[金型寿命を飛躍させる複層PVDコーティング:自動車向けアルミダイカストの課題解決策]
本技術概要は、[Janette Brezinová]らが執筆し、[Acta Mechanica Slovaca]([2022]年)に掲載された学術論文「[Use of Duplex PVD Coatings to Increase the Life of Moulds and Cores for die Casting of Aluminium Alloys in the Automotive Industry]」に基づいています。CASTMANがAIの支援を受け、技術専門家向けに分析・要約したものです。

キーワード
- 主要キーワード: PVDコーティング 金型寿命
- 副次キーワード: アルミニウムダイカスト, 熱疲労, 表面処理, nACRo³コーティング, 自動車産業, レーザー表面処理
エグゼクティブサマリー
多忙なプロフェッショナルのための30秒概要
- 課題: 高圧アルミニウムダイカストにおける金型やコアは、熱疲労、溶損、焼付きにより寿命が著しく制限されるという業界共通の課題があります。
- 手法: 金型母材(Uddeholm Dievar鋼)の表面に局所的なレーザー加熱処理を施し、その上に複層PVDコーティング(AIXN³およびnACRo³)を成膜する革新的なアプローチを採用しました。
- 重要なブレークスルー: レーザー前処理と複層PVDコーティングの組み合わせは、金型表面の耐性を大幅に向上させ、680±20°Cのアルミニウム溶湯中に300分間浸漬した後でも、緻密で一体性のある保護膜を維持することを確認しました。
- 結論: このデュプレックス処理技術は、自動車産業で要求される過酷なダイカスト条件下において、金型寿命を延ばし、生産性を向上させるための実証された有効な手段です。
課題:なぜこの研究がHPDC専門家にとって重要なのか
高圧アルミニウムダイカストは、自動車産業において軽量部品を大量生産するための最も費用対効果の高い技術です。しかし、このプロセスの生産性は金型寿命に大きく左右されます。金型やコアは、最大120MPaの高圧、最大600°Cの高温、そしてアルミニウム溶湯の高速な流れといった、極めて過酷な熱的、機械的、化学的負荷にさらされます。
これらの要因が引き起こす最も一般的な問題は「熱疲労」によるクラックの発生です。微細なクラックのネットワークは、表面材料の欠損につながり、鋳造品質を低下させます。さらに、溶湯の金型への局所的な付着(焼付き)や、溶鋼の溶損も、金型寿命を縮める深刻な問題です。これらの損傷は、生産停止、メンテナンスコストの増大、製品品質のばらつきを招き、すべてのHPDC専門家が直面する大きな課題となっています。本研究は、これらの根本的な問題に対処し、金型の耐久性を向上させるための新しい表面処理技術の確立を目指したものです。
アプローチ:研究手法の解明
本研究では、金型表面の耐久性を向上させるため、レーザー表面処理とPVDコーティングを組み合わせた革新的な「デュプレックス処理」が採用されました。
- 母材: 自動車産業のダイカスト金型で広く使用されている、優れた靭性と高温強度を持つUddeholm社のDievar鋼が使用されました。
- 表面前処理: 出力400Wの固体レーザーを用いて、金型表面に局所的なインパルス加熱を行いました。この処理は、材料を溶融させることなく再結晶温度範囲で加熱することを目的としています。レーザー処理後、コーティングの厚さに合わせて表面を研削し、最終的な寸法精度を確保しました。
- PVDコーティング: 2種類の複層PVDコーティングがLarc技術を用いて成膜されました。
- AIXN³: CrNの接着層の上にAl/CrNのナノレイヤーを積層し、最上層をAlCrNとした、高温での耐摩耗性に優れたコーティングです。
- nACRo³ (TripleCoatings3): CrNの接着層、AlCrNの中間層の上に、非晶質のSi3N4マトリックス中にAlCrNナノ結晶粒子が埋め込まれたナノコンポジット最上層を持つ、より先進的なコーティングです。
- 品質評価: コーティングの品質は、スクラッチテスト(密着性評価)、メルセデステスト(ロックウェル圧子を用いた密着性・凝集性評価)、およびISO 25178に準拠した表面マイクロジオメトリの評価によって厳密に検証されました。さらに、コーティングされたサンプルを680±20°CのAl-Si系合金溶湯に120分および300分間浸漬し、耐食性を評価しました。
ブレークスルー:主要な研究結果とデータ
本研究により、デュプレックスPVDコーティングが金型寿命を延ばす上で非常に有効であることが、具体的なデータによって示されました。
発見1:高温のアルミ溶湯に対する優れたバリア性能
コーティングされたサンプルを高温のアルミニウム溶湯に長時間浸漬する耐食性試験において、デュプレックスコーティングは優れた保護性能を発揮しました。論文の図14に示されているように、レーザー処理された表面に成膜されたAIXN³およびnACRo³コーティングは、680±20°Cの溶湯に300分間浸漬された後でも、母材と溶湯の間に緻密で一体性のあるバリアを形成し続けました。これは、コーティングが溶損や焼付きに対して強力な耐性を持つことを示しています。
発見2:レーザー前処理によるコーティング密着性の大幅な向上
コーティングの品質評価試験により、非常に高い密着性が確認されました。スクラッチテストでは、実用上「満足のいく密着性」とされる臨界荷重40Nを大幅に上回る約50Nで基材の露出が確認されました。また、1500Nの荷重をかけるメルセデステスト(図12、図13参照)では、圧痕周囲のクラックはごくわずかで、剥離も最小限に抑えられており、密着性等級はHF 1-2(良好な密着性)と評価されました。これらの結果は、レーザー前処理がPVDコーティングの密着性を高める上で有効であることを裏付けています。
実務への示唆:研究開発と製造現場への応用
本論文の考察と結論に基づき、各専門分野のプロフェッショナルに向けた実用的な知見を以下に示します。
- プロセスエンジニア向け: この研究は、レーザーによる局所的な表面加熱と複層PVDコーティングを組み合わせることで、金型の耐熱疲労性や耐溶損性を大幅に向上させられることを示唆しています。これにより、サイクルタイムの短縮や生産効率の向上に貢献する可能性があります。
- 品質管理チーム向け: 論文で用いられたスクラッチテストやメルセデステストは、自社の金型に施されたコーティングの密着性や品質を評価するための有効な基準となり得ます。特に、臨界荷重(Fz)や密着性等級(HF)といった指標は、新しい品質検査基準を策定する上で参考になります。
- 設計エンジニア向け: この研究結果は、金型の機能表面にデュプレックス処理を施すことで、熱的・機械的ストレスに対する耐久性が向上することを示しています。これにより、従来は早期の金型損傷が懸念されたような、より複雑な形状や薄肉の製品設計の可能性が広がります。
論文詳細
[Use of Duplex PVD Coatings to Increase the Life of Moulds and Cores for die Casting of Aluminium Alloys in the Automotive Industry]
1. 概要:
- Title: Use of Duplex PVD Coatings to Increase the Life of Moulds and Cores for die Casting of Aluminium Alloys in the Automotive Industry
- Author: Janette Brezinová, Ján Viňáš, Miroslav Džupon, Dagmar Jakubeczyová, Jakub Brezina, Henrich Sailer, Ján Hašuľ, Michal Považan
- Year of publication: 2022
- Journal/academic society of publication: Acta Mechanica Slovaca
- Keywords: PVD coatings, laser surface remelting, die casting of aluminium, tribology
2. Abstract:
The paper presents the results of research aimed at increasing the life of moulds and cores for high-pressure aluminium casting. The castings produced are intended for the automotive industry. Local impulse heating was applied to the surface of the base material of the Uddeholm Dievar moulds. Three heating rates were used. After surface treatment, structural analysis was performed. PVD coating nACRo³ was applied to the surface treated in this way. Coating deposition was performed by Larc technology. The quality of the coating was evaluated on the basis of the Scratch test and the Mercedes test. After laser treatment of the material surface and application of nACRo³ coating, the surface microgeometry was evaluated according to ISO 25 178. The coated surface was then immersed in an Al – Si-based alloy melt at a temperature of 680 ± 20°C and remaining in the melt for 120 and 300 min. Experimental work has confirmed that the resistance of the mould surface has significantly increased.
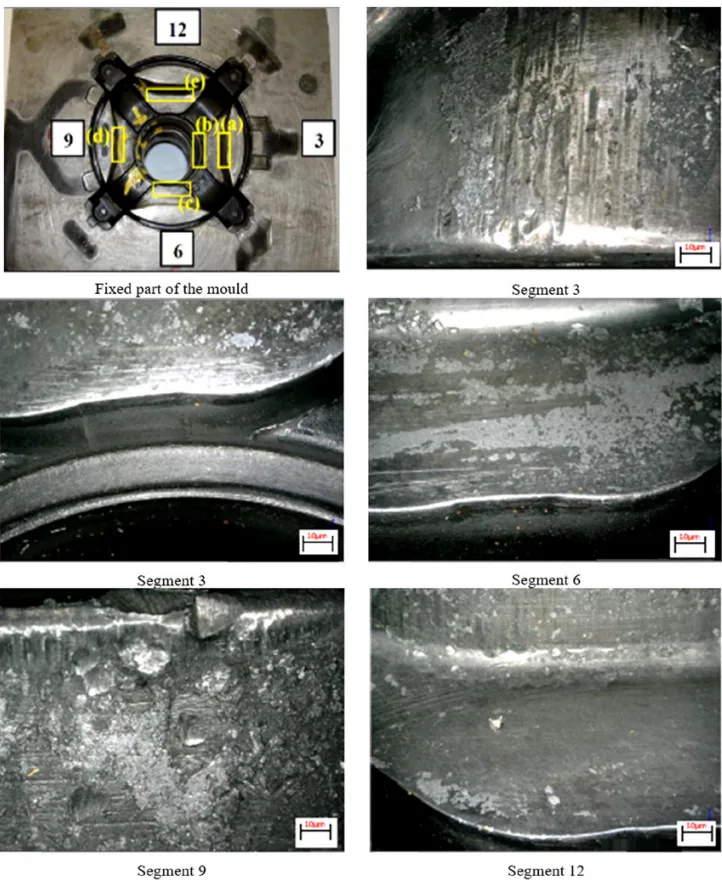

3. Introduction:
Aluminium and plastic castings are of great importance in the automotive industry. They are usually produced in metal moulds for die casting and injection moulding. Die casting moulds are made of chrome or tool steel and are heat treated to a hardness between 29 and 48 HRC. Mould life is a major factor in the die casting process and this strongly affects the productivity of mass production. Depending on the application of the casting or mould, different types of mould damage occur. Cracking caused by thermal fatigue is the most common mistake in the life cycle of a mould. Thermal fatigue cracking is often observed on the tool surface as a network of fine cracks or as individual and distinct cracks. The formation of thermal fatigue cracks leads to the loss of surface material in the form of small fragments. Other common reasons for damage are tensile cracks caused by structural notches, local adhesion of the casting alloy to the tool, i.e. soldering, and steel erosion supported by the casting of molten metal or plastic. Plastic injection moulds are exposed to lower operating temperatures, while pressure cycles are more demanding, and therefore mechanical fatigue damage and overload failures can occur [1]. The mould parts and mould cores for casting aluminium alloys must have suitable physical and mechanical properties at elevated temperatures. These properties are essentially defined by thermal and mechanical stress, as well as the interaction at the interface between the mould and the aluminium alloy melt. In particular, high rates of turbulent to dispersive filling of the mould cavity with an aluminium alloy melt, high hydrodynamic pressures generated by the melt on the mould part and relatively high temperatures on the surface of the mould parts can significantly shorten the life of moulds and cores.
4. 研究の概要:
研究トピックの背景:
自動車産業におけるアルミニウム鋳造部品の生産性向上には、金型寿命の延長が不可欠である。金型は熱疲労、摩耗、溶損、腐食といった複合的な要因で損傷し、特に熱疲労によるクラックが最も一般的な損傷形態である。
従来の研究状況:
これまでにも様々な表面処理技術が研究されてきたが、特に高圧ダイカストのような過酷な環境下では、コーティングの密着性や耐久性が課題となっていた。PVDコーティングの性能を最大限に引き出すためには、コーティング前の母材表面の改質が重要であると考えられている。
研究の目的:
本研究の目的は、局所的なレーザー加熱による表面前処理と、それに続く複層PVDコーティングの成膜を組み合わせた「デュプレックス処理」を開発し、高圧アルミニウムダイカスト用金型およびコアの寿命を向上させることである。
研究の核心:
研究の核心は、Uddeholm Dievar鋼製の金型母材に対し、レーザー加熱処理を施した上で、従来型のAIXN³コーティングと新規設計のnACRo³ナノコンポジットコーティングを成膜し、その機械的特性、密着性、耐食性を評価することにある。
5. 研究方法
研究デザイン:
本研究は、実験室レベルでの表面処理と評価を組み合わせた実験的アプローチを採用している。まず、レーザー処理パラメータ(スキャン速度)を最適化し、その後、2種類のPVDコーティングを施したサンプルを作製した。これらのサンプルの性能を、未処理のサンプルと比較評価した。
データ収集と分析方法:
- 機械的特性: マイクロビッカース硬さ試験(HV0.025)
- 密着性: スクラッチテスト、メルセデステスト(ロックウェルC圧子による圧痕評価)
- 表面形状: ISO 25178に準拠した3D表面粗さ測定
- 耐食性: Al-Si系合金溶湯への浸漬試験
- 微細構造: FIB(集束イオンビーム)加工による断面観察、SEM(走査型電子顕微鏡)観察
研究対象と範囲:
研究対象は、自動車産業向けの高圧アルミニウムダイカストに使用される金型およびコアである。母材としてUddeholm Dievar鋼を用い、レーザー加熱と2種類のPVDコーティング(AIXN³、nACRo³)を組み合わせた表面処理の効果を検証することに範囲を限定している。
6. 主要な結果:
主要な結果:
- レーザー前処理とPVDコーティングを組み合わせたデュプレックス処理により、金型表面の耐性が大幅に向上した。
- コーティングは、スクラッチテストとメルセデステストにおいて高い密着性を示した(HF等級1-2)。
- 680±20°CのAl-Si系合金溶湯に300分間浸漬した後でも、コーティングは緻密で一体性を保ち、母材と溶湯の間の有効なバリアとして機能した。
- ISO 25178に基づく表面マイクロジオメトリのパラメータは、レーザー熱処理と研削による表面前処理によって大きな影響を受けなかった。
図の名称リスト:
- Figure 1: Cross section of AIXN³ coating made on a FIB (Focused Ion Beam) device
- Figure 2: Cross section of nACRo³ coating performed on a FIB device
- Figure 3: Worn solid half of the mould part - mould insert
- Figure 4: Shaped part of the mould after capillary testing
- Figure 5: Appearance of cracks at the bottom of the mould
- Figure 6: Detail of the worn form; a) Crack around the ejector and the core cavity b) Separating means on the surface of the moulded part c) Contact of the movable core and the moulded part
- Figure 7: Laser surface hardening
- Figure 8: Surface of PVD coatings of control samples and samples after laser treatment and deposition of coatings
- Figure 9: Indents for the nACRo coated sample
- Figure 10: Hardness test HV0.025 from the surface towards the substrate
- Figure 11: Scratch test systems o PVD coatings - laser heat treated substrate; a) PVD coating duplex AIXN³; b) PVD coating duplex nACRo³; c) PVD coating duplex AIXN³ on a laser terated surface; d) PVD coating duplex nACRo3 on a laser terated surface
- Figure 12: Morphology of indentation impression in AIXN3 coating (X = Cr)
- Figure 13: Morphology of indentation indentation into the coating nACR03, LM
- Figure 14: PVD coatings duplex on laser treated and ground surfaces after exposure in Al mel; a) Duplex AIXN³/120 minutes/680+/-20°C/Al-Si; b) Duplex AIXN³/300 minutes/680 +/-20°C/Al-Si; c) Duplex nACRo³/120 minutes/680+/-20°C/Al-Si; d) Duplex nACRo³/300 minutes/680+/-20°C/Al-Si
7. 結論:
本研究では、金型成形部品の革新的な処理方法を開発した。これは、材料を溶融させることなく再結晶温度範囲でレーザー照射による局所的かつ集中的な加熱を行い、その後、必要な形状に仕上げ研削し、アルミニウム鋳造温度で化学的に安定な複層PVDコーティングを成膜するものである。PVDコーティングは高品質であり、スクラッチテストとメルセデステストによって確認された。Al-Si系合金の溶湯に680±20°Cで浸漬した後、コーティングは緻密で一体性を保ち、高温腐食試験後も母材と溶湯の間にバリアを形成した。ISO 25178に従って評価された複層PVDコーティングの表面マイクロジオメトリパラメータは、レーザー熱処理と研削による表面前処理によって大きな影響を受けなかった。
8. 参考文献:
- Changrong Chen et al.: Energy based approach to thermal fatigue life of tool steels for die casting dies. In: International Journal of Fatigue Volume 92, Part 1, November 2016, Pages 166-178.
- J. Lin et al.: Design methodology for optimized die coatings: The case for aluminium pressure die-casting In: Surface and Coatings Technology 201 (2006) pp. 2930-2941.
- K. Domkin, J.H. Hattel, J. Thorborg, Modeling of high temperature- and diffusion-controlled die soldering in aluminium high pressure die casting, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 209 (8) (2009) 4051-4061.
- Sundqvist M., Hogmark S.: Effects of liquid aluminium on hot-work tool steel Tribol. Int. 26 (1993) in International Journal of Fatigue p. 129.
- H. Zhu, J. Guo, J. Jia, Experimental study and theoretical analysis on die soldering in aluminium die casting, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 123 (2) (2002) 229-235.
- Z.W. Chen, M.Z. Jahedi, Die erosion and its effect on soldering formation in high pressure die casting of aluminium alloys, Mater. Des. 20 (6) (1999) 303-309.
- K. Venkatesan, R. Shivpuri, Experimental and numerical investigation of the effect of process parameters on the erosive wear of die casting dies, J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 4 (2) (1995) 166-174. R. Markežič et al. Engineering Failure Analysis 95 (2019) 171-180179.
- A Mohammed, M.B. Marshall, R. Lewis, Development of a method for assessing erosive wear damage on dies used in aluminium casting, Wear 332-333 (2015)1215-1224.
- LF. Hou, Y.H. Wei, Y.G. Li, B.S. Liu, H.Y. Du, C.L. Guo, Erosion process analysis of die-casting inserts for magnesium alloy components, Eng. Fail. Anal. 33 (2013)457-564.
- D.W.C. Baker, K.H. Jolliffe, D. Pearson, The resistance of materials to impact erosion damage, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 260 (1110) (1966) 193-203.
- A. Persson, S. Hogmark, J. Bergström, Temperature profiles and conditions for thermal fatigue cracking in brass die casting dies, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 152(2) (2004) 228-236.
- C. Rosbrook, Analysis of Thermal Fatigue and Heat Checking in Die-Casting Dies: A Finite Element Approach, PhD thesis Ohio State University, 1992.
- F. Medjedoub, G. Dour, S. Le Roux, P. Lamesle, M. Salem, P. Hairy, F. Rézaï-Aria, Experimental conditions and environment effects on thermal fatigue damage accumulation and life of die-casting steel X38CrMoV5 (AISI H11), Int. J. Microstruct. Mater. Propert. 3 (2-3) (2008).
- P. Hansson, "Modern prehardened tool steels in die-casting applications," Materials and Manufacturing Processes, vol. 24, no. 7-8, pp. 824-827, 2009.
- Uddeholm, "Dievar," 2014, (18.10.2021) internet: http://www.uddeholm.com
- D. Klobčar, J. Tušek, B. Taljat, Thermal fatigue of materials for die-casting tooling, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 472 (1) (2008) 198-207.
- D. Schwam, J. F. Wallace, and S. Birceanu, "Die Materials for Critical Applications and Increased Production Rates," Case Western Reserve University, 2002.
- Methodical measurement and evaluation of adhesive cohesive behavior of thin film - substrate systems, 2005, (19.10.2021) internet: https://www.opi.zcu.cz/adheze.html
- J. Tkáčová, E. Zdravecká, E. Evin, M. Tomáš, D. Jakubéczyová: Koroze a ochrana materiálu 63(4) 159-166 (2019).
- D. Klobčar, et al.: Thermo fatigue cracking of die casting dies. In: Engineering Faliure Analysis Volume 20, March 2012, pp. 43-53.
- D. Jakubéczyová, M. Džupon: Effect of the roughness on the adhesive properties of nanocomposite PVD coatings. In Vrstvy a povlaky 2016: 15. ročník konferencie. Rožnov pod Radhoštěm, 17.-18.10.2016. - Plzeň: Západočeská univerzita, 2016, p. 49-55.(Layers and coatings 2016)
専門家Q&A:あなたの疑問に答えます
Q1: なぜPVDコーティングの前にレーザー前処理が必要だったのですか?
A1: レーザー前処理は、母材の表面特性を改質し、その後のPVDコーティングとの密着性を高めるために行われました。この局所的な加熱により、母材表面の微細構造が変化し、より強固なデュプレックス(複層)システムを構築することができます。これにより、コーティング単体よりも高い耐久性と耐熱疲労性を実現することが、この研究の狙いです。
Q2: 論文では「nACRo³」と「AIXN³」の2つのコーティングが言及されていますが、主な違いは何ですか?
A2: AIXN³はAlCrNをベースとした従来型のナノ多層膜コーティングです。一方、nACRo³は、非晶質のSi3N4マトリックス中にAlCrNナノ結晶を分散させた、より新しいナノコンポジットコーティングです。この研究では、従来型(AIXN³)と新規設計(nACRo³)の両方を試験することで、新しいナノコンポジット構造が過酷なダイカスト環境下でどのような性能向上をもたらすかを比較評価しています。
Q3: レーザー処理による硬さの向上はどの程度でしたか?
A3: 論文によると、レーザー処理を施した基材上のコーティング領域では、母材と比較して約18.6~25%のHV0.025硬度の上昇が記録されました。この硬度上昇は、レーザー加熱による表面層の微細構造変化に起因するもので、耐摩耗性の向上に寄与すると考えられます。
Q4: 論文で言及されている「メルセデステスト」とは、通常のロックウェル硬さ試験とどう違うのですか?
A4: メルセデステストは、単に硬さを測定するのではなく、コーティングシステムの密着性・凝集性を評価するために特化した圧痕法です。ロックウェル圧子を用いて1500Nという高い荷重をかけ、圧痕の周囲に発生するクラックや剥離の形態をHF1からHF6までの等級で評価します。これにより、コーティングが基材にどれだけ強固に密着しているかを質的に判断することができます。
Q5: レーザー処理後、コーティング前に表面を研削した目的は何ですか?
A5: 研削の目的は2つあります。第一に、レーザー処理によって表面に生じる可能性のある微細な欠陥を除去することです。第二に、PVDコーティングの膜厚(この研究では2マイクロメートル)分だけ表面をあらかじめ削り込む(アンダーカットする)ことで、コーティング後の最終的な金型コアの寸法が要求される公差内に収まるようにするためです。これにより、寸法精度を維持したまま表面改質が可能になります。
結論:より高い品質と生産性への道を開く
高圧アルミニウムダイカストにおける金型寿命の短さは、生産性を制限する根深い課題です。本研究で示された、レーザー表面前処理と複層PVDコーティング 金型寿命を延ばすためのデュプレックス処理は、この課題に対する強力かつ実証された解決策を提示しています。特に、高温のアルミニウム溶湯に対する優れたバリア性能と、基材への高い密着性は、熱疲労や溶損といった金型損傷の主要因を効果的に抑制することを示唆しています。
この研究は、製造現場のエンジニアにとって、金型のメンテナンス間隔を延長し、ダウンタイムを削減し、最終的にはより高い生産性と安定した鋳造品質を実現するための新たな道筋を示すものです。
CASTMANでは、お客様がより高い生産性と品質を達成できるよう、最新の業界研究を応用することに尽力しています。本稿で議論された課題がお客様の事業目標と一致する場合、これらの原理を貴社の部品にどのように実装できるか、ぜひ当社のエンジニアリングチームにご相談ください。
著作権情報
- 本コンテンツは、[Janette Brezinová]らによる論文「[Use of Duplex PVD Coatings to Increase the Life of Moulds and Cores for die Casting of Aluminium Alloys in the Automotive Industry]」を基にした要約および分析です。
- 出典: https://doi.org/10.21496/ams.2022.003
本資料は情報提供のみを目的としています。無断での商業利用は禁じられています。
Copyright © 2025 CASTMAN. All rights reserved.