1. 개요:
- 제목: Die Casting of Lightweight Thin Fin Heat Sink Using Al-25%Si
- 저자: Toshio Haga and Hiroshi Fuse
- 발행 연도: 2024
- 발행 학술지/학회: Metals (MDPI)
2. 연구 배경:
경량화 및 비용 효율적인 히트싱크에 대한 수요가 증가하고 있다. 복잡한 형태의 히트싱크를 경제적으로 제조하는 일반적인 방법은 다이캐스팅이다. 다이캐스팅 히트싱크의 무게를 줄이기 위해 핀과 베이스를 얇게 만드는 것이 일반적인 방법이다.
기존 연구에서는 반고체 주조, 고밀도 주조, 고진공 다이캐스팅과 같은 기술을 사용하여 얇은 핀을 가진 히트싱크를 제작했지만, 고성능 다이캐스팅 장비가 필요하여 경제성이 떨어진다는 한계가 있다. 또한, 경량성과 우수한 열전도율을 지닌 복합재료를 사용한 히트싱크도 연구되었지만, 복잡한 공정, 고가의 원료, 재활용 어려움 등의 단점이 있다.
본 연구는 경제적인 이점을 가진 기존의 다이캐스팅 기계를 이용하여 얇은 핀과 베이스를 가진 히트싱크를 제작하고자 한다. 특히, 우수한 유동성을 지닌 알루미늄 합금을 사용하여 얇은 핀 제작의 어려움을 해결하고자 한다.
3. 연구 목적 및 연구 질문:
- 연구 목적: 기존 다이캐스팅 장비를 이용하여 Al-25%Si를 사용, 경량화된 얇은 핀 히트싱크를 제작하고, 그 특성을 평가하는 것이다.
- 핵심 연구 질문:
- Al-25%Si의 유동성은 기존 알루미늄 합금(ADC12)보다 얼마나 우수한가?
- 핀 두께, 핀 높이, 핀 개수, 베이스 두께가 열 방출 및 경량화에 미치는 영향은 무엇인가?
- 본 연구에서 제작된 Al-25%Si 히트싱크의 무게와 열 방출 성능은 상용 히트싱크와 비교했을 때 어떠한가?
- 연구 가설: Al-25%Si의 우수한 유동성을 이용하면 기존 다이캐스팅 장비로도 얇은 핀과 베이스를 가진 히트싱크를 경제적으로 제작할 수 있으며, 무게를 줄이면서 동등한 열 방출 성능을 유지할 수 있다.
4. 연구 방법론:
- 연구 설계:
- 실험 설계. Al-25%Si와 ADC12를 사용하여 다이캐스팅을 통해 다양한 형태의 히트싱크를 제작하고, 열 방출 및 무게를 측정하여 비교 분석한다.
- 데이터 수집 방법:
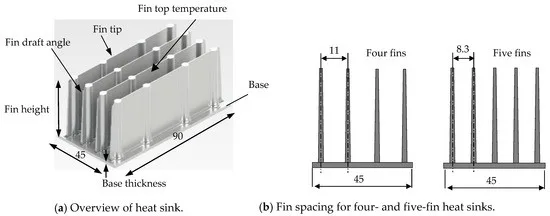
- 500kN 용량의 냉각형 다이캐스팅 기계를 사용하여 다양한 핀 두께, 핀 높이, 핀 개수, 베이스 두께를 갖는 히트싱크를 제작하였다.
- 열 방출 특성은 10mm x 10mm 마이크로 세라믹 히터를 사용하여 측정하였다.
- 히터와 히트싱크 사이에는 0.5mm 두께의 열 전달 재료를 사용하였다.
- 유동성 비교에는 나선형 다이를 사용했다.
- 분석 방법:
- 열 방출량은 히터 온도를 측정하여 분석하였다.
- 유동성은 나선형 다이를 이용한 주조 길이를 측정하여 분석하였다.
- 다양한 변수들의 영향을 분석하기 위해 분산분석(ANOVA) 등의 통계적 방법을 사용하였다.
- 미세구조 분석을 위해 광학 현미경을 사용하였다.
- 연구 대상 및 범위:
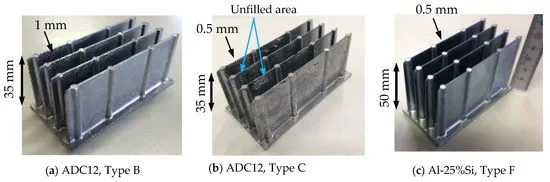
- Al-25%Si와 ADC12 합금을 사용하여 다양한 핀 두께(0.5mm, 1mm), 핀 높이(20mm~50mm), 핀 개수(4개, 5개), 베이스 두께(2mm, 4mm)를 갖는 히트싱크를 제작하였다.
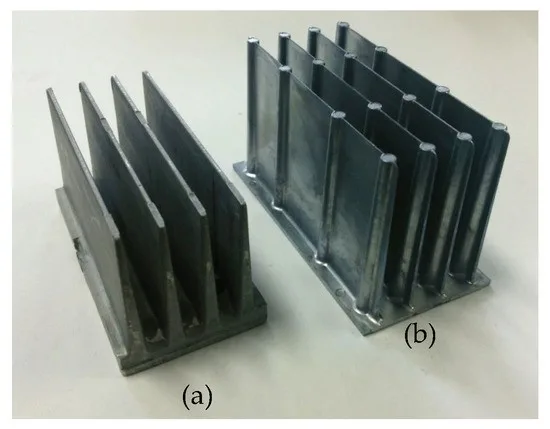
- 상용 히트싱크와의 비교 분석도 수행하였다.
5. 주요 연구 결과:
- 핵심 발견사항:
- Al-25%Si는 ADC12보다 유동성이 훨씬 우수하다 (0.5mm 및 1mm 나선형 다이에서 Al-25%Si의 유동 길이는 ADC12의 1.7배).
- Al-25%Si를 사용하면 기존 다이캐스팅 장비로도 0.5mm의 얇은 핀 두께, 0.5도의 드래프트 각도, 50mm의 핀 높이를 가진 히트싱크를 성공적으로 제작할 수 있다.
- 얇은 핀 두께는 열 방출에 큰 영향을 미치지 않지만, 무게를 크게 줄일 수 있다.
- 핀 높이가 증가할수록 열 방출이 향상되고, 핀 개수가 증가할수록 열 방출이 향상된다. 단, 일정 무게를 유지하는 경우 핀 높이 증가가 핀 개수 증가보다 열 방출 개선에 더 효과적이다.
- 베이스 두께가 증가할수록 열 방출이 향상되지만, 무게도 증가한다.
- 다공성은 열 방출에 거의 영향을 미치지 않는다.
- 미세구조 불균일성은 열 방출에 미치는 영향이 미미하다.
- Al-25%Si 히트싱크는 상용 히트싱크보다 무게는 35%~68% 가볍지만 동등한 열 방출 성능을 보였다.
- 통계적/정성적 분석 결과:
- 본 연구에서는 다양한 실험 데이터를 바탕으로 ANOVA 등의 통계적 분석을 수행하여 각 변수의 유의미한 영향을 검증하였다.
- 또한, 광학 현미경을 이용한 미세구조 관찰을 통해 정성적인 분석을 병행하였다. 자세한 통계 결과는 논문에 제시되어 있다.
- 데이터 해석:
- Al-25%Si의 우수한 유동성은 얇은 핀의 제작을 가능하게 하였고, 이를 통해 히트싱크의 경량화를 달성하였다.
- 다양한 변수들의 분석 결과를 통해 경량화된 히트싱크 설계에 대한 최적화 방향을 제시할 수 있다.
- Figure List and Description:
- 논문에 제시된 그림들은 다양한 변수 (핀 두께, 핀 높이, 핀 개수, 베이스 두께)가 열 방출과 무게에 미치는 영향을 시각적으로 보여주고 있다.
- 또한, Al-25%Si와 ADC12의 유동성 비교, 상용 히트싱크와의 비교 결과, 미세구조 분석 결과 등을 포함하고 있다.
6. 결론 및 논의:
본 연구는 기존 다이캐스팅 장비를 사용하여 Al-25%Si 합금으로 얇고 키가 큰 핀을 가진 경량 히트싱크를 성공적으로 제작하였다. Al-25%Si의 우수한 유동성 덕분에 0.5mm의 얇은 핀 두께와 0.5도의 작은 드래프트 각도를 구현할 수 있었다.
얇은 핀 두께는 열 방출에는 큰 영향을 미치지 않지만, 히트싱크의 무게를 상당히 줄일 수 있다는 것을 확인하였다. 핀 높이, 핀 개수, 베이스 두께는 열 방출 성능에 영향을 미치지만, 일정 무게를 유지하는 경우 핀 높이를 증가시키는 것이 가장 효과적이다.
Al-25%Si 히트싱크는 상용 히트싱크에 비해 무게는 최대 68%까지 가볍지만, 동등한 수준의 열 방출 성능을 유지했다. 본 연구 결과는 경량화된 히트싱크 설계 및 제조에 대한 중요한 시사점을 제공한다.
산업적으로는 자동차 및 고층 건물용 LED 조명 등에 적용 가능하다. 하지만, 다공성 및 미세구조 불균일성에 대한 추가 연구가 필요하다.
7. 향후 후속 연구:
- 후속 연구는 다공성과 미세구조 불균일성이 열 방출에 미치는 영향에 대한 추가적인 연구가 필요하다.
- 다양한 알루미늄 합금을 사용한 비교 연구를 통해 최적의 합금 조성을 찾아낼 수 있다.
- 실제 응용 환경에서의 열 방출 성능 평가를 통해 실용성을 검증해야 한다.
- 복합재료를 이용한 히트싱크와의 비교 연구를 통해 성능 및 경제성을 비교 분석할 필요가 있다.
References
- Car LED Lamp Heat Sink. Available online: https://www.nikkeikinholdings.co.jp/car/detail/a0180.html (accessed on 29 March 2024).
- Car LED Lamp Heat Sink. Available online: http://www.nanshin-grp.co.jp/car_product/ (accessed on 29 March 2024).
- High-Ceiling LED Lamp Heat Sink. Available online: http://ja.perfumecaps.com (accessed on 29 March 2024).
- Şevik, S.; Őzdilli, Ő.; Akbulut, F. Numerical investigation of the effect of different heat sink fin structures on the thermal performance of automotive LED headlights. Int. J. Automot. Sci. Technol. 2022, 6, 17–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafford, J.; Walsh, E.; Egn, V.; Walsh, P.; Muzychka, Y.S. A novel Approach to Low Profile Heat Sink Design. J. Heat Transf. 2010, 132, 091401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.J.; Kim, D.K.; Oh, H.H. Comparison of Fluid Flow and Thermal Characteristics of Plate-Fin and Pin-Fin Heat Sinks Subject to Parallel Flow. Heat Transf. Eng. 2008, 29, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallikarjuna, V.; Rajesh, K.; Ramesh, K.; Reddy, B.R.B. Modeling and Optimization of shape of a Heat Sink Fins on Motherboard. J. Comput. Math. Sci. 2015, 65, 228–251. [Google Scholar]
- Kappranos, P. Current State of Semi-Solid Net-Shape Die Casting. Metals 2019, 9, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- See, A.; Caporale, L. High Density Die Casting (HDDC): New frontiers in the manufacturing of heat sinks. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2014, 525, 012020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jou, R.Y. Thermal analysis of LED Heat Sinks by High-Vacuum Die Casting (HVDC). Adv. Sci. Lett. 2012, 8, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Sun, M.; Guo, H.; Zie, Z.; Du, S. Enhancement effect of a diamond network on the flow boiling heat transfer characteristics of a diamond/Cu heat Sink. Energies 2023, 16, 7228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiorano, L.P.; Castillo, R.; Molina, J.M. Al/Gf composite foams with SiC-engineered interfaces for the next generation of active heat dissipation materials. Compos. Part A 2023, 166, 107367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Ali, H.M.; Rehman, T.; Arsalanloo, A.; Niyas, H. Composite pin-fin for effective hotspot reduction. Heat Trans. 2024, 53, 1816–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ding, L.; Li, J.; Fang, Y.; Li, G.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, L. Progress in preparation of silicon carbide particulate copper composites. Shandong Chem. Ind. 2021, 50, 65–67. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, C.; Xie, Y.; Pan, Z.; Ren, S.; Qu, X. Preparation and research process of high thermal conductivity metal matrix composites. Powder Metall. Technol. 2022, 40, 40–52. [Google Scholar]
- Coia, P.; Dharmasiri, B.; Stojcevski, F.; Hayne, D.J.; Austria, E., Jr.; Akhavan, B.; Razal, J.M.; Usman, K.A.S.; Stanfield, M.K.; Henderson, L.C. Scalable electrochemical grafting of anthraquinone for fabrication of multifunctional carbon fibers. L. JMST 2024, 200, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.K. Mechanical behaviors of Al6063/TiB2 composites fabricated by stir casting process. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 82, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zasadzińska, M.; Strzępek, P.; Mamala, A.; Noga, P. Reinforcement of aluminium-matrix composites with glass fibre by metallurgical synthesis. Materials 2020, 13, 5441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haga, T.; Imamura, S.; Fuse, H. Fluidity Investigation of Pure Al and Al-Si Alloys. Materials 2022, 14, 5372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- JIS H 5032: 2006(E); Aluminum Alloy Die Castings. Japanese Industrial Standards: Tokyo, Japan, 2006.
- Keller, K.P. Cast heatsink Design Advantages. ITherm’98. In Proceedings of the Sixth Intersociety Conference on Thermal and Thermomechanical Phenomena in Electronic Systems (Cat. No.98CH36208), Seattle, WA, USA, 27–30 May 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Z.; Lau, E.; Botting, C.; Bahrami, M. Naturally cooled heat sinks for battery chargers. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 14, 118911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, H.S.; Lee, J.J.; Lai, C.Y. Thermal Analysis and Optimum Fin Length of a Heat Sink. Heat Transf. Eng. 2003, 24, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goshayeshi, H.R.; Ampofo, F. Heat Transfer by Natural Convection from a Vertical and Horizontal Surfaces Using Vertical Fins. Int. J. Energy Power Eng. 2009, 1, 85–89. Available online: http://www.scirp.org/journal/epe (accessed on 2 November 2022). [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Ishikawa, A.; Hashimoto, R.; Kanematsu, H.; Utsumi, Y. Effect of Heat Sink Structure on Cooling Performance of LED Bulb. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Design Engineering and Science, ICDES, Pilsen, Czech Republic, 31 August–3 September 2014; pp. 171–174. [Google Scholar]
- Shengxiong, C.; Daqing, Z. Heat Analysis and Optimal Design of Heat Sink of LED Fish Aggregation Lamp. Sens. Mater. 2018, 30, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, R.; Wang, C.C. A novel heat dissipation fi design applicable for natural convection augmentation. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer. 2014, 59, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, Y.; Kurkute, V.; Deshmukh, S.M.; Pathan, K.A.; Attar, A.R. The influence of Plate Fin Heat Sink Orientation under Natural Convection on Thermal Performance: An Experimental and Numerical Study. J. Adv. Res. Fluid Mech. Therm. Sci. 2024, 114, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasangika, A.H.D.K.; Nasif, M.S.; Pao, W.; Al-Waked, R. Effect of fin spacing on the vibration-assisted thermal performance of hat sink. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1281, 012059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, P.; Radhakrishnan, S.; Mahalingam, A.; Vellaiyan, S. Heat dissipation effects of different nanocoated Lateral Fins an Experimental investigation. Therm. Sci. 2024, 28, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, V.; Kamkari, B.; Zandimaghm, M.; Hewitt, N. Transient Thermal Behavior of a passive heat sink integrated with phase change material: A numerical simulation. Int. J. Thermofluids 2023, 20, 100454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, J.; Yang, H.; Feng, B.; Zhang, Q.; Song, X. Study on performance of the thermoelectric cooling device with novel subchannel Finned Heat Sink. Energies 2022, 15, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, S.; Hyeon, S.; Lee, K.S. Guide vane for thermal enhancement of a LED heat sink. Energies 2022, 15, 2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, N.; Siddiqi, M.U.R.; Tahir, M. Thermal analysis of proposed heat sink design under natural convection for the thermal management of electronics. Therm. Sci. 2022, 26, 1487–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekpu, M.; Ogbodo, E.A.; Ngobigha, F.; Njoku, J.E. Thermal Effect of Cylindrical Heat Sink on Heat Management in LED Applications. Energies 2022, 15, 7583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradikazerouni, A.; Afrand, M.; Alsarraf, J.; Wongwises, S.; Asadi, A.; Nguyen, T.K. Investigation of a Computer CPU Heat Sink under Laminar Forced Convection Using a Structural Stability Method. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 134, 1218–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wengang, H.; Lulu, W.; Zongmin, Z.; Yanhua, L.; Mingxin, L. Research on simulation and experimental of thermal performance of LED array heat sink. Procedia Eng. 2017, 205, 2084–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muneeshwaran, M.; Tsai, M.K.; Wang, C.C. Heat transfer augmentation of natural convection heat sink through notched fin design. Mass Trans. 2023, 142, 106676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, A.; Alabdullatif, M.I.; Jabbal, M.; Yan, Y. Towards the thermal management of electronic devices: A parametric investigation of finned heat sink filled with OCM. Mass Trans. 2021, 129, 105643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, M.B.B.; Hatami, M. Optimimization of Fins Arrangements for the square Light Emitting Diode (LED) cooling through nanofluid-filled microchannel. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payandeh, M.; Belov, I.; Jarfors, A.E.; Wessén, M. Effect of Material Inhomogeneity on Thermal Performance of a Rheocast Aluminum Heatsink for Electronics Cooling. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2016, 25, 2116–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, M.M.A.; Hassan, S.F.; Saheb, N.; Patel, F. Metal Matrix Composite in Heat Sink Application: Reinforcement, Processing, and Properties. Materials 2021, 14, 6257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Die Casting Machine. Available online: https://hishinuma.jp/menu/2013/09/hc50f.html (accessed on 22 April 2022).
- Temperature Controller. Available online: https://hishinuma.jp/menu/cat/cat132/cat1/ (accessed on 22 April 2022).
- Zhang, Z.; Collins, M.; Lau, E.; Botting, C.; Bahrami, M. The Role of Anodization in Naturally Cooled Heat Sinks for Power Electronic Devices. J. Heat Transf. 2020, 142, 05290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
저작권 및 참고 자료
본 자료는 Toshio Haga and Hiroshi Fuse 저자의 논문 "Die Casting of Lightweight Thin Fin Heat Sink Using Al-25%Si"를 기반으로 작성되었습니다.
논문 출처: Metals 2024, 14(6), 622; https://doi.org/10.3390/met14060622
본 자료는 위 논문을 바탕으로 요약 작성되었으며, 상업적 목적으로 무단 사용이 금지됩니다.
Copyright © 2025 CASTMAN. All rights reserved.