본 논문 요약은 "Effect of Addition of Grain Refiner and Modifier on Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of Squeeze Cast A356 Alloy"으로 "Transactions of the Indian Institute of Metals"에 발표된 논문을 기반으로 작성되었습니다.
1. 개요:
- 제목: 압착 주조 A356 합금의 미세 구조 및 기계적 특성에 미치는 결정립 미세화제 및 개질제 첨가의 영향
- 저자: Reeturaj Tamuly, Amit Behl, Hemant Borkar
- 발행 연도: 2022년
- 출판 저널/학술 단체: Transactions of the Indian Institute of Metals (인도 금속 학회 논문집)
- 키워드: 압착 주조, 결정립 미세화제, 개질제, A356 합금
2. 연구 배경:
자동차, 항공 우주, 방위 산업 등 여러 산업 분야에서 알루미늄-실리콘(Al-Si) 합금, 특히 A356 등급은 낮은 밀도와 더불어 높은 강도, 우수한 주조성, 뛰어난 열전도율, 우수한 내식성 및 내마모성과 같은 다양한 장점 덕분에 널리 사용됩니다. 선행 연구에서는 중력 다이캐스팅 Al-Si 합금의 기계적 특성이 붕소 및 티타늄과 같은 결정립 미세화제와 스트론튬과 같은 개질제의 첨가에 의해 향상될 수 있음이 밝혀졌습니다. 압력 보조 주조 공정인 압착 주조는 알루미늄 합금의 기계적 특성을 개선하는 것으로 알려져 있습니다.
그러나 기존 연구는 결정립 미세화 및 모합금 개질을 모두 거친 주조 Al-합금의 압착 주조 적용에 대한 포괄적인 연구가 부족합니다. 따라서 이러한 복합 공정의 효과에 대한 추가 조사가 필요합니다. 그러므로 본 연구는 Al-Si 합금에 대한 결정립 미세화 및 개질과 함께 압착 주조의 영향을 탐구하는 데 중요합니다.
3. 연구 목적 및 연구 질문:
- 연구 목적:
본 연구는 압착 주조 A356 Al-Si 합금에 결정립 미세화 목적으로 알루미늄-티타늄-붕소(Al-Ti-B) 합금을 첨가하는 효과와 미세 구조 개질 목적으로 Al-Ti-B와 다양한 수준의 스트론튬(Sr)을 복합 첨가하는 효과를 조사하는 것을 목표로 합니다. 또한, 본 연구는 이러한 압착 주조 합금의 미세 구조 및 기계적 특성에 미치는 T6 용체화 열처리 효과를 분석합니다. - 주요 연구 질문:
- Al-Ti-B 결정립 미세화제 첨가가 압착 주조 A356 합금의 미세 구조 및 기계적 특성에 미치는 영향은 무엇인가?
- Al-Ti-B 결정립 미세화제와 Sr 개질제의 복합 첨가가 압착 주조 A356 합금의 미세 구조 및 기계적 특성에 미치는 복합적인 영향은 무엇인가?
- T6 용체화 열처리가 결정립 미세화제 및 개질제 첨가 유무에 따른 압착 주조 A356 합금의 미세 구조 및 기계적 특성에 미치는 영향은 무엇인가?
- 연구 가설:
핵심 가설은 결정립 미세화제 및 개질제의 첨가가 압착 주조 A356 합금의 기계적 특성 향상으로 이어진다는 것입니다. 더 나아가, 열처리 적용이 이러한 향상된 기계적 특성을 더욱 증진시킬 것이라고 가정합니다.
4. 연구 방법론
- 연구 설계:
본 연구는 결정립 미세화제 및 개질제 첨가와 열처리가 압착 주조 A356 합금의 미세 구조 및 기계적 특성에 미치는 영향을 체계적으로 평가하기 위해 실험적 설계를 채택했습니다. - 데이터 수집 방법:
본 연구에서는 데이터 수집을 위해 첨단 현미경 기술과 기계적 시험 기술을 조합하여 활용했습니다.- 광학 현미경: 일반적인 미세 구조 및 결정립 크기 분석에 사용되었습니다.
- 주사 전자 현미경(SEM): Si 입자 형태 및 금속간 화합물 상을 포함한 미세 구조 특징의 고해상도 이미징에 사용되었습니다.
- 에너지 분산 분광법(EDS): SEM과 통합되어 미세 구조 구성 요소의 원소 조성을 분석하는 데 사용되었습니다.
- 인장 시험: 범용 시험기를 사용하여 항복 강도, 인장 강도 및 연신율(%)과 같은 기계적 특성을 정량화하기 위해 수행되었습니다.
- 분석 방법:
수집된 데이터는 질적 및 양적 분석 방법을 모두 사용하여 분석되었습니다.- 미세 구조 분석: 현미경 이미지로부터 결정립 형태, 2차 덴드라이트 암 간격(SDAS) 및 Si 입자 특성에 대한 질적 평가를 수행했습니다. SDAS의 정량적 측정 또한 수행되었습니다.
- 기계적 특성 분석: 인장 시험 데이터의 통계 분석을 통해 항복 강도, 인장 강도 및 연신율의 평균값과 경향을 파악했습니다.
- 연구 대상 및 범위:
본 연구는 압착 주조 공정으로 제작된 A356 알루미늄 합금에 초점을 맞추었습니다. 연구 범위는 다음과 같습니다.- 합금 조성: 기준 A356 합금, Al-5Ti-1B 결정립 미세화제(Ti 750 ppm, B 150 ppm)를 첨가한 A356 합금, Al-5Ti-1B 결정립 미세화제와 Al-10Sr 개질제(Sr 200 ppm 및 Sr 300 ppm)를 복합 첨가한 A356 합금.
- 공정 조건: 제어된 매개 변수를 사용한 압착 주조 공정 및 선택된 시편에 적용된 T6 열처리.
- 특성 분석: 모든 합금 조성에 대해 주조 상태 및 열처리 상태 모두에서 포괄적인 미세 구조 및 기계적 특성 평가를 수행했습니다.
5. 주요 연구 결과:
- 주요 연구 결과:
- 압착 주조 효과: 압착 주조는 A356 합금의 2차 덴드라이트 암 간격(SDAS)을 45(± 2) μm에서 26(± 2) μm으로 50% 유의미하게 감소시켰습니다.
- 결정립 미세화 효과: Al-Ti-B 결정립 미세화제 첨가는 α-Al 상의 형태를 덴드라이트에서 구상 형태로 변화시키고 SDAS를 20(± 3) μm로 더욱 감소시켰습니다. 그러나 결정립 미세화제로 인한 SDAS 감소는 제한적이었으며(6(± 1) μm), 이는 결정립 미세화제의 페이딩 효과 때문일 수 있습니다.
- 결정립 미세화 및 개질 복합 효과: Al-Ti-B 결정립 미세화제와 Sr 개질제의 복합 첨가는 Si 입자 및 Fe계 금속간 화합물의 형태 변화를 유도했습니다. 평균 SDAS는 Sr 첨가량이 200 ppm 및 300 ppm 모두에서 약 20(± 3) μm로 유지되어 SDAS에 대한 Sr의 영향이 제한적임을 나타냅니다. 그러나 Sr은 Si 입자의 형태를 개질하는 데 효과적이었습니다.
- 열처리 효과: T6 열처리는 모든 시편에서 공정정 Si의 구상화 및 조대화, 그리고 경화상(Mg₂Si 및 Fe계 금속간 화합물)의 석출을 유도했습니다.
- 기계적 특성 - 비열처리: 결정립 미세화제 단독 첨가는 결정립 미세화제의 페이딩 효과로 인해 인장 강도(205 MPa에서 172.667 MPa로), 항복 강도(110.6 MPa에서 109.3 MPa로) 및 연신율(10%에서 6.33%로) 감소를 초래했습니다. 결정립 미세화제와 개질제의 복합 첨가는 결정립 미세화제 단독 첨가 시편에 비해 항복 강도를 향상시켰습니다.
- 기계적 특성 - 열처리: 열처리는 모든 합금 조성에서 인장 강도와 항복 강도를 향상시켰지만 연신율은 감소시켰습니다. 열처리된 A356 + Al-5Ti-1B + Al-10Sr (300 ppm Sr) 합금에서 193 MPa의 가장 높은 항복 강도가 달성되었습니다.
- 통계적/질적 분석 결과:
- SDAS 감소: 압착 주조는 SDAS를 50% 감소시켰습니다. 결정립 미세화제는 SDAS를 더 작은 폭으로 추가 감소시켰습니다.
- 인장 특성 (비열처리): 기준 A356 합금은 인장 강도 205 MPa, 항복 강도 110.6 MPa, 연신율 10%를 나타냈습니다. 결정립 미세화제 첨가 시 이러한 값은 감소했습니다. 결정립 미세화제와 개질제 복합 첨가 시 항복 강도는 회복되었고, 연신율은 300 ppm Sr 첨가 시 향상되었습니다.
- 인장 특성 (열처리): 열처리된 기준 A356 합금은 인장 강도 235 MPa, 항복 강도 184 MPa, 연신율 8.16%를 나타냈습니다. 열처리된 결정립 미세화제 및 개질제 첨가 합금은 다양한 인장 특성을 보였으며, 가장 높은 항복 강도는 300 ppm Sr 개질 합금에서 달성되었습니다.
- 데이터 해석:
결과는 압착 주조가 A356 합금의 미세 구조를 미세화하는 데 효과적임을 나타냅니다. 결정립 미세화는 미세 구조 미세화를 더욱 향상시키지만, 결정립 미세화제 페이딩으로 인해 주조 상태에서 인장 특성 감소를 초래할 수 있습니다. Sr 개질제 첨가는 Si 입자 형태를 부분적으로 개질하고, 결정립 미세화제와 함께 항복 강도를 향상시킬 수 있습니다. T6 열처리는 모든 합금 조성에서 강도를 최대화하는 데 중요하지만 연신율은 감소시킵니다. - 그림 목록:
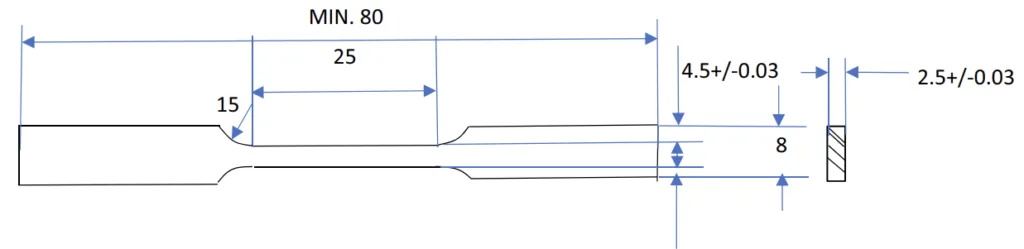
- Fig. 1 인장 시험편 (모든 치수는 mm)
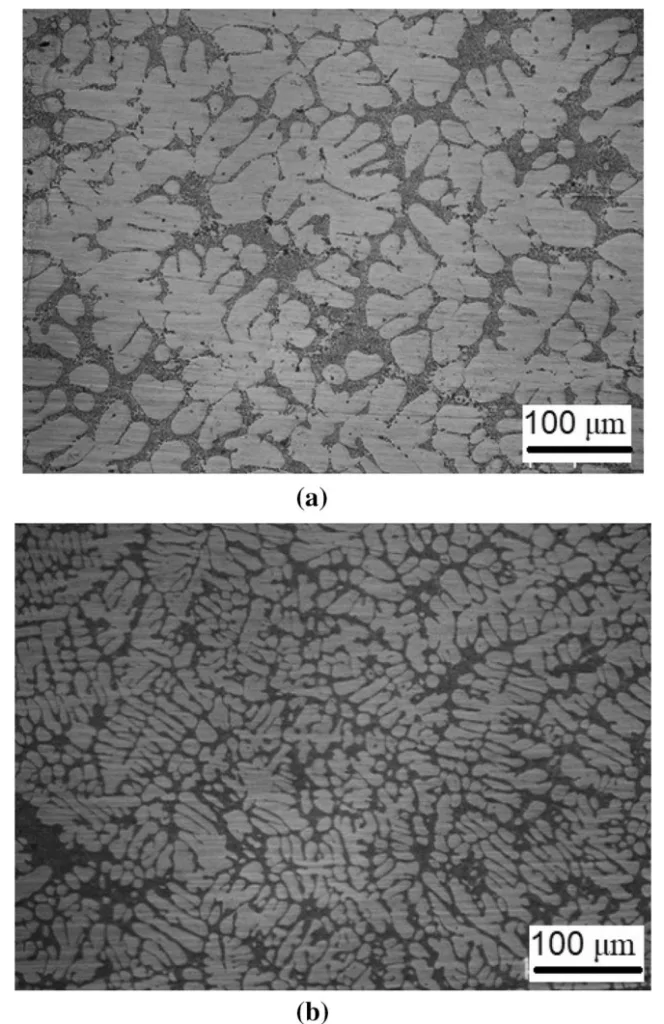
- Fig. 2 a) 주조 상태 A356 합금, b) 압착 주조 A356 합금의 광학 이미지
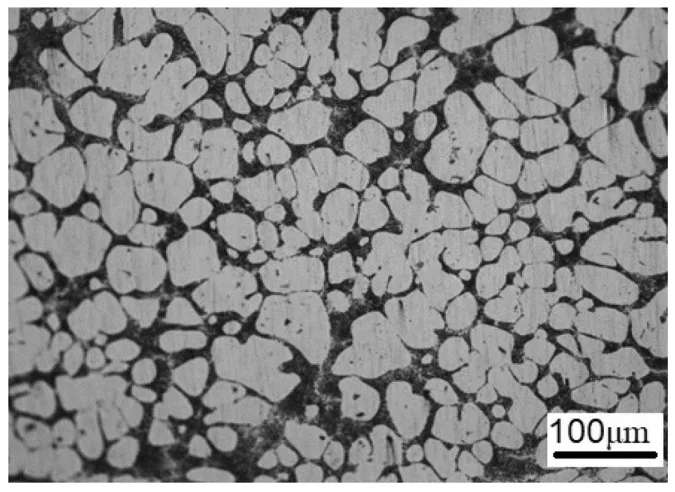
- Fig. 3 Al-5Ti-1B를 사용하여 결정립 미세화된 합금 시편의 광학 이미지 (단일 배율, Ti 750 ppm, B 150 ppm)
- Fig. 4 a) Al-5Ti-1B 및 Al-10Sr (Ti 750 ppm, B 150 ppm, Sr 200 ppm) 사용, b) Al-5Ti-1B 및 Al-10Sr (Ti 750 ppm, B 150 ppm, Sr 300 ppm) 사용 결정립 미세화 및 개질된 합금 시편의 광학 이미지
- Fig. 5 a) Al-5Ti-1B (Ti 750 ppm, B 150 ppm) 사용, b) Al-5Ti-1B 및 Al-10Sr (Ti 750 ppm, B 150 ppm, Sr 200 ppm) 사용, c) Al-5Ti-1B 및 Al-10Sr (Ti 750 ppm, B 150 ppm, Sr 300 ppm) 사용 열처리된 시편의 광학 이미지
- Fig. 6 a) 저배율, b) 고배율에서 구상화된 Si 입자를 보여주는 열처리된 시편의 SEM 이미지
- Fig. 7 (합금 조성 언급) Mg₂Si 입자 및 열처리 후 Fe계 금속간 화합물의 존재를 보여주는 EDS 분석
- Fig. 8 a) α-Al 및 Si 공정상, b) 공정 영역에서 개질되지 않은 Si 입자를 보여주는 Al-5Ti-1B를 사용한 결정립 미세화된 합금 시편의 SEM 이미지
- Fig. 9 a) Al-5Ti-1B를 사용하여 Si 입자를 보여주는 합금 시편의 SEM 이미지, b) Al-5Ti-1B 및 Al-10Sr을 사용하여 Si 입자의 부분적 개질을 보여주는 합금 시편의 SEM 이미지, c) 저배율에서 α-Al 및 Si 공정상을 보여주는 Al-5Ti-1B 및 Al-10Sr을 사용한 합금 시편의 SEM 이미지, d) 저배율에서 공정 영역에서 부분적으로 개질된 Si 입자를 보여주는 Al-5Ti-1B 및 Al-10Sr을 사용한 합금 시편의 SEM 이미지 (Ti 750 ppm, B 150 ppm, Sr 300 ppm)
- Fig. 10 a) A356 + Al-5Ti-1B(Ti 750 ppm, B 150 ppm) + Al-10Sr (Sr 200 ppm), b) A356 + Al-5Ti-1B(Ti 750 ppm, B 150 ppm) + Al-10Sr (Sr 300 ppm) 압착 주조 A356 합금 시편의 BSE 이미지, c) 밝은 영역을 나타내는 스펙트럼 10, d) Fe 금속간 화합물의 존재를 보여주는 EDX 분석
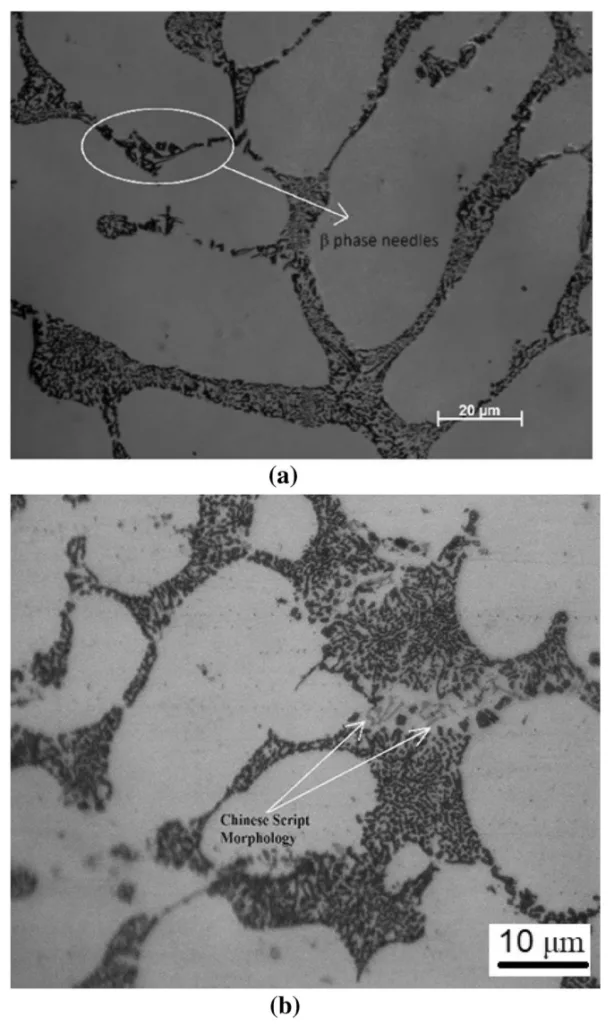
- Fig. 11 a) 개질되지 않은 A356 합금의 광학 이미지, Fe계 β상 침상정 존재, b) Sr 개질 합금의 광학 이미지, 중국문자 형태의 Fe계 α상 금속간 화합물
6. 결론 및 논의:
- 주요 결과 요약:
본 연구는 압착 주조, Al-Ti-B를 사용한 결정립 미세화, Sr 개질, T6 열처리가 A356 알루미늄 합금의 미세 구조 및 기계적 특성에 미치는 유의미한 영향을 명확히 입증합니다. 압착 주조는 SDAS를 감소시켜 미세 구조를 효과적으로 미세화합니다. 결정립 미세화제 첨가는 α-Al 상을 더욱 미세화하는 반면, Sr 개질은 Si 입자 형태를 변화시킵니다. T6 열처리는 공정정 Si의 구상화 및 석출 경화를 유도하여 강도를 향상시킵니다. - 연구의 학문적 의의:
본 연구는 Al-Si 합금에 대한 압착 주조, 결정립 미세화 및 개질의 시너지 효과에 대한 귀중한 통찰력을 제공합니다. 압착 주조, 결정립 미세화 및 개질된 A356 합금의 상변태 및 강화 메커니즘에 대한 이해를 높여 상세한 미세 구조 및 기계적 특성 분석을 제공합니다. 본 연구 결과는 특히 알루미늄 합금 가공 및 최적화와 관련하여 재료 과학 및 공학 분야에 중요한 의미를 갖습니다. - 실용적 의미:
본 연구의 실용적 의미는 다이캐스팅 산업에 상당합니다. 본 연구는 압착 주조와 결정립 미세화 및 개질을 결합하여 고성능 A356 합금 부품을 생산할 수 있는 잠재력을 강조합니다. 확인된 최적화된 공정 매개 변수 및 합금 조성은 높은 강도와 경량화가 중요한 요구 사항인 자동차, 항공 우주 및 기타 엔지니어링 응용 분야를 위한 주조 부품의 기계적 특성을 개선하는 데 직접적으로 적용될 수 있습니다. 또한 본 연구는 최대 기계적 특성을 달성하기 위한 중요한 후처리 공정으로서 T6 열처리의 중요성을 강조합니다. - 연구의 한계:
본 연구는 결정립 미세화제의 잠재적인 페이딩 효과를 포함한 특정 한계를 인정하며, 이는 일부 조건에서 미세 구조 미세화 및 특성 향상 정도를 제한했을 수 있습니다. Sr에 의한 부분적인 개질은 Sr 함량의 추가 최적화 필요성을 시사합니다. 또한, T6 처리에서 사용된 비교적 높은 담금질 온도는 연신율에 영향을 미쳤을 수 있으며, 이는 담금질 민감도 및 냉각 속도 최적화에 대한 추가 조사의 필요성을 나타냅니다.
7. 향후 후속 연구:
- 후속 연구 방향:
향후 연구는 확인된 한계를 해결하고 합금 조성 및 공정 매개 변수를 더욱 최적화하는 데 초점을 맞춰야 합니다. 주요 방향은 다음과 같습니다.- Sr 함량 최적화: Si 입자의 완전한 개질을 달성하고 부작용 없이 기계적 특성을 최대화하기 위한 최적 Sr 함량 조사.
- 붕소 함량 최적화: 페이딩 효과를 완화하고 결정립 미세화 효율을 향상시키기 위해 Al-Ti-B 결정립 미세화제에서 붕소의 역할 및 최적 함량에 대한 추가 연구.
- 담금질 온도 최적화: 높은 강도를 유지하면서 연신율을 향상시키기 위해 T6 열처리 중 더 낮은 담금질 온도의 효과 탐구.
- Sr:B 비율 효과: 압착 주조 A356 합금에서 효과적인 Sr 개질 및 결정립 미세화를 위한 최적 균형을 결정하기 위한 Sr:B 비율에 대한 상세 연구.
- 추가 탐구가 필요한 영역:
- 페이딩 메커니즘: 압착 주조 조건에서 Al-Ti-B 결정립 미세화제의 페이딩 메커니즘에 대한 심층 조사 및 이러한 효과를 완화하기 위한 전략 개발.
- 열처리 매개 변수 최적화: 최적의 강도 및 연신율 조합을 달성하기 위해 용체화 온도 및 시간, 담금질 속도 및 매체, 시효 온도 및 시간을 포함한 T6 열처리 매개 변수의 체계적인 최적화.
- 다른 개질제의 효과: 압착 주조 A356 합금에서 우수한 미세 구조 제어 및 기계적 특성을 달성하기 위해 결정립 미세화제와 함께 대체 또는 복합 개질제 사용 탐구.
8. 참고 문헌:
- Davies J R, Associates, Aluminium and Aluminium Alloys. ASM International, ASM World Headquarter, Material Park, Novelty, OH (1993)
- Jakob O, Svensson I L, Pascal L, and Dimitri D, Characterisation and investigation of local variations in mechanical behaviour in cast aluminium using gradient solidification, Digital Image Correlation and finite element simulation. Mater Design (1980-2015) 56 (2014): 755
- Kumar, P., and J. L. Gaindhar. "DAS, Solidification Time and Mechanical Properties of Al-11% Si Alloy V-Processed Castings (97-09)." Transactions of the American Foundrymen's Society 105 (1997): 635-638.
- Goulart, Pedro R., José E. Spinelli, Wislei R. Osório, and Amauri Garcia. "Mechanical properties as a function of microstructure and solidification thermal variables of Al-Si castings." Materials Science and Engineering: A 421, no. 1-2 (2006): 245-253.
- Seifeddine, Salem, Sten Johansson, and Ingvar L. Svensson. "The influence of cooling rate and manganese content on the β-Al5FeSi phase formation and mechanical properties of Al-Si-based alloys." Materials Science and Engineering: A 490, no. 1-2 (2008): 385-390.
- Ceschini, Lorella, Iuri Boromei, Alessandro Morri, Salem Seifeddine, and Ingvar L. Svensson. "Microstructure, tensile and fatigue properties of the Al-10% Si-2% Cu alloy with different Fe and Mn content cast under controlled conditions." Journal of Materials Processing Technology 209, no. 15-16 (2009): 5669-5679.
- Caceres, C. H., C. J. Davidson, J. R. Griffiths, and Q. G. Wang. "The effect of Mg on the microstructure and mechanical behavior of Al-Si-Mg casting alloys." Metallurgical and materials transactions A 30, no. 10 (1999): 2611-2618.
- Stadler, F., H. Antrekowitsch, W. Fragner, H. Kaufmann, E. R. Pinatel, and Peter J. Uggowitzer. "The effect of main alloying elements on the physical properties of Al-Si foundry alloys." Materials Science and Engineering: A 560 (2013): 481-491.
- Sritharan, T., and H. Li. "Influence of titanium to boron ratio on the ability to grain refine aluminium-silicon alloys." Journal of Materials Processing Technology 63, no. 1-3 (1997): 585-589.
- Jones, G. Pcarson, and J. Pearson. "Factors affecting the grain-refinement of aluminum using titanium and boron additives." Metallurgical Transactions B 7, no. 2 (1976): 223-234.
- Mayes, C. D., D. G. McCartney, and G. J. Tatlock. "Influence of microstructure on grain refining performance of Al-Ti-B master alloys." Materials science and technology 9, no. 2 (1993): 97-103.
- Mohanty, P. S., and J. E. Gruzleski. "Grain refinement mechanisms of hypoeutectic Al Si alloys." Acta materialia 44, no. 9 (1996): 3749-3760.
- Spittle, J. A. "Grain refinement in shape casting of aluminium alloys." International Journal of Cast Metals Research 19, no. 4 (2006): 210-222.
- Schumacher, P. "Nucleation Mechanisms during Grain Refinement of Al-Si-Alloys." Giesserei-Rundschau 50 (2003): 228-230.
- Mohanty, P. S., F. H. Samuel, and J. E. Gruzleski. "Studies on addition of inclusions to molten aluminum using a novel technique." Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B 26, no. 1 (1995): 103-109.
- Nafisi, Shahrooz, and Reza Ghomashchi. "Boron-based refiners: implications in conventional casting of Al-Si alloys." Materials Science and Engineering: A 452 (2007): 445-453.
- Lu, L., and A. K. Dahle. "Effects of combined additions of Sr and AlTiB grain refiners in hypoeutectic Al-Si foundry alloys." Materials Science and Engineering: A 435 (2006): 288-296.
- Limmaneevichitr, C., and W. Eidhed. "Fading mechanism of grain refinement of aluminum-silicon alloy with Al-Ti-B grain refiners." Materials Science and Engineering: A 349, no. 1-2 (2003): 197-206
- Ghomashchi, Reza. "The evolution of AlTiSi intermetallic phases in Ti-added A356 Al-Si alloy." Journal of Alloys and Compounds 537 (2012): 255-260.
- Lee, Choongdo. "Effect of Ti-B addition on the variation of microporosity and tensile properties of A356 aluminium alloys." Materials Science and Engineering: A 668 (2016): 152-159.
- Sokolowski, J. H., C. A. Kierkus, B. Brosnan, and W. J. Evans. "Formation of Insoluble Ti (Al, Si) 3 Crystals in 356 Alloy Castings and Their Sedimentation in Foundry Equipment: Causes, Effects and Solutions (00-21)." Transactions of the American Foundrymen's Society 108 (2000): 491-496
- Birol, Y. "Grain refinement of pure aluminium and Al-7Si with Al-3B master alloy." Materials Science and Technology 28, no. 3 (2012): 363-367.
- Couture, A. A. F. S. "Iron in aluminum casting alloys-a literature survey." International cast metals journal 6, no. 4 (1981): 9-17.
- Kori S. Auradi A V, Murty B S, and Chakraborty M. Poisoning and fading mechanism of grain refinement in Al-7Si alloy. In: Proceedings of 3rd international conference on advanced materials processing (ICAMP-3), 387-393. Processing (ICAMP-3), Melbourne, Australia, 2004.
- Haro-Rodríguez, Sergio, Rafael E. Goytia-Reyes, Dheerendra Kumar Dwivedi, Víctor H. Baltazar-Hernández, Horacio Flores-Zúñiga, and María J. Pérez-López. "On influence of Ti and Sr on microstructure, mechanical properties and quality index of cast eutectic Al-Si-Mg alloy." Materials & Design 32, no. 4 (2011): 1865-1871.
- Crosley, Phillip Bernard, and L. F. Mondolfo. "The modification of aluminum-silicon alloys." Mod Cast 49, no. 3 (1966): 99-100.
- Lu, Shu-Zu, and A. Hellawell. "The mechanism of silicon modification in aluminum-silicon alloys: Impurity induced twinning." Metallurgical Transactions A 18, no. 10 (1987): 1721-1733.
- Qiu, D., J. A. Taylor, M. X. Zhang, and P. M. Kelly. "A mechanism for the poisoning effect of silicon on the grain refinement of Al-Si alloys." Acta Materialia 55, no. 4 (2007): 1447-1456.
- Liao, Hengcheng, and Guoxiong Sun. "Mutual poisoning effect between Sr and B in Al-Si casting alloys." Scripta materialia 48, no. 8 (2003): 1035-1039.
- Timpel, M., N. Wanderka, R. Schlesiger, T. Yamamoto, N. Lazarev, D. Isheim, G. Schmitz, S. Matsumura, and J. Banhart. "The role of strontium in modifying aluminium-silicon alloys." Acta Materialia 60, no. 9 (2012): 3920-3928.
- Nogita, Kazuhiro, Stuart David McDonald, and Arne Kristian Dahle. "Effects of boron-strontium interactions on eutectic modification in Al-10 mass% Si alloys." Materials Transactions 44, no. 4 (2003): 692-695.
- Chatterjee S, Some observations on the effect of pressure on the solidification of Al-Si eutectic alloys. (1973).
- Chatterjee S, Effects of pressure on the solidification of some commercial aluminium-base casting alloys. (1972).
- Chadwick, G. A., and Tai Man Yue. "Principles and applications of squeeze casting." Metals and materials Bury St Edmunds 5, no. 1 (1989): 6-12.
- Dong, J. X., P. A. Karnezis, G. Durrant, and B. Cantor. "The effect of Sr and Fe additions on the microstructure and mechanical properties of a direct squeeze cast Al-7Si-0.3 Mg alloy." Metallurgical and materials transactions A 30 (1999): 1341.
- Okada, S., N. Fujii, A. Goto, S. Morimoto, and T. Yasuda. "Development of a full automatic squeeze casting machine." AFS Transactions 82 (1982): 135.
- Shivkumar, S., S. Ricci, B. Steenhoff, D. Apelian, and G. Sigworth. "An experimental study to optimize the heat treatment of A356 alloy." AFS Transactions 97 (1989): 791.
- Guodong, Wan Lil Luo Jirong1 Lan, and Qionghua L, Mechanical properties and microstructures of squeezed and cast hypereutectic A390 alloy [J]. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol (Nat Sci Edition) 8 (2008).
- Ma, Z., E. Samuel, A. M. A. Mohamed, A. M. Samuel, F. H. Samuel, and H. W. Doty. "Influence of aging treatments and alloying additives on the hardness of Al-11Si-2.5 Cu-Mg alloys." Materials & Design 31 (2010): 3791.
- Ma Z, Samuel E, Mohamed A MA, Samuel A M, Samuel FH, and Doty H W. Parameters controlling the microstructure of Al-11Si-2.5 Cu-Mg alloys. Mater Design 31(2010): 3791.
- Abou El-khair, M. T. "Microstructure characterization and tensile properties of squeeze-cast AlSiMg alloys." Materials Letters 59, no. 8-9 (2005): 894-900
- Mulazimoglu M H, Electrical conductivity studies of cast Al-Si and Al-Si-Mg alloys Ph.D. Thesis, 1988, McGill University, Montreal, PQ, Canada.
- H.J Li, S. Shivkumar, X.J. Luo and D. Apelian: "Influence of Modification on The Solution Heat Treatment Response of Cast Al-Si-Mg Alloys", Cast Metals, Vol. 1, 1989, pp. 227-234
- I. Kovacs, J. Lendvai and E. Nagy: "Mechanism of Clustering in Supersaturated Solid Solutions AI-Mg2Si Alloys. "Acta Metallurgica, Vol.20, 1972, pp. 975-983.
- Gupta A K and Lloyd D J, In: Aluminum alloys, their physical and mechanical properties (ICAA3), L. Arnberg, O. Lohne, E. Nes and N. Ryum, eds. The Norwegian Institute of Technology, Trondheim, 2 (1992), 21.
- Kashyap, K. T., and T. Chandrashekar. "Effects and mechanisms of grain refinement in aluminium alloys." Bulletin of Materials Science 24, no. 4 (2001): 345-353.
- Cooper P, Hardman A, Boot D, and Burhop E, Characterisation of a new generation of grain refiners for the foundry industry." In: LIGHT METALS-WARRENDALE-PROCEEDINGS-, 923-928. TMS, 2003.
- Lu L, and Arne K. Dahle, Effects of Sr and B interactions in hypoeutectic Al-Si foundry alloys. Light metals (2006): 807.
- Spittle J A, Grain refinement in shape casting of aluminium alloys (2006): 210.
- Wang, Tongmin, Hongwang Fu, Zongning Chen, Jun Xu, Jing Zhu, Fei Cao, and Tingju Li. "A novel fading-resistant Al-3Ti-3B grain refiner for Al-Si alloys." Journal of alloys and compounds 511, no. 1 (2012): 45-49.
- Gazanion F, Grant Chen X, and Dupuis C, Studies on the sedimentation and agglomeration behavior of Al-Ti-B and Al-Ti-C grain refiners." In Materials science forum, 396, p 45-52. Trans Tech Publications Ltd, 2002.
- Schneider W, Kearns M A, McGarry M J, and Whitehead A J, A comparison of the behaviour of AlTiB and AlTiC grain refiners. In: Essential readings in light metals, p 400-408. Springer, Cham, 2016.
- Talaat M M, Salah S, Ezz S, and El-Sayed M. El-Banna. GRAIN REFINEMENT OF A1-3 AND 5% Si ALLOYS.
- Zamkotowicz Z, Stuczynski T, Augustyn B, Lech-Grega M, and Wezyk W, Investigation of grain refinement fading in hypoeutectic aluminium-silicon alloys. In: LIGHT METALS-WARRENDALE-PROCEEDINGS-, p 807-816. TMS, 2004.
- Wang, Tongmin, Yuanping Zheng, Zongning Chen, Yufei Zhao, and Huijun Kang. "Effects of Sr on the microstructure and mechanical properties of in situ TiB2 reinforced A356 composite." Materials & Design 64 (2014): 185-193.
- Tan, Pan, Yi Yang, Yudong Sui, Qudong Wang, and Yehua Jiang. "The influence of Al-10Sr or/and Al-5Ti-1B on microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-12Si-4Cu-2Ni-0.8 Mg alloys." Journal of Alloys and Compounds 809 (2019): 151856.
- Samuel A M, Doty H W, Valtierra S, and Samuel F H, Effect of grain refining and Sr-modification interactions on the impact toughness of Al-Si-Mg cast alloys. Mater Design (1980-2015) 56 (2014) 264.
- Kori S A, Auradi V, Murty B S, Chakraborty M, Poisoning and fading mechanism of grain refinement in Al-7Si alloy. In: Proceedings of 3rd international conference on advanced materials processing (ICAMP-3), p 387-393. Processing (ICAMP-3), Melbourne, Australia, 2004.
- Mohanty, P. S., and J. E. Gruzleski. "Mechanism of grain refinement in aluminium." Acta Metallurgica et Materialia 43, no. 5 (1995): 2001-2012.
- Iqbal, N., N. H. Van Dijk, S. E. Offerman, M. P. Moret, L. Katgerman, and G. J. Kearley. "Real-time observation of grain nucleation and growth during solidification of aluminium alloys." Acta Materialia 53, no. 10 (2005): 2875-2880.
- Murty, B. S., S. A. Kori, and M. Chakraborty. "Grain refinement of aluminium and its alloys by heterogeneous nucleation and alloying." International Materials Reviews 47, no. 1 (2002): 3-29
- Greer A L, Quested T E, and Spalding JE, Modelling of grain refinement in directional solidification. In: LIGHT METALS-WARRENDALE-PROCEEDINGS-, p 687-694. TMS, 2002
- Emadi D, Whiting 1 V, Sahoo M, Sokolowski J H, Burke P, and Hart M. Optimal heat treatment of A356. 2 alloy. In LIGHT METALS-WARRENDALE-PROCEEDINGS-, p 983-990. TMS, 2003.
- Croucher T, and Butler D, Polymer quenching of aluminum castings. In 26th National SAMPE Symposium, p 527-535. 1981.
- Totten G E, and Mackenzie D S Aluminum quenching technology: a review. In: Materials science forum, 331, p 589-594. Trans Tech Publications Ltd, 2000.
- Sverdlin, A. V., G. E. Totten, and G. M. Vebster. "Polyalkyleneglycol base quenching media for heat treatment of aluminum alloys." Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov 6 (1996): 17-19.
- Senatorova O G, Sidelnikov V V, Mihailova I F, Fridlyander I N, Bedarev A S, Spector JI, Tihonova LA Low distortion quenching of aluminium alloys in polymer medium. In: Materials science forum, 396, p 1659-1664. Trans Tech Publications Ltd, 2002.
- Beitz, H. Non-combustible water-based quenchants in forging shops for automotive parts-latest development. In: 1 st international automotive heat treating conference, p 106-109. 1998.
- Zhang, D. L., and L. Zheng. "The quench sensitivity of cast Al-7 wt pct Si-0.4 wt pct Mg alloy." Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A 27, no. 12 (1996): 3983-3991.
- Mohamed AMA, and Samuel FH A review on the heat treatment of Al-Si-Cu/Mg casting alloys. Heat treatment-conventional and novel applications (2012): 55–72.
- Wahyuningtyas P, Syahrial A Z, Putra W N, and Utomo B W. Effect of T6 on mechanical properties of TiB and Sr modified ADC12/SiC composite produced by stir casting. In: E3S web of conferences, 130, 01023. EDP Sciences, 2019.
9. 저작권:
- 본 자료는 Reeturaj Tamuly, Amit Behl, Hemant Borkar의 논문: "Effect of Addition of Grain Refiner and Modifier on Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of Squeeze Cast A356 Alloy"를 기반으로 작성되었습니다.
- 논문 출처: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-022-02607-4
본 자료는 상기 논문을 기반으로 요약되었으며, 상업적 목적으로 무단 사용하는 것을 금지합니다.
Copyright © 2025 CASTMAN. All rights reserved.