 제조 공정에서 부과하는 기하학적 제약 조건을 무시하여 제조가 불가능하거나 매우 어려운 형상의 최적화 설계를 생성하는 경우가 많았습니다.
- 최적화 후 수동 또는 컴퓨터 보조 편집을 통해 제조 가능성을 개선하는 방식은 차선책이 될 수 있습니다.
- 기존 연구는 주로 단일 부품 위상 최적화에 기반하여 다중 부품 조립체에 대한 적용 가능성이 제한적이었습니다.
- 연구의 필요성:
- 제조 가능성을 고려한 다성분 구조물의 통합 설계가 필요합니다.
- 다이캐스팅 공정의 제조 제약 조건을 통합한 다성분 위상 최적화 방법 개발이 필요합니다.
- 계산 효율성이 높은 기울기 기반 최적화 프레임워크 개발이 필요합니다.
- 다이캐스팅 부품의 언더컷 및 내부 공동 문제를 해결하는 최적화 방법 개발이 필요합니다.
3. 연구 목적 및 연구 질문:
- 연구 목적:
- 다이캐스팅 공정으로 제조되는 구조 조립체를 위한 다성분 위상 최적화 방법 (MTO-D)을 제시합니다.
- 각 부품이 금형 인발 방향으로 완전히 밀폐된 공동 및 언더컷이 없도록 보장합니다.
- 각 부품의 분할선 위치 및 방향을 지정하는 새로운 설계 변수를 통합합니다.
- 언더컷 및 완전히 밀폐된 공동의 존재를 평가하는 방법을 제시합니다.
- 제안된 방법의 타당성을 검증하기 위해 수치 예제를 제시합니다.
- 주요 연구 질문:
- 다이캐스팅 공정의 제조 제약 조건을 다성분 위상 최적화에 어떻게 통합할 수 있는가?
- 분할선을 설계 변수로 사용하여 다이캐스팅 부품의 형상을 어떻게 최적화할 수 있는가?
- 언더컷 및 내부 공동을 효과적으로 감지하고 제거하는 방법은 무엇인가?
- 제안된 MTO-D 방법은 다이캐스팅 부품의 제조 가능성을 향상시키는가?
- 연구 가설:
- 분할선을 설계 변수로 사용하고 언더컷 및 내부 공동 제약 조건을 통합한 MTO-D 방법은 다이캐스팅 부품의 제조 가능성을 향상시킬 수 있을 것이다.
- 제안된 방법으로 최적화된 설계는 금형 인발 방향으로 언더컷이 없고 완전히 밀폐된 공동이 없을 것이다.
4. 연구 방법론:
- 연구 설계:
- 기울기 기반 다성분 위상 최적화 (MTO) 프레임워크를 기반으로 MTO-D 방법을 개발했습니다.
- 기존 MTO-S (판금 스탬핑용 다성분 위상 최적화) 연구를 확장하여 다이캐스팅 공정에 특화된 제조 제약 조건을 통합했습니다.
- 새로운 재료 보간법을 제안하여 비분수적 부품 멤버십으로의 수렴을 향상시켰습니다.
- 벡터 기반 밀도 기울기 방법을 다성분 프레임워크로 확장하여 몰드 가능성 평가 방법을 개발했습니다.
- 분할선의 위치 및 방향을 나타내는 새로운 설계 변수를 도입했습니다.
- 등매개변수 투영을 사용하여 분할선 방향의 주기적 특성으로 인한 수치적 불안정성을 방지했습니다.
- 데이터 수집 방법:
- 수치 시뮬레이션을 통해 제안된 방법의 타당성을 검증했습니다.
- 캔틸레버 빔, 브리지 구조, MBB 빔 등 다양한 경계 조건에 대한 수치 예제를 제시했습니다.
- 다양한 격자 크기, MABB 제한 값, 부품 수에 대한 매개변수 연구를 수행했습니다.
- 분석 방법:
- 유한 요소법 (FEM)을 사용하여 구조 해석을 수행했습니다.
- 기울기 기반 최적화 알고리즘을 사용하여 최적 설계를 탐색했습니다.
- 벡터 방법을 사용하여 언더컷 및 내부 공동을 감지했습니다.
- 최소 면적 경계 상자 (MABB)를 사용하여 제조 비용 제약 조건을 모델링했습니다.
- 시그모이드 함수를 사용하여 조건부 변경 및 불연속성을 완화했습니다.
- MATLAB fmincon 함수를 사용하여 최적화 문제를 해결했습니다.
- 연구 대상 및 범위:
- 2차원 다이캐스팅 부품 설계를 연구 대상으로 했습니다.
- 선형 탄성 재료를 사용한 구조물에 대한 컴플라이언스 최소화 문제를 다루었습니다.
- 최대 3개의 부품으로 구성된 조립체를 최적화했습니다.
5. 주요 연구 결과:
- 주요 연구 결과:
- 제안된 MTO-D 방법은 다이캐스팅 부품의 제조 가능성을 향상시키는 것으로 나타났습니다.
- 최적화된 설계는 금형 인발 방향으로 언더컷이 없고 완전히 밀폐된 공동이 없는 것으로 확인되었습니다.
- MTO-D 방법은 MTO-S (판금 스탬핑용 다성분 위상 최적화)에 비해 몰드 가능성이 크게 향상되었습니다.
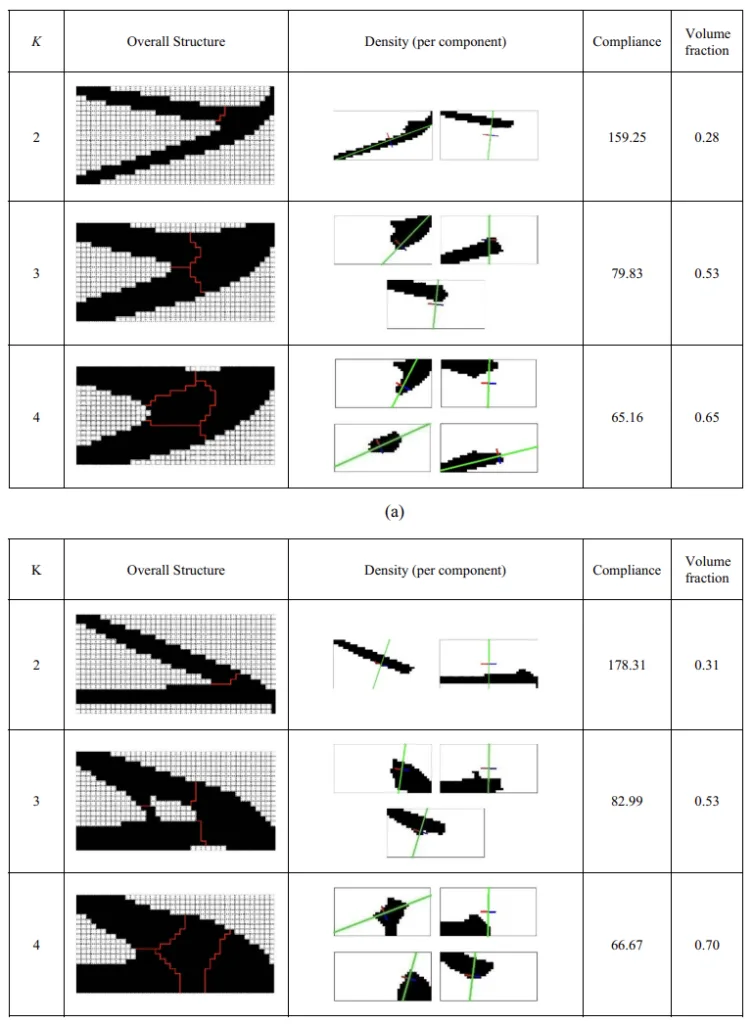
- 최대 MABB 면적 A* 및 최대 허용 부품 수 K 설정은 최적화된 구조의 성능에 상당한 영향을 미치는 것으로 나타났습니다.
- 설계자는 구조적 성능과 제조 비용 간의 절충점을 고려하여 A* 및 K 값을 적절하게 설정해야 합니다.
- 초기 분할선 방향은 전체 위상 구조 및 구조 분해에는 큰 영향을 미치지 않지만 분할선 방향에는 영향을 미치는 것으로 나타났습니다.
- 초기 분할선 방향을 ±45°로 설정하는 것이 편향되지 않은 결과를 얻는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다.
- 격자 크기 변화에 대해 유사한 최적화 결과가 얻어져 제안된 방법의 격자 독립성이 입증되었습니다.
- 통계적/질적 분석 결과:
- 수치 예제를 통해 제안된 방법의 타당성을 질적으로 검증했습니다.
- 다양한 매개변수 연구를 통해 MTO-D 방법의 거동을 분석했습니다.
- 반복 이력 곡선을 통해 최적화 과정의 수렴성을 확인했습니다.
- 데이터 해석:
- MTO-D 방법은 다이캐스팅 부품 설계에 효과적인 도구임을 입증했습니다.
- 제안된 방법은 제조 가능성을 고려한 다성분 구조물 설계에 기여할 수 있습니다.
- MABB 면적 제약 조건은 기존 단일 부품 위상 최적화의 체적 분율 제약 조건과 유사한 역할을 수행하는 것으로 나타났습니다.
- 부품 수 K 증가는 구조물의 체적 분율 증가 및 컴플라이언스 감소로 이어지는 것으로 나타났습니다.
- 그림 목록:
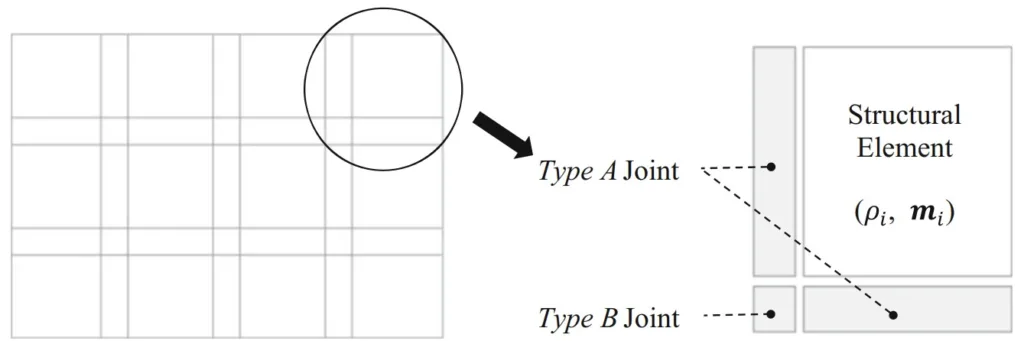
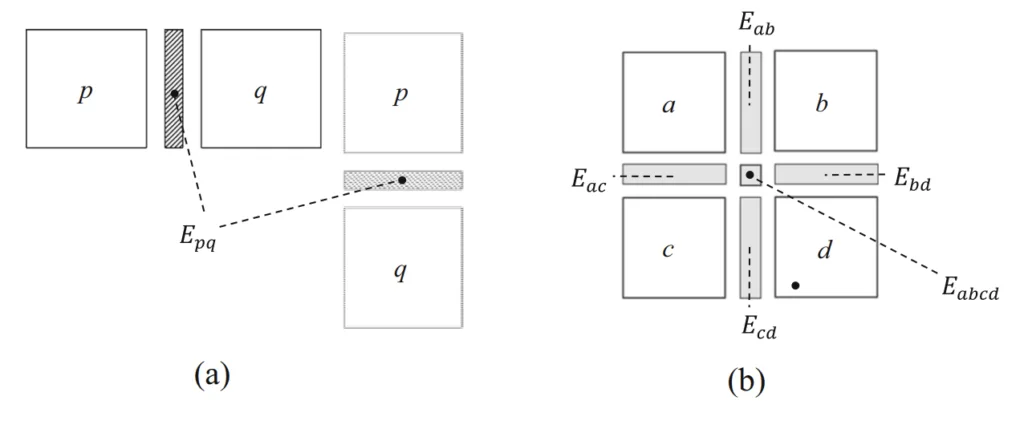
- Fig. 1 Domain discretization and two different joint elements (영역 이산화 및 두 가지 다른 조인트 요소)
- Fig. 2 Stiffness models of joint elements (조인트 요소의 강성 모델)
- Fig. 3 Geometry requirements for cast components (다이캐스팅 부품의 형상 요구 사항)
- Fig. 4 Cartesian representation of orientation in 2D (2D 방향의 데카르트 좌표 표현)
- Fig. 5 Representations of parting line and the drawing direction (분할선 및 인발 방향의 표현)
- Fig. 6 Sigmoid function SL(x) for parting line (분할선에 대한 시그모이드 함수 SL(x))
- Fig. 7 detection of undercuts and internal cavities (언더컷 및 내부 공동 감지)
- Fig. 8 Sigmoid function Su(x) for undercut features (언더컷 특징에 대한 시그모이드 함수 Su(x))
- Fig. 9 Approximation of density gradient (밀도 기울기 근사)
- Fig. 10 Design domain and boundary condition for three test problem (세 가지 테스트 문제에 대한 설계 영역 및 경계 조건)
- Fig. 11 Optimized results for different boundary conditions (다양한 경계 조건에 대한 최적화 결과)
- Fig. 12 Comparison between the results (post-processed) with different grid sizes (다양한 격자 크기에 따른 결과 비교 (후처리))
- Fig. 13 Comparison between the results (post-processed) by MTO-D (left) and MTO-S (right) (MTO-D (좌) 및 MTO-S (우)의 결과 비교 (후처리))
- Fig. 14 Iteration history curve for MBB beam example (MBB 빔 예제에 대한 반복 이력 곡선)
- Fig. 15 Comparison between the results (post-processed) with different initial parting line direction for MBB beam example (MBB 빔 예제에 대한 다양한 초기 분할선 방향에 따른 결과 비교 (후처리))
- Fig. 16 Topology optimization results with different MABB limit value (다양한 MABB 제한 값에 따른 위상 최적화 결과)
- Fig. 17 Topology optimization results with different number of components (다양한 부품 수에 따른 위상 최적화 결과)
6. 결론 및 논의:
- 주요 결과 요약:
- 다이캐스팅 공정으로 제조되는 구조 조립체를 위한 새로운 다성분 위상 최적화 방법 (MTO-D)을 개발하고 제시했습니다.
- 제안된 방법은 분할선을 설계 변수로 사용하고 언더컷 및 내부 공동 제약 조건을 통합하여 다이캐스팅 부품의 제조 가능성을 향상시켰습니다.
- 수치 예제를 통해 제안된 방법의 타당성을 검증하고 다양한 매개변수 연구를 통해 방법의 거동을 분석했습니다.
- 연구의 학문적 의의:
- 다이캐스팅 공정의 제조 제약 조건을 고려한 다성분 위상 최적화 분야에 기여했습니다.
- 분할선을 설계 변수로 사용하는 새로운 최적화 프레임워크를 제시했습니다.
- 언더컷 및 내부 공동 감지를 위한 벡터 기반 방법을 다성분 프레임워크로 확장했습니다.
- 등매개변수 투영을 사용하여 분할선 방향 표현의 수치적 안정성을 개선했습니다.
- 연구의 실제적 의의:
- 다이캐스팅 부품 설계자가 제조 가능성을 고려하여 최적의 다성분 구조물을 설계하는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다.
- 자동차, 항공우주 등 다양한 산업 분야에서 다이캐스팅 부품 설계 및 제조 비용 절감에 기여할 수 있습니다.
- 제안된 방법은 실제 산업 응용 분야에 적용될 수 있는 가능성을 보여줍니다.
- 연구의 한계:
- 2차원 문제에 국한되어 3차원 문제에 대한 적용 가능성은 추가 연구가 필요합니다.
- 제조 비용 모델이 단순화되어 실제 제조 비용을 정확하게 반영하지 못할 수 있습니다.
- 언더컷 감지 방법이 여전히 일부 한계를 가지고 있어 개선의 여지가 있습니다.
- 조인트의 최대 응력, 부품 간 계면 강도, 용접 비용 모델 등 추가적인 제약 조건 및 비용 모델을 고려하지 않았습니다.
- 비직선 분할선 및 완화된 언더컷 제약 조건에 대한 연구가 필요합니다.
7. 향후 후속 연구:
- 후속 연구 방향:
- 3차원 다이캐스팅 부품 설계를 위한 MTO-D 방법 확장
- 보다 정확한 제조 비용 모델 개발 및 통합
- 언더컷 감지 방법 개선 및 정확도 향상
- 조인트 최대 응력, 부품 간 계면 강도, 용접 비용 모델 등 추가적인 제약 조건 및 비용 모델 통합
- 비직선 분할선 및 완화된 언더컷 제약 조건 허용
- 측면 핀 및 코어 리프터와 같은 추가 금형 메커니즘에 대한 비용 모델 기반 언더컷 제약 조건 개발
- 밀도 기울기 계산의 일반화된 공식 개발
- 수치적으로 효율적이고 강력한 3D 구현 개발
- 추가 탐구가 필요한 영역:
- 3D 최소 체적 경계 상자 모델링 및 3D 조인트 강성 모델 개발
- 다양한 산업 분야의 실제 다이캐스팅 부품 설계 문제에 MTO-D 방법 적용
- MTO-D 방법의 계산 효율성 및 최적화 성능 개선
8. 참고 문헌:
- Altair Engineering, Inc (2017) Altair HyperWorks 2017.1 user's manual, www.altairhyperworks.com/product/OptiStruct
- Bendsøe MP, Kikuchi N (1988) Generating optimal topologies in structural design using a homogenization method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 71(2):197-224
- Boothroyd G, Dewhurst P, Knight WA (2010) Product design for manufacture and assembly. CRC Press, Boca Raton
- Bruyneel M, Fleury C (2002) Composite structures optimization using sequential convex programming. Adv Eng Softw 33(7-10):697-711
- Chen J, Shapiro V, Suresh K, Tsukanov I (2007) Shape optimization with topological changes and parametric control. Int J Numer Methods Eng 71(3):313-346
- Chickermane H, Gea HC (1997) Design of multi-component structural systems for optimal layout topology and joint locations. Eng Comput 13(4):235-243
- Fu MW, Nee AY, Fuh JY (2002) The application of surface visibility and moldability to parting line generation. Comput Aided Des 34(6): 469-480
- Gaynor AT, Guest JK (2016) Topology optimization considering overhang constraints: eliminating sacrificial support material in additive manufacturing through design. Struct Multidiscip Optim 54(5): 1157-1172
- Gersborg AR, Andreasen CS (2011) An explicit parameterization for casting constraints in gradient driven topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 44(6):875-881
- Guest JK, Asadpoure A, Ha SH (2011) Eliminating beta-continuation from Heaviside projection and density filter algorithms. Struct Multidiscip Optim 44(4):443-453
- Guirguis D, Hamza K, Aly M, Hegazi H, Saitou K (2015) Multi-objective topology optimization of multi-component continuum structures via a Kriging-interpolated level set approach. Struct Multidiscip Optim 51(3):733-748
- Guo X, Zhou J, Zhang W, Du Z, Liu C, Liu Y (2017) Self-supporting structure design in additive manufacturing through explicit topology optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 323:27-63
- Harzheim L, Graf G (2006) A review of optimization of cast parts using topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 31(5):388-399
- Hicks J (1999) Welded joint design, 3rd edn. Industrial Press, New York
- Hughes TJ (2000) The finite element method: linear static and dynamic finite element analysis. Dover Publications, MI
- Jiang T, Chirehdast M (1997) A systems approach to structural topology optimization: designing optimal connections. J Mech Des 119(1): 40-47
- Johanson R, Kikuchi N, Papalambros P (1994) Simultaneous topology and material microstructure design. Adv Struct Optim:143-149
- Kang Z, Wang Y, Wang Y (2016) Structural topology optimization with minimum distance control of multiphase embedded components by level set method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 306:299-318
- Langelaar M (2017) An additive manufacturing filter for topology optimization of print-ready designs. Struct Multidiscip Optim 55(3): 871-883
- Li Q, Chen W, Liu S, Fan H (2018) Topology optimization design of cast parts based on virtual temperature method. Comput Aided Des 94: 28-40
- Li Q, Steven GP, Xie YM (2001a) Evolutionary structural optimization for connection topology design of multi-component systems. Eng Comput 18(3/4):460-479
- Li Y, Xin X, Kikuchi N, Saitou K (2001b) Optimal shape and location of piezoelectric materials for topology optimization of flextensional actuators. In Proceedings of the 3rd annual conference on genetic and evolutionary computation (pp. 1085-1090). Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc.
- Lim JY, Yoon MJ, Kim SY, Shin HS, Kim TG (2015) Mechanical properties of CO2/MIG welded structural rolled steel and stainless steel. J Mech Sci Technol 29(1):103-108
- Liu J, Gaynor AT, Chen S, Kang Z, Suresh K, Takezawa A, Cheng L. (2018) Current and future trends in topology optimization for additive manufacturing. Struct Multidiscip Optim 57(6):2457-2483.
- Liu P, Kang Z (2018) Integrated topology optimization of multi-component structures considering connecting interface behavior. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 341:851-887
- Liu S, Li Q, Chen W, Tong L, Cheng G (2015) An identification method for enclosed voids restriction in manufacturability design for additive manufacturing structures. Front Mech Eng 10(2):126-137
- Lyu N, Saitou K (2005) Topology optimization of multicomponent beam structure via decomposition-based assembly synthesis. J Mech Des 127(2):170-183
- MathWorks, Inc (2016) MATLAB Primer, R2016a edition. www. mathworks.com
- Mirzendehdel AM, Suresh K (2016) Support structure constrained topology optimization for additive manufacturing. Comput Aided Des 81:1-13
- Nomura T, Dede EM, Lee J, Yamasaki S, Matsumori T, Kawamoto A, Kikuchi N (2015) General topology optimization method with continuous and discrete orientation design using isoparametric projection. Int J Numer Methods Eng 101(8):571-605
- Qian X (2017) Undercut and overhang angle control in topology optimization: a density gradient based integral approach. Int J Numer Methods Eng 111(3):247-272
- Qian Z, Ananthasuresh GK (2004) Optimal embedding of rigid objects in the topology design of structures. Mech Based Des Struct Mach 32(2):165-193
- Ravi B, Srinivasan MN (1990) Decision criteria for computer-aided parting surface design. Comput Aided Des 22(1):11-18
- Rozvany GI, Zhou M, Birker T (1992) Generalized shape optimization without homogenization. Struct Optim 4(3–4):250-252
- Sato Y, Yamada T, Izui K, Nishiwaki S (2017) Manufacturability evaluation for molded components using fictitious physical models, and its application in topology optimization. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 92(1-4):1391-1409
- Sigmund O (2001) A 99 line topology optimization code written in Matlab. Struct Multidiscip Optim 21(2):120-127
- Stegmann J, Lund E (2005) Discrete material optimization of general composite shell structures. Int J Numer Methods Eng 62(14): 2009-2027
- Vanderplaats Research and Development, Inc (2017) GENESIS 16.0 User's Manual, www.vrand.com/products/genesis/
- Vatanabe SL, Lippi TN, de Lima CR, Paulino GH, Silva EC (2016) Topology optimization with manufacturing constraints: a unified projection-based approach. Adv Eng Softw 100:97-112
- Wang Y, Gao J, Kang Z (2018) Level set-based topology optimization with overhang constraint: towards support-free additive manufacturing. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 339:591-614
- Wang Y, Kang Z (2017) Structural shape and topology optimization of cast parts using level set method. Int J Numer Methods Eng 111(13): 1252-1273
- Wang X, Kang Z, Wang Y (2011) Topology design of slender piezoelectric actuators with repetitive component patterns. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 22(18):2161-2172
- Wang MY, Wang X, Guo D (2003) A level set method for structural topology optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 192(1- 2):227-246
- Weinstein M, Manoochehri S (1997) Optimum parting line design of molded and cast parts for manufacturability. J Manuf Syst 16(1):1
- Xia Q, Shi T, Wang MY, Liu S (2010) A level set based method for the optimization of cast part. Struct Multidiscip Optim 41(5):735–747
- Yildiz AR, Saitou K (2011) Topology synthesis of multicomponent structural assemblies in continuum domains. J Mech Des 133(1):011008
- Zhang W, Zhou L (2018) Topology optimization of self-supporting structures with polygon features for additive manufacturing. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 334:56-78
- Zhou M, Fleury R, Shyy YK, Thomas H, and Brennan J (2002) Progress in topology optimization with manufacturing constraints. In 9th AIAA/ISSMO Symposium on Multidisciplinary Analysis and Optimization (p. 5614)
- Zhou Y, Saitou K (2017) Topology optimization of composite structures with data-driven resin filling time manufacturing constraint. Struct Multidiscip Optim 55(6):2073-2086
- Zhou Y, Saitou K (2018) Gradient-based multi-component topology optimization for stamped sheet metal assemblies (MTO-S). Struct Multidiscip Optim 58(1):83-94
- Zhou Y, Nomura T, Saitou K (2018) Multi-component topology and material orientation design of composite structures (MTO-C). Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 342:438-457
- Zhou Y, Nomura T, Saitou K (2019) Multicomponent topology optimization for additive manufacturing with build volume and cavity free constraints. J Comput Inf Sci Eng 19(2):021011
- Zhu JH, Gu XJ, Zhang WH, Beckers P (2013) Structural design of aircraft skin stretch-forming die using topology optimization. J Comput Appl Math 246:278-288
- Zhu J, Zhang W, Beckers P, Chen Y, Guo Z (2008) Simultaneous design of components layout and supporting structures using coupled shape and topology optimization technique. Struct Multidiscip Optim 36(1):29-41
- Zhu JH, Zhang WH, Xia L (2016) Topology optimization in aircraft and aerospace structures design. Archiv Comput Methods Eng 23(4): 595-622
9. 저작권:
- 이 자료는 [Hao Zhou, Junyuan Zhang, Yuqing Zhou, Kazuhiro Saitou]의 논문: [Multi-component topology optimization for die casting (MTO-D)]을 기반으로 작성되었습니다.
- 논문 출처: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-019-02317-4
본 자료는 위 논문을 기반으로 요약되었으며, 상업적 목적으로 무단 사용하는 것을 금지합니다.
Copyright © 2025 CASTMAN. All rights reserved.