ADC12アルミダイカストのポロシティを劇的に削減:タグチメソッドによる工程パラメータ最適化の鍵
本技術概要は、Veeresh G Balikai氏らによる学術論文「Optimization of process parameters of High Pressure Die Casting process for ADC12 Aluminium alloy using Taguchi method」(International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics、2018年)に基づいています。技術専門家の皆様のために、CASTMANが分析・要約しました。
キーワード
- 主要キーワード: ADC12 アルミダイカスト
- 副次キーワード: 高圧ダイカスト, ポロシティ, 鋳造欠陥, タグチメソッド, 工程パラメータ最適化
エグゼクティブサマリー
- 課題: ADC12アルミニウム合金を用いた高圧ダイカスト(HPDC)製品において、生産性を低下させる主要因であるポロシティ(鋳巣)をいかにして削減するか。
- 手法: タグチメソッドのパラメータ設計アプローチを用い、4つの主要な工程パラメータ(溶湯温度、射出圧力、プランジャー速度1速・2速)を5段階で変更するL25直交配列実験を実施。
- 重要なブレークスルー: プランジャー速度(1速および2速)がポロシティ形成に最も大きな影響(寄与率合計65%以上)を与えることを特定し、ポロシティを最小化する最適なパラメータの組み合わせを導出。
- 結論: ADC12アルミダイカストの品質向上と不良率削減には、特にプランジャー速度の厳密な制御を核とした、データに基づく工程パラメータの最適化が不可欠である。
課題:なぜこの研究がHPDC専門家にとって重要なのか
高圧ダイカスト(HPDC)は、自動車、航空宇宙、エレクトロニクス分野で複雑形状の部品を高い生産性で製造する上で不可欠なプロセスです。特にADC12アルミニウム合金は、その優れた機械的特性とコスト効率から広く利用されています。しかし、ADC12のHPDCにおいて最も頻繁に遭遇する問題が「ポロシティ(鋳巣)」です。溶湯がキャビティに充填される際の乱流によって空気やガスが巻き込まれることで発生するこの欠陥は、製品の機械的強度や圧力気密性を著しく低下させ、最終的に高い不良率とスクラップ率を招き、生産性のボトルネックとなります。本研究は、この根深い課題に対し、科学的アプローチで解決策を提示することを目的としています。
アプローチ:研究手法の解明
本研究では、ポロシティを最小化するための最適な工程条件を見出すために、タグチメソッドを用いた実験計画法(DOE)が採用されました。
- 使用材料: ADC12アルミニウム合金
- 使用設備: 400T HMTモデル 高圧ダイカストマシン
- 主要変数: ポロシティ形成に最も影響が大きいと考えられる以下の4つの工程パラメータが選定され、それぞれ5つの水準で実験が行われました。
- 溶湯温度 (T): 660, 670, 680, 690, 700 (°C)
- 射出圧力 (P): 160, 170, 180, 190, 200 (Kg/m³)
- プランジャー速度-1速 (V₁): 0.26, 0.27, 0.28, 0.29, 0.3 (m/s)
- プランジャー速度-2速 (V₂): 2.6, 2.7, 2.8, 2.9, 3 (m/s)
- 実験計画: 上記の4因子5水準の条件を効率的に評価するため、L25直交配列が用いられました。
- 評価方法: 各実験条件で製造された鋳造品のポロシティは、アルキメデスの原理に基づいて密度を測定し、ADC12合金の理論密度(2.67 g/cm³)と比較することで定量的に算出されました。
ブレークスルー:主要な研究結果とデータ
実験と分散分析(ANOVA)の結果、ポロシティ形成に影響を与えるパラメータの重要度と、ポロシティを最小化する最適な条件が明らかになりました。
発見1:プランジャー速度がポロシティ形成の最重要因子である
分散分析(ANOVA)の結果(Table 4)は、ポロシティ形成に対する各パラメータの寄与度を明確に示しました。 - プランジャー速度(1速): 寄与率 34.012% - プランジャー速度(2速): 寄与率 31.602% - 溶湯温度: 寄与率 11.245% - 射出圧力: 寄与率 2.134%
この結果から、プランジャーの1速および2速の速度が、ポロシティを制御する上で圧倒的に重要なパラメータであることが実証されました。両者を合わせると、寄与率は65%を超えます。
発見2:ポロシティを最小化する最適パラメータの特定
本研究により、ポロシティを最小にするための具体的な最適パラメータの組み合わせが特定されました。 - 溶湯温度: 660°C (レベル1) - 射出圧力: 190 kg/cm² (レベル4) - プランジャー速度 (1速): 0.3 m/s (レベル5) - プランジャー速度 (2速): 3.0 m/s (レベル5)
この最適条件下(Table 3, Trial 21)で製造された鋳造品のポロシティは 0.01738% であり、実験中最悪の条件下(Trial 6)で記録された 4.07073% と比較して、劇的な改善が見られました。
研究開発および製造現場への実践的示唆
本研究結果は、ダイカスト製品の品質と生産性を向上させるための具体的な指針を提供します。
- 工程技術者の方へ: この研究は、ポロシティ削減のためには、特にプランジャー速度(1速および2速)の精密な設定と管理が最優先事項であることを示唆しています。既存の工程条件を見直す際、まずこの2つのパラメータの最適化に注力することで、品質の大幅な改善が期待できます。
- 品質管理チームの方へ: 論文のTable 3に示されるデータは、工程パラメータのわずかな違いがポロシティ率にどれほど大きなばらつきを生じさせるかを明確に示しています。これは、安定した品質を確保するためには、確立された最適パラメータを厳密に維持・監視するプロセス管理が極めて重要であることを意味します。
論文詳細
Optimization of process parameters of High Pressure Die Casting process for ADC12 Aluminium alloy using Taguchi method
1. Overview:
- Title: Optimization of process parameters of High Pressure Die Casting process for ADC12 Aluminium alloy using Taguchi method
- Author: Veeresh G Balikai, I G Siddlingeshwar, Mahesh Gorwar
- Year of publication: 2018
- Journal/academic society of publication: International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics
- Keywords: Optimisation, DOE, Taguchi Method, HPDC, Process parameters, Porosity
2. Abstract:
A study has been carried out to optimize the die casting process parameters in order to achieve the improved quality of high pressure die casting (HPDC) products, which is the challenge for the small and large scale manufacturers of HPDC products. In this study the approach used is the experimental study to optimize the die casting process parameters for the ADC12 aluminum alloys. The ADC12 aluminum alloy components were chosen for the study and objective was to reduce the porosity in these components which help to obtain the good quality castings. The porosity is the most common defect frequently encountered in aluminium high pressure die castings, which increases the rejection rate and scrap rate and reduces the productivity. Porosity formation is closely related to die casting process parameters. Hence in order to minimize the porosity, this paper investigated the effect of process parameters on porosity formation in HPDC of ADC12 alloys and optimization of process parameters carried out using Taguchis parameter design approach. Experiments were conducted by varying selected process parameters with different levels as per Taguchi method. ANOVA was performed to find the significance of parameters on porosity formation in die castings. Results indicated that selected process parameters have significant effect on porosity formation. The optimum process parameters were obtained for minimum porosity in HPDC of ADC12 alloy.
3. Introduction:
High pressure die casting (HPDC) process is an efficient manufacturing process to produce complex, thin and thick wall components economically with high productivity and high dimensional accuracy for automotive, aerospace, defence and other industries [9,13]. In aluminium high pressure die casting process, molten aluminium alloy is injected into a metal mould at high speed and allowed to solidify under high holding pressure [10]. ADC12 based alloys have been widely used in the field of HPDC process to produce lightweight components with low cost, good mechanical properties and high corrosion resistance for electric, electronic and automobile and other applications [5]. In high pressure die casting of ADC12 aluminium alloys, Porosity is the most common defect caused due to entrapment of air/gas and oxides due to the turbulent flow of metal during the cavity filling [8]. This defect is classified as gas porosity (caused due to air trapped air in sleeve), shrinkage porosity (due to solidification of the metal in the gate before solidification in other areas of the casting) and flow porosity (caused due to insufficient pressure towards the end of cavity filling). The mechanical properties and pressure tightness are affected due to presence of porosity in castings. Porosity in a high pressure die casting varies both with part geometry of component and casting parameters of the process [9].
4. Summary of the study:
Background of the research topic:
Porosity is the most common defect in high pressure die castings of ADC12 aluminium alloy, leading to increased rejection rates and reduced productivity. Its formation is closely linked to process parameters.
Status of previous research:
Previous literature has focused on the influence of various process parameters on porosity formation. Studies by Verran et al. (2008), Tsoukalas (2003), and Syrcos (2003) investigated the optimization of injection parameters, machine parameters, and general process parameters using the Taguchi method to reduce porosity and improve casting density.
Purpose of the study:
The objective was to investigate the effects of selected process parameters on casting porosity in ADC12 aluminium alloy and to optimize these parameters using the Taguchi method to minimize porosity and obtain good quality castings.
Core study:
The study involved conducting experiments using an L25 orthogonal array to vary four key process parameters (pouring temperature, injection pressure, 1st phase plunger velocity, 2nd phase plunger velocity) at five different levels. The resulting porosity of the ADC12 castings was measured, and the data was analyzed using S/N ratios and ANOVA to determine the optimal parameter settings for minimum porosity.
5. Research Methodology
Research Design:
The study employed Taguchi's parameter design approach, an experimental technique to find the best combination of process parameters and levels. The quality characteristic for porosity was "Lower the better".
Data Collection and Analysis Methods:
Experiments were conducted on a 400T HMT HPDC machine. For each of the 25 experimental runs defined by the L25 OA, three castings were produced. The density of each casting was measured using Archimedes' principle. Porosity was calculated by comparing the measured apparent density to the theoretical density of ADC12 (2.67 g/cm³). The results were analyzed using Signal-to-Noise (S/N) ratios and Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) to identify the significance of each parameter and the optimal levels.
Research Topics and Scope:
The research focused on optimizing the HPDC process for ADC12 aluminium alloy. The scope was limited to four selected process parameters: pouring temperature, injection pressure, 1st phase plunger velocity, and 2nd phase plunger velocity. The primary response variable was casting porosity.
6. Key Results:
Key Results:
- Plunger velocity (1st phase) and Plunger velocity (2nd phase) were identified as the most significant factors affecting porosity, with contributions of 34.012% and 31.602%, respectively.
- Pouring temperature had a moderate effect (11.245% contribution), while intensification pressure had the least effect (2.134% contribution) within the tested range.
- The optimal process parameters for minimum porosity were determined to be: Pouring temperature at 660°C (Level 1), Intensification pressure at 190 kg/cm² (Level 4), Plunger velocity (1st phase) at 0.3 m/s (Level 5), and Plunger velocity (2nd phase) at 3.0 m/s (Level 5).
- Under these optimal conditions, a minimum porosity of 0.01738% was achieved.
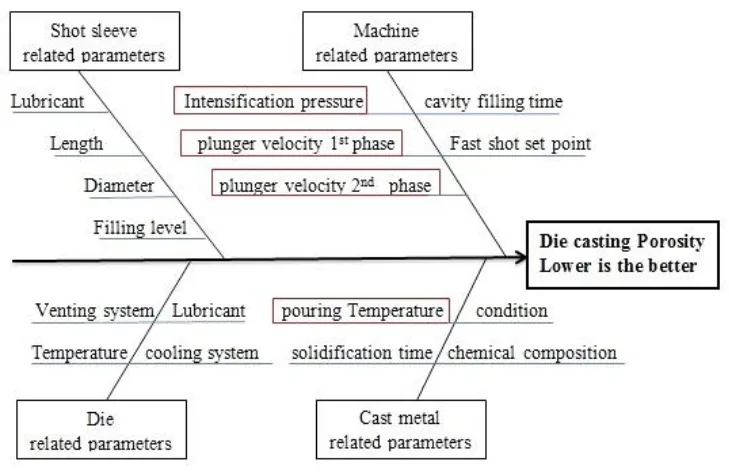
Figure Name List:
- Fig.1. Cause and effect diagram (Ishikawa diagram) for casting porosity
7. Conclusion:
The experimental results show that variations in die casting process parameters have significant effects on the porosity formation of aluminium alloy die casting. Pouring temperature, intensification pressure, plunger velocity (1st phase), and plunger velocity (2nd phase) are influential process parameters affecting porosity in ADC12 aluminium alloy castings. The percentage contribution of each parameter and the optimum process parameters for minimum porosity were determined. The Taguchi Method parameter design approach for the optimisation of the process parameters in HPDC for ADC12 alloy has given satisfactory results by reducing the porosity and improving the quality of the castings.
8. References:
- [1] S. W. Choi, Y. C. Kim, J. I. Cho & C. S. Kang (2008), Influence of die casting process parameters on castability and properties of thin walled aluminium housings, International Journal of Cast Metals Research, 21:1-4, pp.330-333.
- [2] Murray, M.T. (2011) High pressure die casting of aluminium and its alloys, M Murray & Associates Pty Ltd, Australia.
- [3] G.O. Verran, R.P.K. Mendes, L.V.O. Dalla Valentina (2008), DOE applied to optimization of aluminium alloy die castings journal of materials processing technology, 200 pp.120125.
- [4] G.P.Syrcos (2003), Die casting process optimization using Taguchi method, journal of materials processing technology, 135, pp.68-74.
- [5] M.A. Irfan, D. Schwam, A. Karve, R. Ryder (2012), Porosity reduction and mechanical properties improvement in die cast engine blocks, Materials Science and Engineering A 535, pp.108 114.
- [6] V. D. Tsoukalas (2003), The effect of die casting machine parameters on porosity of aluminium die castings, International Journal of Cast Metals Research, 15:6, pp.581-588.
- [7] Guilherme Ourique Verran, Rui Patrick Konrad Mendes, Marco Aurelio Rossi, Influence of injection parameters on defects formation in die casting Al12Si1.3Cu alloy: Experimental results and numeric simulation, Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 179 (2006) pp.190195.
- [8] Anilchandra R. Adamane, Lars Arnberg, Elena Fiorese, Giulio Timelli, Franco Bonollo, (2015), Influence of Injection parameters on the porosity and tensile properties of High pressure die cast Al-Si Alloys: A Review, International Journal of Metalcasting, Volume 9, Issue 1.
- [9] Laihua Wang, Peter Turnley, Gary Savage (2011), Gas content in high pressure die castings, Journal of Materials Processing Technology 211, pp.15101515.
- [10] V.D. Tsoukalas (2008), Optimization of porosity formation in AlSi9Cu3 pressure die castings using genetic algorithm analysis, Materials and Design 29, pp.20272033.
- [11] Roy, R. K. Design of Experiments Using the Taguchi Approach: 16 Steps to Product and Process Improvement, 2001 (J. Wiley, New York).
- [12] Taguchi, G. and Konishi, S. Orthogonal Arrays and Linear Graphs, 1987 (American Supplier Institute, Dearborn, Michigan).
- [13] Quang-Cherng Hsu and Anh Tuan Do (2013), Minimum Porosity Formation in Pressure Die Casting by Taguchi Method, Mathematical Problems in Engineering.
- [14] Taguchi G. Introduction to quality engineering. 1st ed. New York: Asian Productivity Organization, UNIPUB; 1986.
- [15] Logothetis N. Total quality control. 2nd ed. UK: Prentice-Hall International Limited; 1992.
- [16] K.Ch.Apparao and Anil Kumar Birru, Optimization of Die casting process based on Taguchi approach, Materials Today: Proceedings 4 (2017) pp.18521859.
専門家Q&A:技術的な疑問にお答えします
Q1: なぜこの研究では、溶湯温度、射出圧力、プランジャー速度1速・2速という4つのパラメータが選ばれたのですか?
A1: 論文では、これら4つのパラメータが「ポロシティを最小化するために最も重要な工程パラメータとして選ばれた」と述べられています。これは、Fig.1に示されている特性要因図(石川ダイアグラム)を用いて、ポロシティに影響を与える可能性のある多くの要因の中から、特に影響度が大きいと予想されるものが絞り込まれた結果です。このアプローチにより、効率的かつ効果的に最適化を進めることが可能になります。
Q2: 射出圧力の寄与率は2.134%と非常に低いですが、これは圧力が重要ではないということですか?
A2: そうとは限りません。この結果は、実験で設定された範囲(160~200 kg/cm²)においては、他のパラメータ(特に速度)と比較して影響が小さかったことを示しています。しかし、最適条件として190 kg/cm²(レベル4)が選ばれていることから、全体の最適化においては依然として重要な役割を担っています。圧力が低すぎたり高すぎたりすれば影響は大きくなる可能性があり、この範囲内での微調整の効果が比較的小さかったと解釈するのが適切です。
Q3: この分析でS/N比(シグナル対ノイズ比)が使われた実践的な意義は何ですか?
A3: 論文によれば、S/N比は「制御不可能なプロセスパラメータによる応答のばらつきを最小化する」ために使用されます。つまり、単に平均的なポロシティ率を下げるだけでなく、製造ロットごとや製品ごとの品質のばらつきを抑え、常に安定して低いポロシティを達成できる、ロバスト(頑健)な工程条件を見つけ出すことが目的です。これは量産における品質安定化に直結する重要な考え方です。
Q4: この研究ではL25直交配列が使用されていますが、このアプローチの利点は何ですか?
A4: 4つのパラメータをそれぞれ5水準で評価する場合、すべての組み合わせを試す総当たり試験(完全実施要因計画)では5の4乗、つまり625回の実験が必要です。L25直交配列を用いることで、わずか25回の実験で各パラメータが品質に与える影響を効率的かつ統計的に評価できます。これにより、開発期間とコストを大幅に削減しながら、信頼性の高い最適条件を導き出すことが可能になります。
Q5: ポロシティはどのように測定され、その方法は信頼できるものですか?
A5: 論文では、アルキメデスの原理を用いて鋳造品の密度を測定したと記載されています。これは、製品の水中重量と空気中重量を測定することで体積を算出し、密度を求める標準的な手法です。この実測密度を、欠陥のないADC12合金の理論密度(2.67 g/cm³)と比較することで、製品に含まれる空隙の割合、すなわちポロシティ率を算出します。この方法は非破壊で、部品全体の平均的なポロシティを評価するための信頼性が高い手法として広く用いられています。
結論:より高い品質と生産性への道筋
本研究は、ADC12 アルミダイカストにおけるポロシティという長年の課題に対し、タグチメソッドを用いた科学的アプローチが極めて有効であることを示しました。特に、プランジャーの1速および2速の速度が品質を左右する最重要因子であることをデータで裏付け、ポロシティを劇的に削減する最適条件を具体的に提示しました。この知見は、不良率の削減、生産性の向上、そして最終製品の信頼性向上に直接貢献します。
CASTMANでは、こうした最新の業界研究を常に取り入れ、お客様がより高い生産性と品質目標を達成するためのお手伝いをしています。本稿で議論された課題が貴社の製造目標と合致する場合、これらの原理を貴社の部品にどのように適用できるか、ぜひ当社の技術チームにご相談ください。
著作権情報
- このコンテンツは、Veeresh G Balikai氏らによる論文「Optimization of process parameters of High Pressure Die Casting process for ADC12 Aluminium alloy using Taguchi method」を基にした要約および分析です。
- 出典: http://www.acadpubl.eu/hub/
この資料は情報提供のみを目的としています。無断での商業利用は禁じられています。 Copyright © 2025 CASTMAN. All rights reserved.