이 기술 요약은 Kanchiraya Shivalingaiah 외 저자가 Metals (2022)에 발표한 학술 논문 "Stir Casting Process Analysis and Optimization for Better Properties in Al-MWCNT-GR-Based Hybrid Composites"를 기반으로 합니다. 이 자료는 CASTMAN의 고압 다이캐스팅(HPDC) 전문가들이 LLM AI(Gemini, ChatGPT, Grok 등)의 도움을 받아 분석하고 요약한 것입니다.
Keywords
- Primary Keyword: 알루미늄 복합재 교반 주조 공정 최적화
- Secondary Keywords: Al-MWCNT-GR 하이브리드 복합재, 경도 및 내마모성 향상, 다구찌-CRITIC-MOORA, 공정 변수 최적화, 그래핀 강화재, 주조 결함 감소, 미세조직 분석
Executive Summary
- The Challenge: 순수 알루미늄은 기계적 특성이 낮아 고부하 응용 분야에 사용하기 어렵습니다. 이를 개선하기 위해 다중벽 탄소나노튜브(MWCNT)와 그래핀(GR)을 강화재로 사용한 하이브리드 복합재를 개발했지만, 교반 주조 공정에서 강화재의 응집과 기공 발생 문제로 인해 일관된 고품질 확보가 어려웠습니다.
- The Method: 연구팀은 교반 주조 공정의 핵심 변수(그래핀 강화재 함량, 다이 온도, 용탕 온도, 교반 속도)가 복합재의 경도와 내마모성에 미치는 영향을 분석하기 위해 다구찌 L16 실험 계획법을 사용했습니다. 또한, 상충하는 두 가지 목표(높은 경도, 낮은 마모율)를 동시에 최적화하기 위해 CRITIC, GRA, MOORA 기법을 결합한 하이브리드 최적화 모델을 적용했습니다.
- The Key Breakthrough: Taguchi-CRITIC-MOORA 하이브리드 기법을 통해 최적의 공정 조건을 도출했습니다. 최적 조건은 그래핀 3 wt.%, 다이 온도 180°C, 용탕 온도 740°C, 교반 속도 520rpm으로 확인되었습니다.
- The Bottom Line: 최적화된 공정 조건으로 제작된 Al-MWCNT-GR 복합재는 초기 조건 대비 경도가 31.77% 증가하고 마모율은 36.33% 감소하는 획기적인 성능 향상을 보였습니다. 이는 데이터 기반 공정 최적화가 고성능 금속 매트릭스 복합재 생산의 핵심임을 입증합니다.
The Challenge: Why This Research Matters for HPDC Professionals
자동차, 항공우주 등 고성능 부품 산업에서는 경량화와 동시에 우수한 기계적 특성을 갖춘 소재에 대한 요구가 끊임없이 증가하고 있습니다. 알루미늄은 경량 소재의 대표주자이지만, 순수 알루미늄만으로는 강도, 경도, 내마모성이 부족하여 구조 부품으로 사용하기에 한계가 있습니다 (Ref. [1]).
이러한 한계를 극복하기 위해 탄소나노튜브(CNT)나 그래핀과 같은 탄소 기반 나노 강화재를 알루미늄 기지에 첨가하는 연구가 활발히 진행되고 있습니다. 이들 강화재는 강철보다 수백 배 강하고 다이아몬드보다 단단하며, 자기 윤활 특성까지 지녀 복합재의 기계적, 마찰학적 특성을 획기적으로 향상시킬 수 있습니다 (Ref. [22], [25]).
하지만 이러한 잠재력에도 불구하고, 실제 생산 현장에서의 적용은 쉽지 않습니다. 특히 경제성과 대량 생산에 유리한 교반 주조(Stir Casting) 공정을 사용할 경우, 나노 강화재 입자들이 서로 뭉치는 응집 현상이나, 교반 중 가스가 유입되어 기공이 발생하는 등의 문제가 빈번하게 발생합니다 (Ref. [33-36]). 이는 복합재의 성능 저하와 품질 불균일의 직접적인 원인이 됩니다. 따라서 고성능 하이브리드 복합재를 안정적으로 생산하기 위해서는 이러한 문제들을 해결할 수 있는 교반 주조 공정의 최적화가 반드시 필요합니다.
The Approach: Unpacking the Methodology
연구팀은 이 문제를 해결하기 위해 체계적인 실험 및 분석 프레임워크를 구축했습니다. (Figure 3)
- 소재 준비 및 교반 주조: 알루미늄 기지에 MWCNT와 그래핀(GR) 강화재를 첨가하여 Al-MWCNT-GR 하이브리드 복합재를 제작했습니다. 이때, 강화재의 균일한 분산을 위해 교반 주조 공정을 사용했습니다.
- 다구찌 실험 계획법(Taguchi Method): 최소한의 실험으로 공정 변수의 영향을 파악하기 위해 다구찌 L16 직교배열표를 활용했습니다. 분석한 핵심 공정 변수는 다음과 같습니다.
- 그래핀 강화재 함량(PR): 1, 2, 3, 4 wt.%
- 다이 온도(DT): 140, 180, 220, 260 °C
- 용탕 온도(MT): 680, 710, 740, 770 °C
- 교반 속도(SS): 480, 520, 560, 600 rpm
- 하이브리드 다중 목표 최적화: 경도(높을수록 좋음)와 마모율(낮을수록 좋음)이라는 상충하는 두 가지 목표를 동시에 최적화하기 위해 다음과 같은 하이브리드 기법을 적용했습니다.
- CRITIC (Criteria Importance Through Intercriteria Correlation): 각 출력 변수(경도, 마모율)의 상대적 중요도(가중치)를 객관적으로 산출하는 데 사용되었습니다.
- GRA (Grey Relational Analysis) & MOORA (Multi-Objective Optimization by Ratio Analysis): CRITIC으로 계산된 가중치를 적용하여 여러 출력 변수를 단일 성능 지수로 변환하고, 최적의 공정 조건 조합을 찾는 데 사용되었습니다.
이러한 접근법을 통해 연구팀은 복잡한 공정 변수 간의 상호작용을 분석하고, 최고의 물성을 구현할 수 있는 최적의 '레시피'를 과학적으로 도출하고자 했습니다.
The Breakthrough: Key Findings & Data
본 연구를 통해 도출된 핵심 결과는 다음과 같습니다.
Finding 1: 그래핀 함량이 가장 지배적인 변수
Pareto ANOVA 분석 결과, 그래핀 강화재 함량(PR)이 경도와 내마모성 모두에 가장 큰 영향을 미치는 변수로 확인되었습니다. 그래핀 함량은 경도 변화에 76.77%, 마모율 변화에 80.31%의 기여도를 보여, 다른 변수들(용탕 온도, 교반 속도, 다이 온도)보다 월등히 높은 영향력을 가졌습니다 (Table 3, Table 4). 이는 원하는 기계적 특성을 얻기 위해 강화재의 양을 정밀하게 제어하는 것이 얼마나 중요한지를 보여줍니다.Finding 2: Taguchi-CRITIC-MOORA 기법의 우수성 확인
두 가지 하이브리드 최적화 모델(Taguchi-CRITIC-GRA, Taguchi-CRITIC-MOORA)을 비교한 결과, MOORA 기반 모델이 더 우수한 결과를 예측했습니다. MOORA 모델이 예측한 최적 조건에서 제작된 복합재는 GRA 모델보다 더 높은 경도와 더 낮은 마모율을 보였습니다.Finding 3: 최적 공정 조건 및 성능 향상
Taguchi-CRITIC-MOORA 모델을 통해 도출된 최적의 공정 조건은 PR3-DT2-MT3-SS2, 즉 그래핀 3 wt.%, 다이 온도 180°C, 용탕 온도 740°C, 교반 속도 520rpm 입니다 (Table 12). 이 조건으로 제작된 복합재는 초기 조건(PR 1%, DT 140°C, MT 680°C, SS 480rpm) 대비 경도는 85 HV에서 112 HV로 31.77% 증가했고, 마모율은 2.89 x 10⁻³ mm³/min에서 1.84 x 10⁻³ mm³/min으로 36.33% 감소했습니다 (Table 13).Finding 4: 미세구조 분석을 통한 성능 검증
SEM(주사전자현미경) 분석 결과, 최적 조건에서 제작된 복합재는 기공이 거의 없고 강화재가 균일하게 분산된 조밀한 미세구조를 나타냈습니다 (Figure 8b). 반면, 초기 조건에서는 기공과 강화재 응집이 관찰되었습니다 (Figure 8a). 또한, 마모 시험 후 표면 분석에서 최적 조건의 시편은 마모 트랙이 얇고 균일하며 균열 전파가 적어, 강화재에 의한 자기 윤활 효과가 효과적으로 발현되었음을 확인했습니다 (Figure 10c).
Practical Implications for HPDC Products
이 연구 결과는 실제 다이캐스팅 생산 환경에 다음과 같은 중요한 시사점을 제공합니다.
- For Process Engineers: 이 연구는 고경도, 저마모 특성이 요구되는 알루미늄 하이브리드 복합재 생산을 위한 구체적인 '공정 레시피'(그래핀 3%, 다이 온도 180°C, 용탕 온도 740°C, 교반 속도 520rpm)를 제공합니다. 이는 새로운 고성능 부품 개발 시 시행착오를 줄이고 개발 기간을 단축하는 데 기여할 수 있습니다.
- For Quality Control: Figure 8과 Figure 10에서 볼 수 있듯이, 공정 조건이 미세구조(기공, 강화재 분산)에 직접적인 영향을 미치고, 이는 최종 제품의 기계적 특성으로 이어집니다. 이는 공정 변수를 엄격하게 관리하는 것이 일관된 품질을 보증하는 핵심임을 다시 한번 강조합니다.
- For Die Design: 이 연구는 다이 온도와 용탕 온도의 최적 조합이 최종 응고 구조와 기공 형성에 중요한 역할을 함을 보여줍니다. 이는 금형 설계 시 냉각 채널의 위치나 효율을 최적화하여 이상적인 온도 프로파일을 구현하는 것이 제품 품질에 얼마나 중요한지를 시사합니다 (Abstract, Conclusion).
Paper Details
Stir Casting Process Analysis and Optimization for Better Properties in Al-MWCNT-GR-Based Hybrid Composites
1. Overview:
- Title: Stir Casting Process Analysis and Optimization for Better Properties in Al-MWCNT-GR-Based Hybrid Composites
- Author: Kanchiraya Shivalingaiah, Vinayaka Nagarajaiah, Chithirai Pon Selvan, Smitha Thothera Kariappa, Nandini Gowdru Chandrashekarappa, Avinash Lakshmikanthan, Manjunath Patel Gowdru Chandrashekarappa and Emanoil Linul
- Year of publication: 2022
- Journal/academic society of publication: Metals
- Keywords: Al-MWCNT-GR composite; hardness; wear rate; stir casting process; Taguchi-CRITIC-MOORA; Taguchi-CRITIC-GRA
2. Abstract:
Pure aluminium poses inferior properties that limit its use in load-bearing applications. Reinforcing multiwall carbon nano-tube (solid lubricant) and graphene to aluminium matrix offers better (antifriction, hardness, and wear resistance) properties in composites for such applications. A stir casting processing route is employed to prepare the hybrid composite (aluminium-multiwall carbon nanotube-graphene Al-MWCNT-GR). The Taguchi L16 experimental matrix representing four variables (percent reinforcement of graphene, die temperature, melt temperature, and stir speed) operating at four levels were studied to analyze and obtain higher hardness and low wear rate in hybrid composites. Percent reinforcement of graphene showed maximum impact, and die temperature resulted with the least contribution towards both the responses. Criteria importance through intercriteria correlation (CRITIC) method is applied to determine the weight fractions (importance) for hardness and wear rate equal to 0.4752 and 0.5482, respectively. Grey relational analysis (GRA) and multi-objective optimization by the ratio analysis (MOORA) method converts multiple objective functions into a single objective function with weight fractions assigned to each output. Taguchi-CRITIC-MOORA outperformed the Taguchi-CRITIC-GRA method, which could result in 31.77% increase in hardness and a 36.33% decrease in wear rate compared to initial conditions. The optimal conditions ensure a dense microstructure with minimal pores, result in enhanced properties compared to that obtained for initial and average stir casting conditions. The worn-out surface results in a few thin and slender grooves between tracks with less crack propagation, ensuring self-lubrication in composites fabricated with the optimized condition. The better properties resulted in the hybrid composites correspond to optimized stir casting conditions and can be implemented in industries for large-scale applications.
3. Introduction:
Modern industries aimed at developing components possessing attractive properties (strength, stiffness, corrosion, wear resistance, etc.). Composites constitute two or more constituent materials and offer distinguished physical and chemical properties that ensure desired properties. Compared to individual constituent materials, the composite materials showed superior properties. In composite materials, the metal matrix (rather than polymer or mineral) offers better conductivity (thermal and electrical), moisture-free, mechanical, and tribological properties. Thereby, metal matrix composites (MMCs) are widely used in biomedical (knives, blades), electrical, automotive, and aerospace applications. MMCs used in automotive industries are replacing steel parts with composite materials for economic benefits (i.e., reduced fuel consumption). To ascertain both technological and economic benefits with desired properties, an extensive study on the selection of constituent materials for developing composites is of industrial relevance. The use of graphene material ensures better technological and economical benefits in composites. Although a lot of research is reported in developing composites, most of them are fabricated, viz., powder metallurgy, extrusion, and the forming process route. It is imperative from the above literature review that the study of the economical processing route for fabricating composites (reinforcing graphene and CNTs in aluminium matrix) are of industrial relevance.
4. Summary of the study:
Background of the research topic:
Pure aluminum has limitations for load-bearing applications due to its inferior properties. Reinforcing it with materials like multiwall carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) and graphene (GR) can significantly improve antifriction, hardness, and wear resistance properties. Stir casting is an economical and versatile method for producing these metal matrix composites (MMCs).
Status of previous research:
While stir casting is advantageous for its simplicity and high production rate, it suffers from drawbacks like agglomeration of reinforcement particles, gas entrapment, and impurity inclusion, which can degrade the final properties. Previous research has shown that optimizing stir casting parameters (e.g., stir speed, time, reinforcement percentage) using methods like the Taguchi method can improve properties like strength and hardness. However, optimizing for multiple conflicting objectives simultaneously (e.g., high hardness and low wear rate) requires more advanced, hybrid optimization approaches, and a universal method has not yet been established.
Purpose of the study:
This study aims to analyze and optimize the stir casting process parameters for Al-MWCNT-GR hybrid composites to achieve superior properties, specifically higher hardness and a lower wear rate. The research seeks to establish a systematic framework using a hybrid optimization approach (Taguchi-CRITIC-MOORA and Taguchi-CRITIC-GRA) to find the single set of optimal conditions that can be practically implemented in industries for large-scale applications.
Core study:
The core of the study involves:
1. Fabricating Al-MWCNT-GR hybrid composites using a stir casting process.
2. Conducting experiments based on a Taguchi L16 orthogonal array, varying four parameters at four levels: percent reinforcement of graphene (PR), die temperature (DT), melt temperature (MT), and stir speed (SS).
3. Measuring the resulting hardness (HV) and wear rate (WR).
4. Applying the CRITIC method to determine the objective weights for hardness and wear rate.
5. Using GRA and MOORA methods to combine the multiple objectives into a single performance index.
6. Performing Pareto ANOVA to identify the optimal parameter levels and their percentage contribution.
7. Validating the optimal conditions through confirmation experiments and microstructural analysis (SEM, EDS) of the composites and their worn surfaces.
5. Research Methodology
Research Design:
The study employed a systematic, multi-stage research design. It began with materials preparation (pure Al, MWCNT, and Graphene powders) and characterization (SEM, EDS). The core of the design was the Taguchi L16 orthogonal array to structure the experiments, which efficiently studies the effects of four factors at four levels. The output responses measured were Vickers hardness (HV) and wear rate (WR).
Data Collection and Analysis Methods:
Hardness was measured using a Vickers hardness tester according to ASTM E384 standards. Wear rate was determined using a pin-on-disc wear test rig as per ASTM G99. The collected experimental data was then transformed into signal-to-noise (S/N) ratios. Data analysis was performed using a hybrid multi-objective optimization framework. This involved:
- CRITIC method: To calculate objective weights for hardness and wear rate.
- GRA and MOORA methods: To convert the multi-response problem into a single-response problem (Grey Relational Grade - GRG, and MOORA Index).
- Pareto Analysis of Variance (ANOVA): To determine the percentage contribution of each process parameter and identify the optimal levels.
- SEM and EDS: To analyze the microstructure and worn surfaces of the composites fabricated under initial, average, and optimal conditions.
Research Topics and Scope:
The research focused on the fabrication and optimization of Al-MWCNT-GR hybrid composites via the stir casting route. The scope was limited to four key process parameters: percent reinforcement of graphene (1-4 wt.%), die temperature (140-260 °C), melt temperature (680-770 °C), and stir speed (480-600 rpm). The study's outputs were confined to two critical mechanical properties: hardness and wear rate. The goal was to find a single set of optimal parameters for industrial application.
6. Key Results:
Key Results:
- Percent reinforcement of graphene (PR) was the most influential factor, contributing 76.77% to hardness and 80.31% to wear rate. Die temperature (DT) had the least effect. (Table 3, Table 4)
- The CRITIC method determined the objective weights for hardness and wear rate to be 0.4752 and 0.5428, respectively, indicating wear rate was slightly more critical in this multi-objective optimization. (Table 8)
- The Taguchi-CRITIC-MOORA method proved superior to the Taguchi-CRITIC-GRA method in finding the best process conditions.
- The optimal process conditions determined by the MOORA method were: 3 wt.% graphene reinforcement, 180 °C die temperature, 740 °C melt temperature, and 520 rpm stir speed. (Table 12)
- Under these optimal conditions, the composite's hardness increased by 31.77% (from 85 to 112 HV) and the wear rate decreased by 36.33% compared to the initial experimental conditions. (Table 13)
- SEM analysis confirmed that the optimal conditions produced a dense microstructure with minimal porosity and uniform reinforcement distribution, which explains the enhanced properties. (Figure 8)
- The worn surface analysis of the optimized composite showed thin, slender grooves and less crack propagation, indicating effective self-lubrication. (Figure 10)
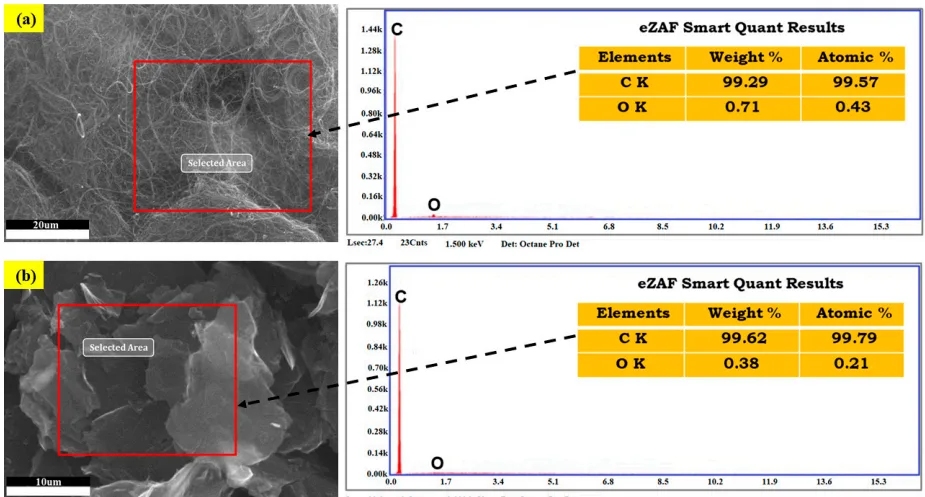
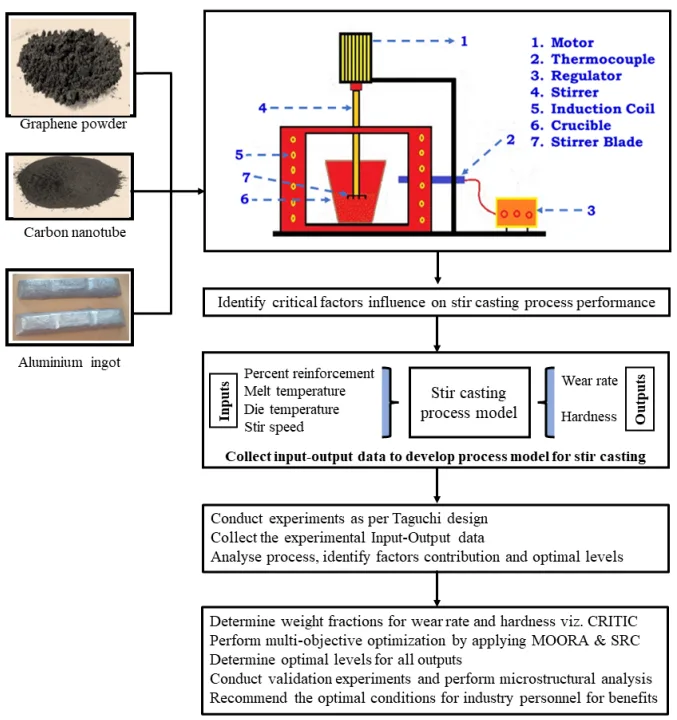
Figure Name List:
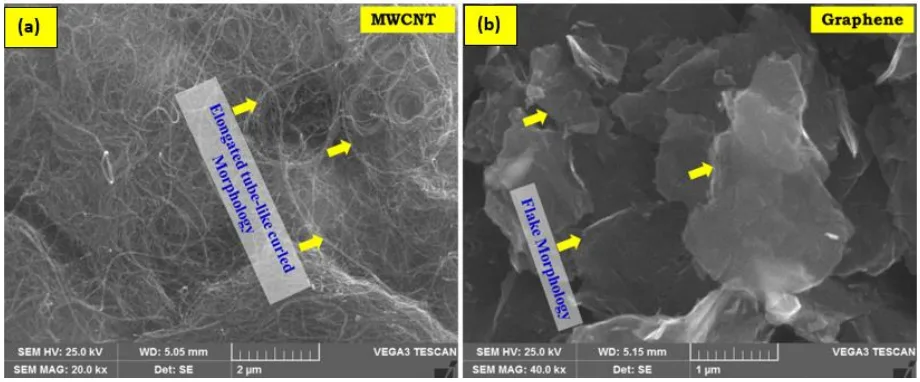
- Figure 1. SEM morphologies of reinforcement materials: (a) MWCNT Nano-powder and (b) Graphene Nano-powder in pristine state.
- Figure 2. EDS analysis of reinforcement materials: (a) MWCNT Nano-powder and (b) Graphene Nano-powder in pristine state.
- Figure 3. Schematic representation and framework of stir cast process modeling and optimization.
- Figure 4. Details of dimensions of wear rate and hardness of stir cast composite samples.
- Figure 5. Framework of the hybrid approach to perform modeling and optimization.
- Figure 6. Main effect plots of hardness of stir casting composites.
- Figure 7. Main effect plots of wear rate of stir casting composites.
- Figure 8. SEM Morphology studies for different stir casting conditions: (a) PR1DT1MT1SS1 Condition (initial experiment: PR: 1%, DT: 140 °C, MT: 680 °C, and SS: 480 rpm), (b) PR3DT2MT3SS2 Condition (optimal condition: PR: 3%, DT: 180 °C, MT: 740 °C, and SS: 520 rpm), (c) PR2DT3MT4SS1 Condition (PR: 2%, DT: 220 °C, MT: 770 °C, and SS: 480 rpm).
- Figure 9. Microhardness indentation images of the present investigation.
- Figure 10. Wear Track and Wear Debris SEM images of the present investigation.
7. Conclusion:
The study successfully established a systematic framework for analyzing and optimizing the stir casting process for Al-MWCNT-GR hybrid composites. Key conclusions are:
1. Percent reinforcement of graphene is the most dominant factor affecting both hardness and wear rate.
2. The objective weights for hardness and wear rate were determined to be 47.52% and 54.28%, respectively, using the CRITIC method.
3. The hybrid Taguchi-CRITIC-MOORA optimization approach was highly effective, outperforming the GRA-based method.
4. The optimal conditions (3 wt.% GR, 180°C die temp, 740°C melt temp, 520 rpm stir speed) led to a significant 31.77% increase in hardness and a 36.33% decrease in wear rate.
5. These optimal conditions result in a dense, low-porosity microstructure, which is the cause of the enhanced properties.
6. The findings provide a practical, data-driven guideline for the industrial production of high-performance Al-based hybrid composites for load-bearing applications.
8. References:
- [List the references exactly as cited in the paper, Do not translate, Do not omit parts of sentences.]
- Swamy, P.K.; Mylaraiah, S.; Gowdru Chandrashekarappa, M.P.; Lakshmikanthan, A.; Pimenov, D.Y.; Giasin, K.; Krishna, M. Corrosion Behaviour of High-Strength Al 7005 Alloy and Its Composites Reinforced with Industrial Waste-Based Fly Ash and Glass Fibre: Comparison of Stir Cast and Extrusion Conditions. Materials 2021, 14, 3929.
- Ramanathan, A.; Krishnan, P.K.; Muraliraja, R. A review on the production of metal matrix composites through stir casting—Furnace design, properties, challenges, and research opportunities. J. Manuf. Processes 2019, 42, 213–245.
... [and all other references from 3 to 88 as listed in the paper] ... - Lakshmikanthan, A.; Udayagiri, S.B.; Koppad, P.G.; Gupta, M.; Munishamaiah, K.; Bontha, S. The effect of heat treatment on the mechanical and tribological properties of dual size SiC reinforced A357 matrix composites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 6434–6452.
- Lakshmikanthan, A.; Bontha, S.; Krishna, M.; Koppad, P.G.; Ramprabhu, T. Microstructure, mechanical and wear properties of the A357 composites reinforced with dual sized SiC particles. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 786, 570–580.
Expert Q&A: Your Top Questions Answered
Q1: 이 연구에서 가장 중요한 공정 변수는 무엇이며, 그 이유는 무엇입니까?
A1: 단연 그래핀 강화재의 함량(PR)입니다. Pareto ANOVA 분석 결과, 그래핀 함량은 경도 특성 변화에 76.77%, 마모율 특성 변화에 80.31%의 기여도를 보여 다른 모든 변수들을 압도하는 가장 지배적인 영향력을 가졌습니다. 이는 원하는 기계적 특성을 달성하기 위해 강화재의 양을 정밀하게 제어하는 것이 가장 중요하다는 것을 의미합니다. [Source: Table 3, Table 4]
Q2: 최적의 공정 조건으로 제작된 복합재는 초기 조건 대비 얼마나 성능이 향상되었나요?
A2: Taguchi-CRITIC-MOORA 방법을 통해 찾은 최적 조건(그래핀 3%, 다이 온도 180°C, 용탕 온도 740°C, 교반 속도 520rpm)에서 제작된 복합재는 상당한 성능 향상을 보였습니다. 초기 조건 대비 경도는 31.77% 증가했으며, 마모율은 36.33% 감소했습니다. 이는 공정 최적화가 제품의 성능을 극대화하는 데 얼마나 효과적인지를 명확히 보여주는 결과입니다. [Source: Table 13]
Q3: 왜 여러 최적화 기법(Taguchi, CRITIC, MOORA, GRA)을 결합한 하이브리드 접근법을 사용했나요?
A3: 단일 기법의 한계를 극복하고 더 신뢰성 있는 결과를 얻기 위해서입니다. 다구찌 기법은 단일 목표 최적화에는 유용하지만, 경도(최대화)와 마모율(최소화)처럼 상충하는 여러 목표를 동시에 다루기에는 한계가 있습니다. GRA와 MOORA는 이런 다중 목표를 단일 성능 지수로 변환해 주지만, 각 목표의 상대적 중요도(가중치)를 객관적으로 결정하는 과정이 필요합니다. 여기서 CRITIC 기법이 데이터의 내재적 특성을 기반으로 각 목표의 가중치를 과학적으로 산출하는 역할을 하여, 전체 최적화 과정의 객관성과 정확성을 높였습니다. [Source: Abstract, Section 3.3, Figure 5]
Q4: 최적 조건에서 제작된 복합재의 미세구조는 어떻게 다른가요?
A4: SEM 이미지 분석 결과, 최적 조건에서 제작된 복합재는 기공이 거의 없고 강화재(MWCNT, 그래핀)가 기지 내에 균일하게 분산된 매우 조밀한 미세구조를 보였습니다. 이는 초기 조건에서 관찰된 기공 및 강화재 입자들의 응집 현상과 뚜렷하게 대조됩니다. 이러한 조밀하고 균일한 미세구조가 하중 전달을 효율적으로 만들고, 재료의 파괴 저항성을 높여 향상된 경도와 내마모성의 직접적인 원인이 됩니다. [Source: Figure 8]
Q5: 이 연구 결과가 실제 산업 현장에서 어떻게 활용될 수 있나요?
A5: 이 연구는 고경도, 저마모 특성이 요구되는 고성능 부품(예: 자동차 엔진 밸브, 커넥팅 로드, 임펠러)을 위한 Al-MWCNT-GR 하이브리드 복합재의 대량 생산에 직접 적용할 수 있는 구체적인 공정 가이드라인을 제공합니다. 제시된 최적화된 공정 조건을 통해, 기업들은 시행착오를 줄이면서 일관된 고품질의 제품을 안정적으로 생산할 수 있으며, 이는 제품 개발 기간 단축과 생산 비용 절감으로 이어질 수 있습니다. [Source: Abstract, Conclusion]
Conclusion & Next Steps
이 연구는 데이터 기반의 체계적인 접근법이 고성능 알루미늄 하이브리드 복합재 개발의 핵심임을 명확하게 보여줍니다. 교반 주조 공정의 네 가지 핵심 변수를 정밀하게 제어하고, Taguchi-CRITIC-MOORA와 같은 고급 최적화 기법을 적용함으로써, 경도와 내마모성을 동시에 극대화하는 것이 가능함을 입증했습니다.
이는 더 이상 감이나 경험에 의존하는 것이 아닌, 과학적 분석을 통해 최고의 성능을 이끌어낼 수 있다는 명확한 로드맵을 제시합니다.
CASTMAN은 최신 산업 연구 결과를 실제 고객의 다이캐스팅 문제 해결에 적용하는 데 전념하고 있습니다. 본문에 논의된 내용이 귀사의 운영 목표와 관련이 있다면, 저희 엔지니어링 팀에 연락하여 이러한 고급 원칙을 귀사의 부품에 어떻게 적용할 수 있을지 논의해 보시기 바랍니다.
Copyright
- This material is a paper by "Kanchiraya Shivalingaiah, et al.". Based on "Stir Casting Process Analysis and Optimization for Better Properties in Al-MWCNT-GR-Based Hybrid Composites".
- Source of the paper: https://doi.org/10.3390/met12081297
This material is for informational purposes only. Unauthorized commercial use is prohibited. Copyright © 2025 CASTMAN. All rights reserved.