본 소개 논문은 [제목: 이산 형상 형상에 대한 새로운 하이브리드 금형 탈형성 분석 방법] 논문을 기반으로 작성되었으며, [출판사: Computer-Aided Design]에 게재되었습니다.
1. 개요:
- 제목: A new hybrid method for demoldability analysis of discrete geometries (이산 형상 형상에 대한 새로운 하이브리드 금형 탈형성 분석 방법)
- 저자: Jorge Manuel Mercado-Colmenero, M. A. R. Paramio, Jesus Maria Perez-Garcia, Cristina Martin-Doñate
- 출판 연도: 2022년 (논문 게재 시점 기준, 파일 내 명시된 저작권은 2025년)
- 출판 저널/학회: Computer-Aided Design
- 키워드: Demoldability analysis, geometric analysis, injection molding, computer aided manufacturing (금형 탈형성 분석, 형상 분석, 사출 성형, 컴퓨터 지원 제조)
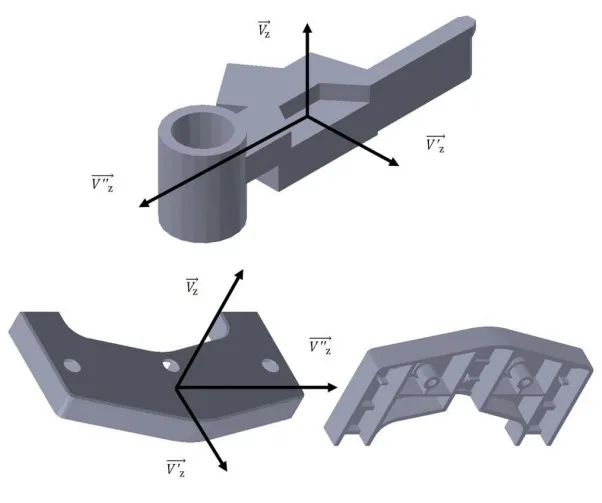
2. 연구 배경:
- 연구 주제의 사회적/학문적 맥락: 사출 성형은 복잡한 형상과 자유 곡면을 가진 플라스틱 부품 제조에 널리 사용되지만, 금형 설계 과정에서 금형 탈형성 분석은 품질 및 제조 비용에 큰 영향을 미치는 중요한 단계입니다. 설계 초기 단계에서 금형 탈형성을 신속하게 검증하고 제조 불가능 영역을 식별하는 것이 중요합니다. 기존 상용 CAD 시스템은 금형 탈형성 분석에 많은 수동 작업을 필요로 하며, CAD 툴에 대한 숙련도와 제조 경험이 요구됩니다.
- 기존 연구의 한계: 기존 연구들은 모델러에 종속적이거나, GPU와 같은 추가적인 컴퓨팅 장치를 필요로 하거나, 모든 종류의 플라스틱 부품 분석에 유효하지 않다는 단점이 있습니다.
- 연구의 필요성: 설계 및 제조 시간 단축, 제품 정밀도 및 품질 향상, 설계 변경에 대한 신속한 대응을 위해 플라스틱 부품의 금형 탈형성 분석 프로세스 자동화가 필요합니다. 기존 방법들의 단점을 극복하고 모든 종류의 플라스틱 부품에 적용 가능한 새로운 금형 탈형성 분석 방법 개발이 요구됩니다.
3. 연구 목적 및 연구 질문:
- 연구 목적: 플라스틱 사출 성형 부품의 금형 탈형성 자동 분석을 위한 새로운 방법론 제시. 특히, 삼각 메쉬로 이산화된 부품 형상에 기반하여 메쉬 노드와 패싯 모두에 대한 하이브리드 이산 금형 탈형성 분석 방법을 개발하는 것을 목표로 합니다.
- 핵심 연구 질문:
- 이산화된 플라스틱 부품 형상(삼각 메쉬)을 이용하여 금형 탈형성을 효과적으로 분석할 수 있는가?
- 메쉬 노드와 패싯을 모두 고려하는 하이브리드 분석 방법이 기존 방법보다 더 정확하고 효율적인 금형 탈형성 분석을 제공하는가?
- 개발된 알고리즘이 다양한 형상의 플라스틱 부품 및 CAD 시스템에 독립적으로 적용 가능한가?
- 개발된 알고리즘이 언더컷 영역뿐만 아니라 금형 탈형 불가능 영역을 정확하게 감지하고 설계자에게 유용한 정보를 제공하는가?
- 연구 가설: 제시된 하이브리드 이산 금형 탈형성 분석 방법은 기존 방법의 한계를 극복하고, 다양한 플라스틱 부품의 금형 탈형성 분석을 자동화하여 설계 시간 단축 및 품질 향상에 기여할 것이다.
4. 연구 방법론:
- 연구 설계: 새로운 하이브리드 금형 탈형성 분석 알고리즘 개발 및 구현.
- 데이터 수집 방법: 산업 현장에서 제조된 플라스틱 부품 5가지 및 실제 부품 2가지 (총 7가지)를 대상으로 알고리즘 적용 및 검증.
- 분석 방법: 개발된 알고리즘을 C++ 언어로 구현하고, 다양한 형상의 플라스틱 부품에 적용하여 금형 탈형성 분석 성능 및 계산 비용 평가. Isoobstructing 알고리즘과 Inproject 알고리즘의 계산 비용 비교 분석.
- 연구 대상 및 범위: 플라스틱 사출 성형 부품, 삼각 메쉬 기반 이산 형상 모델, 금형 탈형성 분석, 컴퓨터 지원 제조.
5. 주요 연구 결과:
- 핵심 연구 결과: 개발된 하이브리드 금형 탈형성 분석 알고리즘은 플라스틱 부품의 금형 탈형성을 효과적으로 분석하고, 금형 탈형 가능 영역, 불가능 영역, 사이드 코어 필요 영역 등을 정확하게 식별합니다. 알고리즘은 초기 이산 형상 모델을 입력으로 받아 새로운 가상 이산 형상 모델을 생성하며, 이는 부품의 제조 정보를 포함합니다.
- 통계적/정성적 분석 결과: 다양한 케이스 스터디를 통해 알고리즘의 유효성을 검증했습니다. 특히, Inproject 알고리즘은 Isoobstructing 알고리즘에 비해 계산 시간이 6% 수준으로 매우 효율적인 것으로 나타났습니다.
- 데이터 해석: 개발된 알고리즘은 CAD 모델러에 독립적이며, 다양한 형상의 플라스틱 부품에 적용 가능합니다. 또한, 언더컷 영역뿐만 아니라 금형 탈형 불가능 영역을 감지하여 설계자가 설계 초기 단계에서 문제를 해결할 수 있도록 지원합니다.
- 그림 목록:
- Fig.1a.- Converting a CAD model to a virtual faceted model.
- Fig.1b.- Definition of facets and nodes, triangular shell elements.
- Fig 2- Defining the set of nodes / facets belonging to Plk.
- Fig 3- Representation of facets Fi for the level k of Ik, definition of Ck
- Fig 4.- Projection of facets Fi and contour border Fr(Ck) for the level k of Ik .
- Fig5.- Partial demoldability analysis for a plane (Plk)
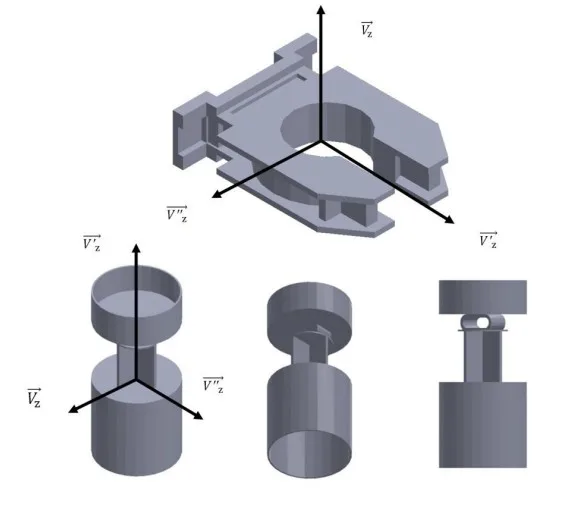
- Fig6.- Result of the algorithm InProject in the analysis (+V₂).
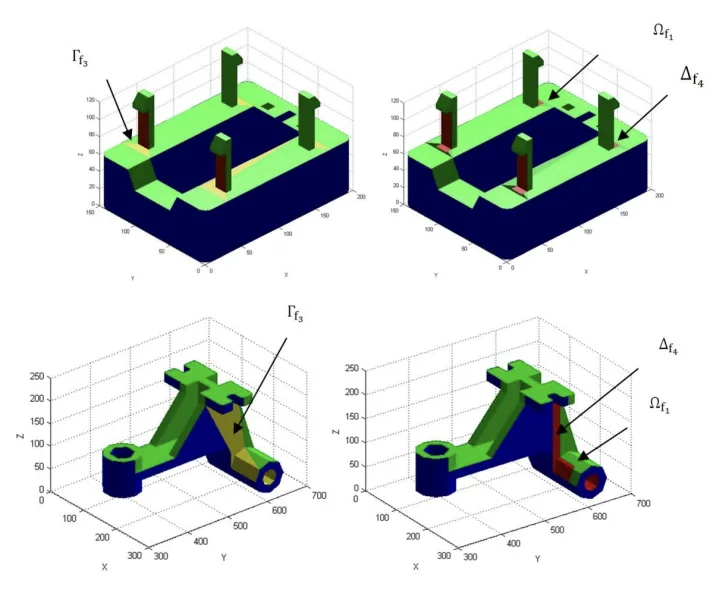
- Fig7.- Example of location of the region Of₁
- Fig8.- Example of location of the region [If U Af₄].
- Fig 9.- Example location of demoldable facets, perpendicular to V2.
- Fig 10.- Reorientation of the geometry as the new direction of analysis, and comparison of results of different analyses performed.
- Fig 11.- Results of the analysis of demoldability in +Vz, -Vz after the implementation of the boundary conditions 3.3.2
- Fig12.- Example of resolution of semi-demoldable facets, Boolean operation (intersection and subtraction).
- Fig 13a.- Allocation of non-demoldable facets to side core facets, Example I.
- Fig13b.- Allocation of non-demoldable facets to side core facets, Example II.
- Fig 14.- Geometric definition of the parting line.
- Fig 15.- Optimizing the geometrical definition of the parting line.
- Fig 16.- Case A and B, demoldable parts by means of upper and lower cavities.
- Fig 17.- Parts C, D with resoluble demolding regions by means of side cores.
- Fig18.- Part E, parts with non-demoldable regions.
- Fig 19.- Cases F and G. Parts with non demoldable regions, geometrically modified to improve their demoldability.
- Fig20.- Results of demoldability, Cases A, B, C, D, E.
- Fig21.- Results of demoldability, Cases F, G original part and Cases F',G' optimized part..
- Fig22.- CPU Computational Cost of Demoldability Algorithm.
- Fig23.- Formal definition of Gauss points of a facet.
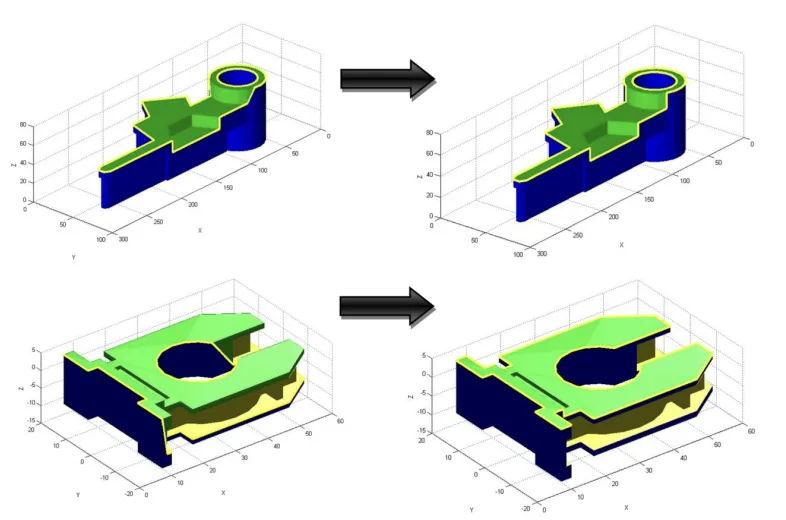

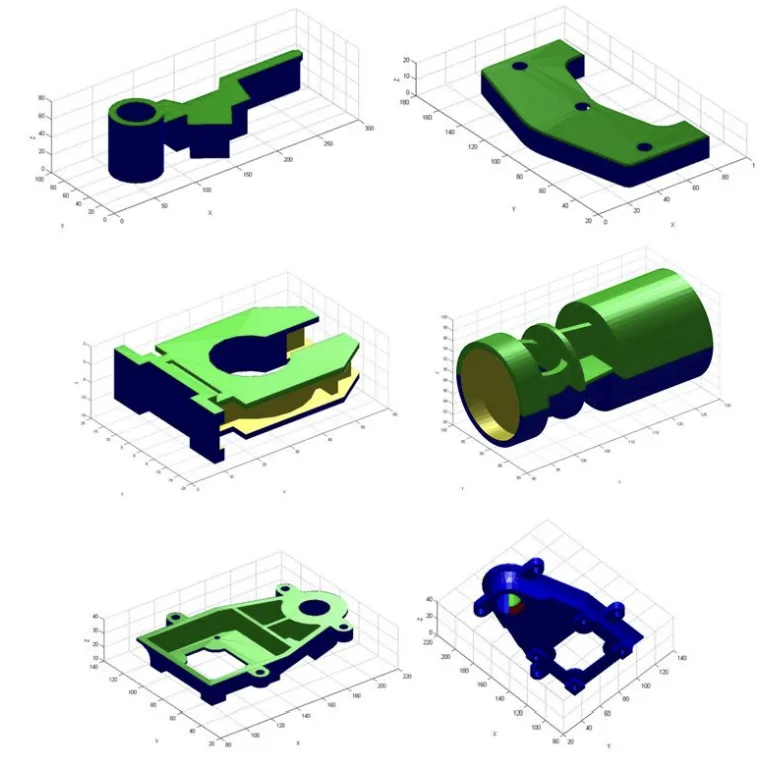
Parts F and G have been used as an example of optimizing the geometry of the part as a methodology in order to enhance its demoldability, Table 2 shows the results of applying the demoldability analysis algorithm over both parts.
6. 결론 및 논의:
- 주요 결과 요약: 본 연구에서는 플라스틱 부품의 금형 탈형성 분석을 위한 새로운 하이브리드 방법을 제시했습니다. 이 방법은 이산 메쉬 모델과 가상 형상 개념을 결합하여 메쉬 노드와 패싯 모두를 분석합니다. 개발된 알고리즘은 다양한 산업 부품에 적용되어 금형 탈형성 분석의 효율성과 정확성을 입증했습니다.
- 연구의 학문적 의의: 본 연구는 기존 금형 탈형성 분석 방법의 한계를 극복하고, 하이브리드 이산 요소 기반의 새로운 접근 방식을 제시함으로써 금형 설계 분야의 발전에 기여합니다. 특히, Inproject 알고리즘의 높은 계산 효율성은 복잡한 형상의 부품 분석에 대한 적용 가능성을 높입니다.
- 실용적 시사점: 개발된 알고리즘은 플라스틱 부품 설계자가 설계 초기 단계에서 금형 탈형성을 자동적으로 검증하고, 제조 가능성을 평가하는 데 유용하게 활용될 수 있습니다. 이는 설계 시간 단축, 제조 비용 절감, 제품 품질 향상에 기여할 수 있습니다.
- 연구의 한계: 본 연구는 특정 종류의 플라스틱 부품 및 사출 성형 공정에 초점을 맞추고 있습니다. 다양한 플라스틱 재료 및 성형 조건에 대한 알고리즘의 성능 검증 및 최적화가 필요합니다.
7. 향후 후속 연구:
- 후속 연구 방향:
- 다양한 플라스틱 재료 및 사출 성형 조건에 대한 알고리즘의 성능 평가 및 최적화 연구.
- 개발된 알고리즘을 상용 CAD/CAE 시스템에 통합하여 실용성을 높이는 연구.
- 금형 냉각 시스템 설계, 이젝터 시스템 설계 등 다른 금형 설계 단계와의 연계 연구.
- 알고리즘의 계산 효율성을 더욱 향상시키기 위한 GPU 활용 연구.
- 추가 탐색 영역:
- 복잡한 형상 및 미세 형상 부품에 대한 금형 탈형성 분석 정확도 향상 연구.
- 금형 탈형성 분석 결과를 기반으로 한 자동 금형 설계 시스템 개발 연구.
8. 참고 문헌:
- [1] Chen L.L., Woo T.C. Computational geometry on the sphere with application to automated machining. ASME Transactions. Journal of Mechanical Design 114, 288-295.
- [2] Chen L.L., Chou S.Y, Woo T.C. Parting directions for mould and die design. Computer Aided Design 1993;25 (12): 762-8.
- [3] Chen L.L., Chou S.Y, Woo T.C. Partial visibility for selecting a parting direction in mold and die design. Journal of Manufacturing Systems 1995; 14 (5):.
- [4] Weinstein M, Manoochehri S. Optimal parting direction of molded and cast parts for manufacturability. Journal of Manufacturing Systems 1997; 16(1):1-12.
- [5] Fu M.W, Fuh J.Y.H., Nee A.Y.C. Undercut feature recognition in an injection mould design system. Computer Aided Design 1999; 31(12):777-790.
- [6] Fu M.W., Fuh J,Y.H., Nee A.Y.C. Generation of optimal parting direction based on undercut features in injection molded parts. IIE Transactions 1999; 31: 947-55.
- [7] Fu M.W, Nee A.Y.C., Fuh J.Y.H. The application of surface visibility and moldability to parting line generation. Computer Aided Design 2002; 34(6): 469-480.
- [8] Fu M.W., Nee A.Y.C., Fuh J.Y.H. A core and cavity generation method in injection mold design. International Journal of Production Research 2001; 39:121-38.
- [9] Fu M.W., The application of surface demoldability and moldability to side core design in die and mold CAD. Computer Aided Design 2008; 40(5): 567-575.
- [10] Ran JQ, Fu MW. Design of internal pins in injection mold CAD via the automatic recognition of undercut features. Computer Aided Design. 2010;42(7):582-597.
- [11] Wuerger D, Gadh R. Virtual prototyping of die design part one: theory and formulation. J Concurrent Engng: Res Appl 1997; 5(4):307–15.
- [12] Wuerger D, Gadh R. Virtual prototyping of die design part two: algorithmic, computational, and practical considerations. J Concurrent Engng: Res Appl 1997; 5(4):317–26.
- [13] Kurth GR, Gath R. Virtual prototyping of die-design: determination of die-open directions for neat-net shape manufactured parts with extruded or rotational features. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems 1997; 10(1):69-81.
- [14] Lu HY, Lee WB. Detection of interference elements and release directions in die-cast and injection-moulded components. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part B Journal of Engineering Manufacture 2000; 214(6):431-41.
- [15] Yin ZP, Han Ding, You-Lun Xiong: Virtual prototyping of mold design: geometric mouldability analysis for near-net-shape manufactured parts by feature recognition and geometric reasoning. Computer-Aided Design 2001: 33(2): 137-154
- [16] Ye X.G. Fuh JYH, Lee K.S.: A hybrid method for recognition of undercut features from molded part. Computer-Aided Design 2001; 33(14):1023-34.
- [17] Ye X.G. Fuh JYH, Lee K.S.: Automotive undercut feature recognition for side core design of injection molds. Journal of Mechanical Design 2004; 126:519-26.
- [18] Zhang Chunjie, Zhou Xionghui, Li Congxin. Feature extraction from freeform molded parts for moldability analysis. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology. 2010;48(1-4):273-82.
- [19] Bassi R., Reddy NV, Bedi S.Automatic recognition of intersecting features of side core design in two piece permanent molds. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology. 2010;50(5-8):421-39.
- [20] Surti A., Reddy NV. Non discretized approach to visibility analysis for automatic mold feature recognition using step part model. Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Systems. 2012;11(1): 1-16.
- [21] Singh R, Madan J, Kumar R. Automated identification of complex undercut features for side core design for die casting parts. Journal of Engineering Manufacture. 2014;228(9):1138-1152.
- [22] Nee A.Y.C., Fu, M.W., Fuh J.Y.H., Lee K.S., Zhang Y.F. Determination of optimal parting direction in plastic injection mould design. Annals of the CIRP.1997:,46(1): 429-432.
- [23] Nee A.Y.C., Fu M.W., Fuh J.Y.H, Lee K.S., Zhang Y.F. Automatic determination of 3D parting Lines and Surfaces in Plastic Injection Mould Design. Annals of the CIRP. 1998: 47(1): 95-99.
- [24] Hui K.C., Tan S.T. Mould design with sweep operations, a heuristic search approach.Computer Aided Design . 1992; 24 (2): 81-92.
- [25] Ravi B., Srinivasan M.N. Decision criteria for computer aided parting surface design-Computer Aided Design. 1990; 22(1):11-18.
- [26] Rappaport D, Rosenbloom A. Moldable and castable polygons. Comput Geom: Theory Appl 1994;4:219-33.
- [27] Ahn, H.K., Berg, M.T. de, Bose, J., Cheng, S.W., Halperin, D. & Matouvsek, J. Separating an object from its cast. In Proceedings 13th Annual ACM Symposium on Computational Geometry 1997; 61-83. New York, U.S.A.: ACM Press.
- [28] Ahn, De Berg, Bose, Cheng,Halperin, Matousek, Swartzkopf, Separating an object from its cast. Computer Aided Design. 2002;34: 547-59,.
- [29] Chen X, McMains S. Finding all undercut-free parting directions for extrusions. In: Geometric modeling and processing. Lecture notes in computer science, 2006; 4077: 514-27.
- [30] Mcmains S, Chen X. Determining moldability and parting directions for polygons with curved edges.In: International mechanical engineering congress and exposition. ASME Anaheim, CA; 2004.
- [31] Mcmains S, Chen X. finding undercut free directions for polygons with curved edges. ASME Journal of Computing and Information Science in Engineering.2006; 6(1):60-68.
- [32] Yin ZP, Han Ding, Han-Xiong Li, You-Lun Xiong: Geometric mouldability analysis by geometric reasoning and fuzzy decision making. Computer Aided Design. 2004; 36(1): 37-50.
- [33] Chen YH, Wang YZ, Leung TM. An investigation of parting direction based on dexel and fuzzy decision making. International Journal of Production Research.2000;38:1357-75.
- [34] Huang J, Gupta SK, Stoppel K. Generating sacrificial multi-piece molds using accessibility driven spatial partitioning. Computer Aided Design 2003;35(3):1147-60.
- [35] Dhaliwal S, Gupta SK, Huang J, Computing exact global accessibility cones for polyhedral objects. In ASME Design for Manufacturing Conference Baltimore MD, September 2000.
- [36] Dhaliwal S, Gupta SK, Huang J, Priyadarshi A. Algorithms for computing global accessibility cones. Journal of Computing and Information Science in Engineering 2003;3(3):200-9.
- [37] Priyadarshi A.K.L., Gupta S.K. Geometric Algorithms for automated design of multipiece permanent molds. Computer Aided Design 2004; 36(3): 241-260.
- [38] Bourne D, Corney J, Gupta S.K. Recent advances and future challenges in automated manufacturing planning. Journal of Computing and Information Science in Engineering 2011; 11(2).
- [39] Chen Y, Rosen D. A region based approach to automated design of multipiece molds with application to rapid tooling.In ASME Design Engineering Technical conference, Pittsburgh PA, 2001;613-623.
- [40] Chen Y, Rosen DW. A reverse glue approach to automated construction of multi-piece molds. J. Comput Inf Sci Eng 2003;3(3):219-30.
- [41] Ganter M.A., Tuss L.L. Computer-Assisted Parting Line Development for Cast Pattern Production. AFS Transactions 1990; 795-800.
- [42] Wong T., Tan S.T., Sze W.S. Parting line formation by slicing a trimmed surface model. Proceedings of the 1996 ASME Design Engineering Technical Conference and Computers in Engineering Conference 1996.August 18-22, Irvine, California.
- [43] Rubio M.A., Pérez J.M., Rios J. A Procedure for plastic parts demoldability analysis Robotics and Computer Integrated Manufacturing 2006; 22(1):81-92.
- [44] Martin Doñate C, Rubio Paramio, M. A. New methodology for demoldability analysis based on volume discretization algorithms. Computer Aided Design.2013; 45(2): 229-240.
- [45] Martin Donate Cristina, Rubio Paramio Miguel Angel, Mesa Villar Aurelio. Método de validación automatizada de la fabricabilidad de diseños de objetos tridimensionales en base a su geometría. Patent number: ES2512940
- [46] Khardekar R, McMains S. Finding mold removal directions using graphics hardware. In: ACM workshop on general purpose computing on graphics processors; 2004, pp. C-19, (abstract).
- [47] Khardekar, Burton and McMains. Finding feasible mold parting directions using graphics hardware. Computer Aided Design 2006; 38(4):327-41.
- [48] Chakraborty P., Reddy NV. Automatic determination of parting directions, parting lines and parting surfaces for two piece permanent moulds. Journal of Materials Processing Technology 2000;209(5):2464-76.
- [49] Singh R, Madan J. Systematic approach for automated determination of parting line for die-cast parts. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing. 2013;29(5):346-366.
- [50] Shin K.H. Lee K.W. Design of side cores of injection molds from automatic detection of interference faces. Journal of Design and Manufacturing 1993;3:225-36
- [51] Banerjee A.G., Gupta S.K.Geometrical algorithms for automated design of side actions in injection moulding of complex parts. Computer Aided Design. 2007;39(10): 882-897.
- [52]Li W, Martin RR, Langbein FC. Molds for meshes: Computing smooth parting lines and undercut removal. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering 2009; 6(3):423-32.
9. 저작권:
- 이 자료는 [논문 저자: Jorge Manuel Mercado-Colmenero 외 3명]의 논문: [논문 제목: A new hybrid method for demoldability analysis of discrete geometries]를 기반으로 작성되었습니다.
- 논문 출처: [DOI URL: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cad.2022.103432]
본 자료는 위 논문을 기반으로 요약되었으며, 상업적 목적의 무단 사용을 금지합니다.
Copyright © 2025 CASTMAN. All rights reserved.