この技術要約は、Brian Mason氏、Keith Lawes氏(RCV Engines Limited)、および平川浩一氏(KAAZ株式会社)がSETC2022 New Product Technology Session(2022年)で発表した学術論文「[Rotary Valve 4-Stroke Engines for General Purpose Power Equipment and Unmanned Systems]」に基づいています。本文書は、高圧ダイカスト(HPDC)の専門家向けに、CASTMANの専門家がGemini、ChatGPT、GrokなどのLLM AIの支援を受けて分析・要約したものです。
![Figure 1. Small powered two-wheeler technology trends in Taiwan 2002 to 2022 [3].](https://castman.co.kr/wp-content/uploads/image-2745.webp)
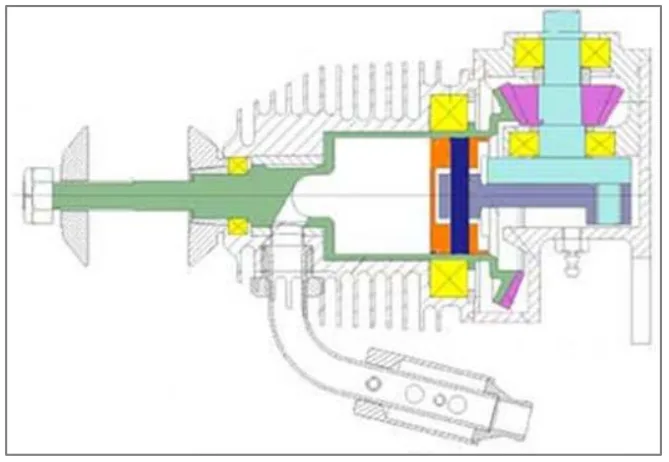
Figure 3. Section through the RCV SP “Rotating Cylinder Valve" model aircraft engine.
キーワード
- 主要キーワード:ロータリーバルブ4ストロークエンジン
- 副次キーワード:高圧ダイカスト(HPDC)、小型エンジン技術、UAVエンジン、マルチ燃料エンジン、ネットゼロカーボン燃料、出力重量比、ADC12ダイカスト
エグゼクティブサマリー
- 課題: プロ用動力工具から長距離UAVに至るまで、小型エンジン応用分野では、厳格化する排ガス規制をクリアし、高い出力重量比を提供し、将来のネットゼロカーボン燃料で稼働できるバッテリー動力の代替技術が求められています。
- 手法: 研究チームは、先進的なロータリーバルブ(RCV)4ストロークエンジンシステムを開発し、テストしました。これには、UAV向けのマルチ燃料「DF」エンジンシリーズと、シリンダーをADC12合金の高圧ダイカスト(HPDC)で製造する高出力量産型「CK1」エンジンが含まれます。
- 核心的な成果: RCVエンジン設計は、卓越した出力重量比(25ccのCK1エンジンは一般的な4ストローク競合モデルより60%高い出力を実現)、JP8や合成燃料を含む真のマルチ燃料対応能力、そして低い排出ガスを、拡張・量産可能なフレームワーク内で全て達成しました。
- 結論: ロータリーバルブ技術は、性能、航続距離、燃料の柔軟性が妥協できないプロフェッショナルおよび無人システム分野において、内燃機関の未来を拓く、検証済みで実現可能な道筋であることを証明しました。
課題:この研究がHPDC専門家にとって重要な理由
数十年にわたり、小型エンジン市場は2ストロークエンジンの「出力」と4ストロークエンジンの「排ガス性能」との間のトレードオフによって定義されてきました。今日、この状況はバッテリー電気(BE)システムへの移行と、2050年までのネットゼロカーボン排出という世界的な目標によってさらに複雑化しています。
BEシステムは多くの消費者向け製品に適していますが、出力、重量、航続距離、迅速な燃料補給が重要となる要求の厳しいプロフェッショナル用途では不十分です。長時間の飛行が必要な無人航空機(UAV)や、遠隔地で使用されるプロ用ハンドヘルド工具は、充電ステーションに縛られるわけにはいきません。
これは、新世代の内燃機関(ICE)を開発するという重大なエンジニアリング課題を提起します。このエンジンは、強力かつ軽量であるだけでなく、低い排出ガス、高い燃費効率、そして将来の持続可能な合成燃料を含む多様な燃料で稼働する能力を備えていなければなりません。本論文は、これらの厳しい基準を満たす強力なソリューションを提示します。
アプローチ:研究方法論の分析
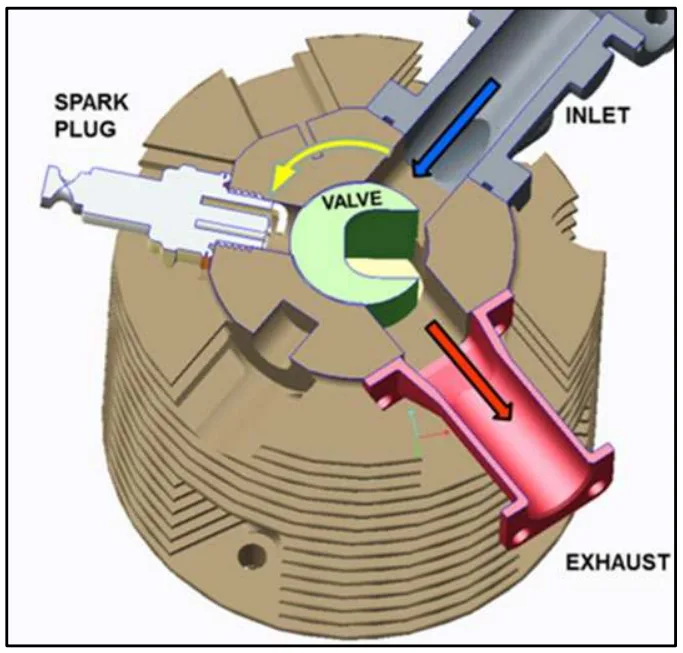
この課題に取り組むため、研究者たちは革新的な「ロータリーバルブ」4ストロークエンジン設計に焦点を当てました。ポペットバルブ、カム、スプリングを備えた従来のエンジンとは異なり、RCVコンセプトは単一の回転バルブを使用して吸気と排気の流れを制御します(図4参照)。このコア技術は、2つの異なる製品ラインに展開されました。
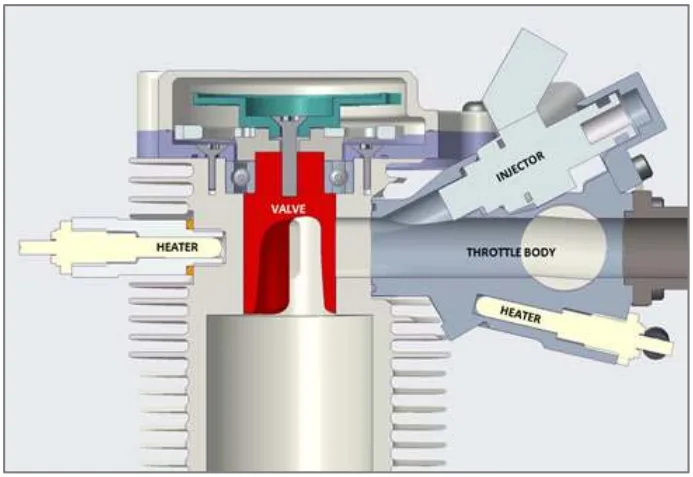
- DFエンジンシリーズ: 高性能UAV用途に特化したこれらのエンジン(35cc~140cc)は、マルチ燃料、特にJP8のような重質燃料への対応能力を重視して設計されており、電子燃料噴射装置を特徴としています。
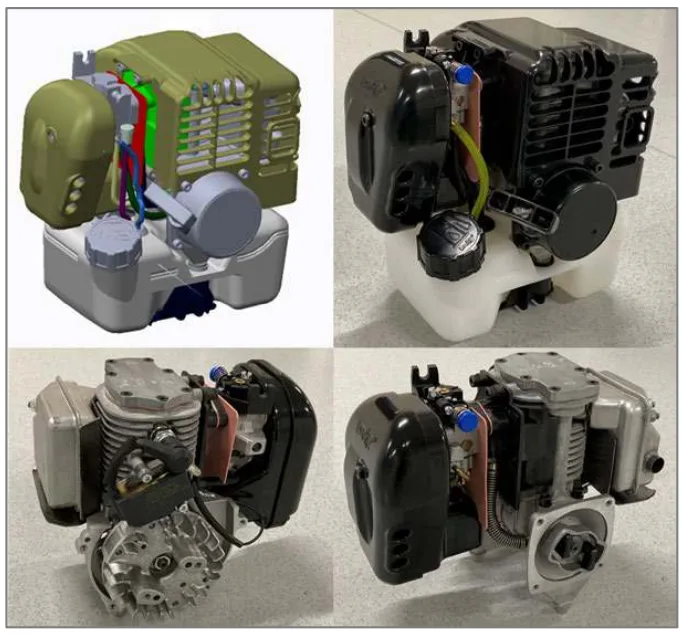
- CK1エンジン: ブラシカッターのような大量生産汎用用途向けに開発された25ccエンジンです。製造業界にとって特に重要なのは、CK1が大量生産を前提に設計されている点です。そのシリンダーはADC12アルミニウム合金でダイカストされ、シリンダーボアとバルブボアにはニッケルシリコンカーバイドコーティングが施されており(図19)、実用的でコスト効率の高い市場投入経路を示しています。
開発プロセスでは、物理的なテストと高度なシミュレーションが組み合わされました。バルブシステムの熱管理のための熱有限要素解析(FEA)(図6)や、冷却システムを最適化するための計算流体力学(CFD)(図18)が活用されました。
核心的な成果:主要な研究結果とデータ
この研究は、RCV技術が出力、燃料柔軟性、製造可能性において明確な優位性を持つことを示す強力な結果を生み出しました。
- 成果1:前例のない出力重量比: 25ccのCK1エンジンは競合製品を圧倒します。市場の一般的な25cc 4ストロークエンジンより60%多い1.2kW以上の出力を発生させます。図21が示すように、広い速度域(8000~11500rpm)で高出力を維持します。これにより、出力重量比は0.35kW/kgとなり、他の4ストロークエンジンよりも著しく優れています(表3)。
- 成果2:真のマルチ燃料およびネットゼロ対応能力: DFエンジンシリーズは、多様な燃料で安定して稼働する能力を証明しました。ガソリンだけでなく、JP8のような低オクタン価の灯油系「重質燃料」でもノッキングを起こさずに作動します。決定的なことに、DF35エンジンは英国空軍(RAF)がネットゼロカーボン合成航空燃料で飛行させた初のドローンに使用され(図13、参考文献[21])、持続可能な未来への実用性を証明しました。
- 成果3:大量HPDC製造のための設計: この研究は、この先進的なエンジンアーキテクチャが単なる理論的な概念ではないことを証明しています。CK1エンジンのシリンダーは、HPDC産業の主力合金であるADC12でダイカストされるように明確に設計されています。ピストンとロータリーバルブの両方を収容するこの複雑な部品を鋳造し、耐久性のあるニッケルシリコンカーバイドコーティングを施す能力(図19)は、この技術がコスト効率の良いスケーラブルな生産の準備が整っていることを裏付けています。
- 成果4:複雑な後処理装置なしでの低排出ガス: CK1エンジンは、厳しいEU Stage Vおよび米国EPA Phase 3の排ガス規制をクリアしています。テスト結果では、CO排出量は118.0 g/kW.h、HC+NOx排出量は20.8 g/kW.hであり、触媒コンバーターを必要とせずに法規制の基準値を大幅に下回っています(表4)。
HPDC製品への実践的示唆
この研究は学術的な実践にとどまらず、高品質・高精度のダイカスト製品にとって重要な新しい市場機会を示唆しています。研究結果は製造業者に直接的な影響を与えます。
- プロセスエンジニアへ: 本論文は、ADC12ダイカスト後に特殊な表面コーティングを施すことで、複雑な高性能エンジン部品を製造する経路を検証しています(図19)。この成功事例は、複雑な内部形状、高い熱安定性、耐摩耗性を要求される部品の生産にHPDCの扉を開き、従来の部品設計の枠を超えさせます。
- 品質管理担当者へ: RCVエンジンの信頼性は、ロータリーバルブとダイカスト製シリンダーボア間の精密な滑り隙間の維持にかかっています。この要件は、ADC12鋳物の寸法精度、安定性、健全性に高い価値を置くものです。これは、このような先進的な高性能アプリケーションの要求を満たすために、HPDCにおける堅牢なプロセス管理と厳格な品質保証の重要性を強調しています。
- 金型設計者へ: 統合されたCK1シリンダーおよびバルブボアユニット(図19)の鋳造成功は、高度に統合された多機能部品を製造するためにHPDCを活用する強力なケーススタディとなります。このアプローチは、部品点数を削減し、組み立てを合理化し、システム全体のコストを削減することで、先進的な思考を持つ製品設計者やダイカストメーカーに競争優位性を提供します。
論文詳細
Rotary Valve 4-Stroke Engines for General Purpose Power Equipment and Unmanned Systems
1. 概要 (Overview):
- Title: Rotary Valve 4-Stroke Engines for General Purpose Power Equipment and Unmanned Systems
- Author: Brian Mason and Keith Lawes (RCV Engines Limited), Koichi Hirakawa (KAAZ Corporation)
- Year of publication: 2022
- Journal/academic society of publication: SETC2022 New Product Technology Session
- Keywords: Rotary valve, 4-stroke, UAV, heavy fuel, general purpose engine, emissions, power to weight
2. 抄録 (Abstract):
A rotary valve 4-stroke combustion system has been applied to engines for unmanned air vehicles (UAVs) and general-purpose power equipment. The RCV rotary valve system can operate on a range of fuels and at high levels of power, together with typical 4-stroke exhaust emissions and fuel economy. The DF35 and DF70 engines, for UAVs and unmanned hybrids, are based around a 35 cc cylinder configured as a single or boxer twin, with either air or liquid cooling. The fuel injected DF engines achieve 63 kW/litre on either gasoline or kerosene-based fuels such as JP8. The 25 cc multi-position general purpose CK1 engine is configured into a brushcutter package. CK1 has completed development for volume production, achieves 48 kW/litre. Recent small engine developments are application specific. Combining the multi-fuel capability of the DF engine with volume production technology of the CK1 engine, the RCV rotary valve combustion system provides a viable technology for future small engine applications.
3. 緒言 (Introduction):
Small internal combustion engines (ICE) are used on lightweight two wheeled vehicles, portable lawn and garden equipment, and unmanned air vehicles. These applications have traditionally favoured 2-stroke over 4-stroke engines for cost and power to weight reasons. However, this position has changed over the last 30 years with legislation to reduce toxic tailpipe exhaust emissions for improved air quality. The market today includes a mix of low emissions 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines, with an increasing uptake of battery/electric (BE) systems. With the global effort to reduce carbon emissions to net-zero by 2050, it is necessary to consider attributes that small engine need to have where BE systems are not viable. The introduction of exhaust emissions legislation has led to shifts in engine technology in two-wheeler and small off-road engine (SORE) markets, with a future challenge being the control of particulate emissions.
4. 研究概要 (Summary of the study):
研究テーマの背景 (Background of the research topic):
The need for high-performance, low-emission, and fuel-flexible small internal combustion engines persists in applications where battery-electric systems are not viable, such as long-range UAVs and professional handheld equipment. This research addresses the challenge of meeting future requirements, including operation on net-zero carbon fuels.
先行研究の状況 (Status of previous research):
Previous developments in small engines have focused on transitioning from 2-stroke to 4-stroke engines to meet emissions regulations, and more recently, the introduction of battery-electric systems. For specific applications like UAVs, efforts have been made to convert small engines to run on heavy fuels (HF), often with a performance penalty. This paper builds on over 20 years of RCV Engines' experience in rotary valve technology.
研究の目的 (Purpose of the study):
The study aims to demonstrate that the RCV (Rotary Valve) 4-stroke combustion system is a viable and superior technology for future small engine applications. It showcases the system's benefits through two distinct engine lines: the multi-fuel DF range for unmanned systems and the high-power, volume-production CK1 engine for general-purpose equipment.
中核的研究 (Core study):
The core of the study is the design, development, testing, and characterization of the RCV engine technology. This involves detailing the engine architecture, materials (including diecast ADC12), and manufacturing processes. Performance metrics such as power output, fuel consumption (BSFC), emissions, and multi-fuel capability are measured and compared against conventional engines and legislative standards.
5. 研究方法論 (Research Methodology)
研究設計 (Research Design):
The research involved the parallel development of two engine platforms based on the same core RCV technology: the specialist DF range for UAVs and the general-purpose CK1. This dual approach allowed for the demonstration of both high-end multi-fuel capabilities and suitability for cost-effective volume production.
データ収集・分析方法 (Data Collection and Analysis Methods):
Data was collected through extensive dynamometer testing to measure power, torque, and BSFC across various engine speeds and fuel types (gasoline, JP8). Emissions were measured by an independent body for EU homologation. Durability was assessed through a 400-hour test cycle, and real-world performance was confirmed via field testing. Engineering analysis tools like FEA and CFD were used to optimize thermal and cooling system designs.
研究テーマと範囲 (Research Topics and Scope):
The research covers the engine's mechanical design, combustion system, heavy fuel operation, manufacturing methods (including HPDC for the CK1 cylinder), performance characteristics, emissions compliance, and application in both UAV/hybrid systems and handheld power tools.
6. 主な結果 (Key Results):
主な結果 (Key Results):
- The RCV DF engines achieve high power density (63 kW/litre) and operate effectively on both gasoline and heavy fuels like JP8.
- The RCV combustion system exhibits low detonation sensitivity, enabling efficient operation on low-octane fuels without performance loss.
- The 25cc CK1 engine produces 1.25 kW, 60% more power than comparable 25cc 4-stroke engines, with a superior power-to-weight ratio of 0.35 kW/Kg.
- The CK1 engine, utilizing a diecast ADC12 cylinder, is designed for volume production and meets stringent EU Stage V and EPA Phase 3 emissions limits.
- The technology has been successfully tested with net-zero carbon synthetic aviation fuel in a UAV application.
図表リスト (Figure Name List):

- Figure 1. Small powered two-wheeler technology trends in Taiwan 2002 to 2022 [3].
- Figure 2. Future small engine application scenarios towards 2050.
- Figure 3. Section through the RCV SP “Rotating Cylinder Valve" model aircraft engine.
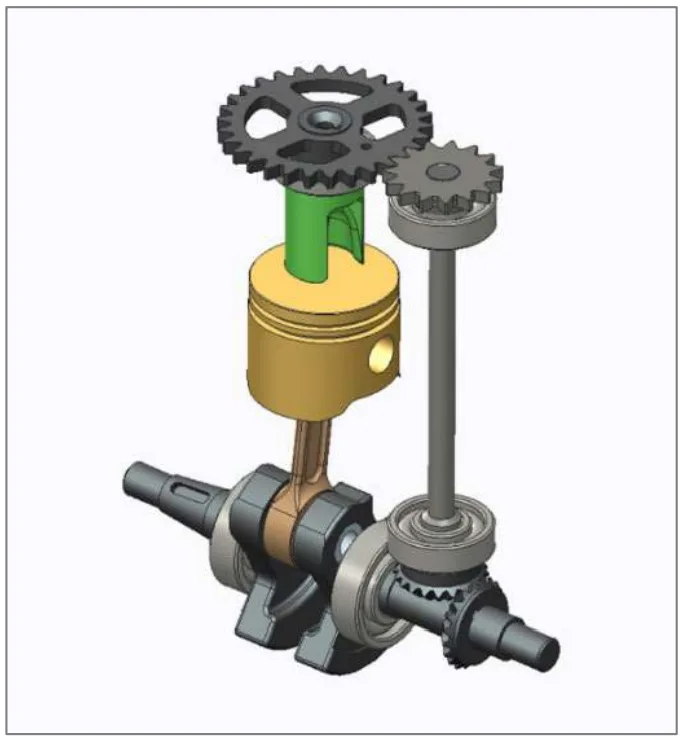
- Figure 4. RCV rotary valve timing drive.
- Figure 5. RCV DF engine – section through the rotary valve, ports, and sparkplug.
- Figure 6. Valve thermal analysis example showing temperature distribution.
- Figure 7. Rotary valve — effective exhaust valve area compared to a mini-4-stroke.
- Figure 8. Section through the DF35 throttle body.
- Figure 9. RCV DF70 combustion system response to AFR on JP8 fuel tested with a 12 x 8 propeller.
- Figure 10. RCV DF Engine Range.
- Table 1. DF35 and DF70 general Specification
- Figure 11. DF35 full load power and BSFC on JP8 fuel.
- Figure 12. RCV EFI Engine Control Unit.
- Figure 13. DF35 flight test on net-zero carbon synthetic aviation fuel.
- Figure 14. DF70 2 kW hybrid module installed an electric motorcycle.
- Figure 15. CK1 engine – external views.
- Table 2. CK1 engine specifications.
- Figure 16. Section through the ports of the CK1 engine.
- Figure 17. Section through the CK1 airbox.
- Figure 18. CFD example from CK1 engine cooling system development.
- Figure 19. Section through the CK1 cylinder with plated surfaces shown in green.
- Table 3. Comparison of general-purpose engine dimensions and power to weight.
- Figure 20. CK1 engine - main dimensions.
- Figure 21. CK1 power and BSFC with catalogue power levels for 25cc and 35cc 4-strokes.
- Table 4. CK1 exhaust emissions compared to current EU and EPA limits
- Figure 22. CK 4-stroke compared to manufacturers catalogue power data for 2-stroke and 4-stroke brushcutter engines.
- Figure 23. CK1 field testing in South Korea.
7. 結論 (Conclusion):
The RCV rotary valve combustion system demonstrates benefits through ICE product applications for UAVs and small general-purpose engines. The multi-fuel DF engine range is established as an ICE option for UAVs and unmanned systems with increased use in hybrid applications. The CK1 engine shows strong power, sustained at high engine speeds with 4-stroke emissions and fuel economy. The combination of the DF multi-fuel combustion system with volume production technology for the CK1 engine demonstrates that RCV rotary valve technology is a viable candidate for future small engines.
8. 参考文献 (References):
- [論文に引用された参考文献を翻訳したり、一部を省略したりせずにそのまま記載します。]
- Kamakaté, F., and Gordon, D., “Managing Motorcycles: Opportunities to Reduce Pollution and Fuel Use from Two- and Three-Wheeled Vehicles”, www.ict.org, 2009.
- Ricardo UK, “Challenges for Future Motorcycle Emissions Control”, https://cdn.ricardo.com/motorcycle/media/events/rmc%207.0/motorcycle-emission.pdf, 2022.
- Taiwan Transportation Vehicle Manufacturers Association, https://www.ttvma.org.tw/en/statistics#2, June 2022.
- Favrere, C., May, J., Bosteels, D., Tromayer, J., and Neumann, G., “A Demonstration of Emissions’ Behaviour of Various Handheld Engines Including Investigations on Particulate Matter”, SAE Technical Paper 2013-32-9130, 2013.
- California Air Resources Board, “CARB approves updated regulations requiring most new small off-road engines to be zero emission by 2024”, https://ww2.arb.ca.gov/news/carb-approves-updated-regulations-requiring-most-new-small-road-engines-be-zero-emission-2024, December 2021.
- Ausserer, J., Polanka, M., Baranski, J., and Litke, P., “Mapping of Fuel Anti-Knock Requirements for a Small Remotely Pilot Aircraft Engine”, SAE Technical Paper 2016-32-0045, 2016.
- Cathcart, G., Dickson, G., and Ahern, S., “The Application of Air-Assist Direct Injection for Spark-ignited Heavy Fuel 2-Stroke and 4-Stroke Engines”, SAE Technical Paper 2005-32-0065, 2005.
… [論文の全参考文献リスト] … - "RAF’s First Synthetic Fuel Drone Flight", https://www.gov.uk/government/news/rafs-first-synthetic-fuel-drone-flight, March 2022.
専門家Q&A:主要な質問への回答
Q1:このロータリーバルブ技術は、なぜ小型エンジンにとって重要な進歩なのですか?
A1: この技術は、従来のポペットバルブエンジンとバッテリーシステム双方の主要な制約を解決します。著しく高い出力重量比を実現し(図21参照)、未来志向のネットゼロカーボン燃料で稼働し、低い排出ガスを維持します。これにより、性能、航続距離、運用の柔軟性が重要となるプロフェッショナル用途に最適です。[出典:「Summary」および「Conclusions」セクション]
Q2:この技術は、本当にJP8のような重質燃料を大きな性能低下なしに扱うことができるのですか?
A2: はい。論文では「RCVロータリーバルブ燃焼システムは重質燃料(HF)でノッキング制限を受けず、ガソリン作動時と同様の出力とBSFCを生成する」と明確に述べています。これは、コンパクトな中央燃焼室と均一な表面温度がデトネーションを防ぐためです。[出典:5ページ、「In terms of abnormal combustion, detonation or knock…」]
Q3:この技術は、軍用UAVのようなハイエンドの専門用途に限定されますか?
A3: いいえ。DFエンジンシリーズは専門的なUAV向けに調整されていますが、CK1エンジンは大量生産される汎用アプリケーション向けに特別に開発されました。論文では、CK1が「大量生産による低コスト化」を目指して設計され、その中核部品であるシリンダーがADC12合金のダイカストであることを強調しており、コスト効率の高いマスマーケット製品への適合性を示しています。[出典:7ページ「CK1 General Purpose Engine」セクションおよび10ページ「Low cost through volume production」]
Q4:製造の観点から、CK1エンジンのシリンダーにおける核心的な革新は何ですか?
A4: 核心的な革新は、メインシリンダーボアと独立したバルブボアを一体的に含む、複雑なADC12ダイカスト製シリンダーの量産設計に成功したことです。このダイカスト部品は、耐久性のあるニッケルシリコンカーバイドコーティングで仕上げられます(図19)。これは、高圧ダイカストがこの先進技術の中核部品を大規模に生産するための商業的に実現可能な方法であることを証明しています。[出典:8ページ、「From a manufacturing perspective…」]
Q5:RCVエンジンの燃焼室が、低オクタン価燃料に対してデトネーションに強いのはなぜですか?
A5: 論文では、この特性をロータリーバルブ設計に固有の「コンパクトな中央燃焼室」と「均一な燃焼室表面温度」に起因するとしています。このデトネーションに対する低い感受性はn-ヘプタン燃料評価で確認され、最適トルク(MBT)から20度進角させてもノッキングが発生しなかったことが示されています。[出典:5ページ、「In terms of abnormal combustion, detonation or knock…」]
結論と次のステップ
この研究は、内燃機関の未来に向けた貴重なロードマップを提供します。従来の設計を超えることで、RCVロータリーバルブ技術は、より強力で、より効率的で、燃料柔軟性を持ち、高圧ダイカストのような確立されたプロセスを用いて大規模に製造可能なエンジンを開発するための、明確でデータに基づいた道筋を示しています。
CASTMANは、お客様の最も困難なダイカスト問題を解決するために、最新の業界研究を応用することに専念しています。この高性能アプリケーションにおけるADC12ダイカストシリンダーの成功は、HPDCの可能性を証明するものです。複雑で耐久性があり、精密な部品の製造という課題が貴社の目標と共鳴するならば、ぜひ当社のエンジニアリングチームにご連絡ください。先進的な設計を現実のものにするお手伝いをいたします。
著作権
- 本文書は、「Brian Mason, Keith Lawes, and Koichi Hirakawa」氏の論文に基づいています。論文名:「Rotary Valve 4-Stroke Engines for General Purpose Power Equipment and Unmanned Systems」。
- 論文出典:SETC2022 New Product Technology Session, Paper NPT2022-028.
本文書は情報提供のみを目的としています。無断での商業利用を禁じます。Copyright © 2025 CASTMAN. All rights reserved.