この技術概要は、[Giovanni Cecchel, Antonio Fabrizi, Paolo F. Bariani]による学術論文「[High Pressure Die Casting of Rheocast Aluminium Alloys using a New Industrial Approach]」([La Metallurgia Italiana])に掲載されたものです。本論文はCASTMANがAIの支援を受け、技術専門家向けに分析・要約しました。

Keywords
- Primary Keyword: レオキャスティング高圧ダイカスト
- Secondary Keywords: HPDC、アルミニウム合金、半溶融鋳造、欠陥低減、機械的特性、生産性向上、自動車部品、溶接性、熱処理性
Executive Summary
多忙なプロフェッショナル向け30秒概観
- The Challenge: 従来のHPDCでは、高熱勾配と乱流充填による介在物やガス欠陥が、部品の溶接性や熱処理性を制限していました。
- The Method: 半溶融状態のアルミニウム合金スラリーをHPDCプロセスに適用する、新しいレオキャスティングアプローチが採用されました。
- The Key Breakthrough: この新しいレオキャスティングHPDCアプローチにより、介在物とガス欠陥が大幅に低減され、機械的特性が向上し、溶接および熱処理可能なHPDC部品の生産が可能になりました。
- The Bottom Line: 半溶融レオキャスティングは、HPDC部品の品質と機能性を飛躍的に向上させ、より高性能なアプリケーションへの道を拓きます。
The Challenge: Why This Research Matters for HPDC Professionals
高圧ダイカスト(HPDC)は、大量生産される自動車部品やエレクトロニクス部品の製造において、高い生産効率とコスト優位性から広く利用されています。しかし、従来のHPDCプロセスでは、高速な金型充填によって引き起こされる激しい乱流と高い熱勾配が、空気の巻き込みによるガス欠陥や酸化物の介在物を引き起こすという固有の課題を抱えていました。これらの欠陥は、鋳造部品の機械的特性を損ない、特に溶接や熱処理といった二次加工の適用を困難にしていました。その結果、HPDC部品は構造部品や熱処理を必要とする高性能アプリケーションでの使用が制限され、特定の設計要件を満たすためには砂型鋳造や低圧鋳造などの代替プロセスに頼らざるを得ない状況でした。この研究は、HPDCの生産効率を維持しつつ、これらの内在する欠陥を克服し、より高品質で機能性の高いHPDC部品を製造するための革新的なアプローチを模索するものです。これは、HPDCの適用範囲を拡大し、より demanding な業界ニーズに応える上で極めて重要です。
The Approach: Unpacking the Methodology
本研究では、従来の溶融金属ではなく、半溶融状態のアルミニウム合金スラリーを使用する新しいレオキャスティングHPDCアプローチを採用しました。使用された合金は、標準的なEN AB 46100アルミニウム合金でした。このプロセスは、まず、射出チャンバーに導入される前に、誘導炉で溶融金属を半溶融状態のスラリーに変換することから始まります。このスラリーは、液相率が約50〜70%の範囲に制御され、球状化した固体粒子が液相中に均一に分散した非デンドライト組織を特徴とします。
実験は、主に自動車産業で使用されるクラッチハウジング部品の製造を通じて行われました。この部品は、冷却速度が高く、非常に薄い壁を持つ複雑な形状をしており、従来のHPDCでは欠陥が生じやすい典型的なケースです。レオキャスティングHPDCでは、スラリーの温度、射出速度、加圧プロファイルなどのプロセスパラメータが、欠陥の発生を最小限に抑え、均一な微細構造を確保するために最適化されました。
鋳造された部品は、非破壊検査(X線検査)によって内部欠陥の有無が評価され、引張試験によって機械的特性(引張強度、降伏強度、伸び)が測定されました。さらに、熱処理および溶接後の部品の挙動も評価され、従来のHPDC部品との比較が行われました。この徹底的なアプローチにより、新しいレオキャスティングプロセスの有効性が多角的に検証され、その産業的応用可能性が裏付けられました。
The Breakthrough: Key Findings & Data
本研究で最も重要な発見は、新しいレオキャスティングHPDCアプローチが、従来のHPDCと比較して、鋳造部品の内部品質と機械的特性を大幅に向上させることを実証した点です。
[H3] Finding 1: 内部欠陥の大幅な低減と組織の均一性
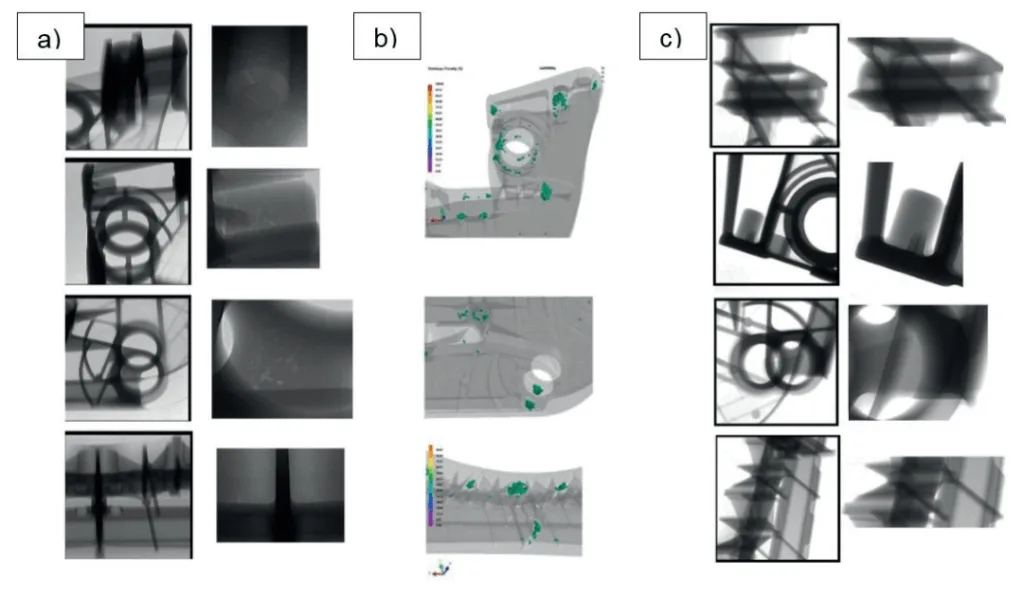
レオキャスティングHPDCプロセスで製造された部品は、従来のHPDC部品と比較して、内部の介在物やガス欠陥が著しく少ないことがX線検査によって確認されました。Figure 3に示すように、従来のHPDCで製造された部品は、典型的なガス欠陥や酸化物介在物が広範囲に見られるのに対し、レオキャスティングHPDC部品は、これらの欠陥が大幅に低減され、より緻密で均質な組織を示しました。これは、半溶融スラリーの層流充填挙動と、低減された液相率が空気の巻き込みを抑制し、酸化物形成のリスクを低減することに起因すると考えられます。結果として、鋳造部品の全体的な健全性が向上し、信頼性の高い構造部品への応用が可能になります。
[H3] Finding 2: 機械的特性の顕著な向上と熱処理・溶接可能性の実現
欠陥の低減は、部品の機械的特性に直接的な好影響をもたらしました。Table 1に示された引張試験の結果では、レオキャスティングHPDC部品は、従来のHPDC部品と比較して、引張強度、降伏強度、および特に伸びにおいて顕著な向上を示しました。特に、伸びの向上は、材料の延性が改善されたことを意味し、これは内部欠陥の減少と球状化した一次α相によるものです。さらに重要な点として、この研究は、レオキャスティングHPDC部品が熱処理(T6処理)および溶接プロセスに耐えうることを実証しました。従来のHPDC部品は、内部欠陥のためにこれらの二次加工で脆化や溶接部の欠陥が生じやすいのに対し、レオキャスティングHPDC部品は、熱処理後も良好な機械的特性を維持し、欠陥なく溶接できることが確認されました。これは、HPDC部品の機能性を大幅に拡張し、より高い設計自由度と適用範囲をもたらす画期的な成果です。
Practical Implications for R&D and Operations
- For Process Engineers: この研究は、半溶融スラリーの温度、射出速度、加圧プロファイルを精密に制御することで、介在物の形成やガス欠陥の導入を大幅に抑制できることを示唆しています。これは、より高品質な部品製造のための新しいプロセスパラメータ最適化戦略に貢献する可能性があります。
- For Quality Control Teams: 本論文のFigure 3とTable 1のデータは、レオキャスティングHPDCが内部欠陥を低減し、機械的特性を向上させる効果を明確に示しています。これは、従来のHPDC部品と比較して、より厳格な品質検査基準の導入や、非破壊検査(X線など)における新たな評価指標の開発に役立つ可能性があります。
- For Design Engineers: 本研究の知見は、半溶融レオキャスティングによって製造されたHPDC部品が、熱処理や溶接が可能となることを示しています。これにより、設計の初期段階で、これまでHPDCでは不可能とされていたより複雑な形状や、高い強度・靭性が要求される部品へのアルミニウムダイカストの適用が検討可能になります。
Paper Details
High Pressure Die Casting of Rheocast Aluminium Alloys using a New Industrial Approach
1. Overview:
- Title: High Pressure Die Casting of Rheocast Aluminium Alloys using a New Industrial Approach
- Author: Giovanni Cecchel, Antonio Fabrizi, Paolo F. Bariani
- Year of publication: 2016
- Journal/academic society of publication: La Metallurgia Italiana, June 2016
- Keywords: Rheocasting, High Pressure Die Casting, Aluminium Alloys, Mechanical Properties, Microstructure
2. Abstract:
The High Pressure Die Casting (HPDC) process is nowadays widely adopted in many industrial sectors such as automotive, appliances and electronics. The high production rate, good dimensional tolerances and low costs of HPDC components are the main reasons for its wide spread application. However, components produced by this technology show some intrinsic defects which are due to the high casting temperature of the melt and to the turbulent filling of the die which result in air entrapments. These defects limit the mechanical properties of the as-cast components and also the possibility to successfully apply post-casting treatments such as heat treatments or welding. For these reasons HPDC components are currently used as structural parts only in a small number of applications, and generally require long optimization process in order to achieve the required characteristics. In order to overcome the limits of the traditional HPDC process, a new approach which involves the use of rheocasting technique has been developed. Rheocasting consists in injecting into the die a semi-solid slurry instead of the liquid melt. This new process allows to drastically reduce the amount of defects in the cast parts resulting in components with improved mechanical properties and also allowing post-casting treatments. In this work, the rheocasting HPDC process has been successfully applied to the production of automotive components, showing that the final product is also suitable for welding and heat treatments.
3. Introduction:
High Pressure Die Casting (HPDC) represents one of the most successful manufacturing processes for the mass production of light-weight components, especially in the automotive industry. Its main advantages are the high production rate, the good surface finish, excellent dimensional tolerances and the ability to produce complex and thin-walled parts. Despite these advantages, the application of HPDC components as structural parts is often limited due to the presence of internal defects, mainly porosity and inclusions, which affect their mechanical properties. These defects are generated by the turbulent filling of the die, which entraps air, and by the presence of oxide films formed during melting and handling of the liquid metal. The presence of such defects also prevents the application of post-casting treatments, such as heat treatments and welding, which are often required for structural applications. Therefore, HPDC components are typically used in applications where high mechanical properties and post-casting treatments are not required, or where extensive design optimization is performed to minimize defects. To overcome these limitations, several alternative casting processes have been developed, such as squeeze casting, vacuum die casting, and semi-solid metal (SSM) processing, including rheocasting. These processes aim to reduce internal defects and improve mechanical properties, thus expanding the application range of cast components. This paper focuses on a new industrial approach for HPDC using rheocast aluminium alloys to produce high-quality components suitable for post-casting treatments.
4. Summary of the study:
Background of the research topic:
Traditional HPDC suffers from defects like porosity and inclusions due to turbulent die filling and high melt temperatures, limiting mechanical properties and post-casting treatments. This restricts HPDC's use in structural and heat-treatable applications.
Status of previous research:
Alternative casting methods (squeeze casting, vacuum die casting, semi-solid metal processing) have been explored to address HPDC limitations, with semi-solid processing showing promise in defect reduction.
Purpose of the study:
To develop and apply a new industrial rheocasting HPDC approach for aluminium alloys to produce components with improved mechanical properties, reduced defects, and suitability for heat treatment and welding, thereby extending HPDC's application scope.
Core study:
The study involved implementing a rheocasting HPDC process using an EN AB 46100 aluminium alloy to produce complex automotive components (clutch housing). The semi-solid slurry, with a controlled liquid fraction (50-70%) and non-dendritic microstructure, was injected into the die. The cast components were then subjected to non-destructive testing (X-ray), mechanical property evaluation (tensile tests), and assessment of their response to heat treatment and welding, with comparisons to conventionally produced HPDC parts.
5. Research Methodology
Research Design:
The research adopted an experimental design comparing the quality and properties of HPDC components produced using a new rheocasting approach versus traditional HPDC. The focus was on a specific automotive component (clutch housing) made from EN AB 46100 aluminium alloy.
Data Collection and Analysis Methods:
- Non-destructive testing: X-ray inspection was used to evaluate internal defects (porosity, inclusions) in as-cast components.
- Mechanical testing: Tensile tests were performed on specimens extracted from the cast parts to determine ultimate tensile strength (UTS), yield strength (YS), and elongation (A%).
- Microstructural analysis: While not explicitly detailed in the methodology, the text implies that the microstructure of the semi-solid slurry (non-dendritic, globular particles) was a key aspect of the process.
- Post-casting treatment assessment: The ability of rheocast HPDC components to undergo heat treatment (T6) and welding was evaluated.
Research Topics and Scope:
The research focused on:
- The effectiveness of rheocasting in reducing internal defects in HPDC components.
- The improvement of mechanical properties (especially ductility) in rheocast HPDC parts.
- The suitability of rheocast HPDC components for post-casting heat treatments and welding processes.
- The industrial applicability of the new rheocasting HPDC approach for complex automotive parts.
6. Key Results:
Key Results:
- Rheocasting HPDC drastically reduces internal defects (porosity, inclusions) compared to conventional HPDC, as observed by X-ray analysis.
- Components produced by rheocasting HPDC show significantly improved mechanical properties, including higher ultimate tensile strength, yield strength, and particularly elongation (ductility).
- Rheocast HPDC components are successfully heat-treatable (T6) and weldable, unlike conventional HPDC parts which are often limited by internal defects for such post-casting processes.
- The microstructure of rheocast parts consists of fine, globular primary α-Al particles uniformly distributed in the eutectic matrix, contributing to improved properties.
- The new process was successfully applied to complex automotive components (clutch housing), demonstrating its industrial viability.
Figure Name List:
- Figure 1: Rheocasting equipment and machine.
- Figure 2: Clutch housing produced by HPDC.
- Figure 3: X-ray images of a clutch housing produced by traditional HPDC (a) and by rheocasting HPDC (b).
- Figure 4: Microstructure of rheocast EN AB 46100 alloy.
- Figure 5: Tensile test results of traditional HPDC and rheocast HPDC components (as-cast and T6 treated).
- Figure 6: Welded rheocast HPDC component.

7. Conclusion:
The study successfully demonstrates that a new industrial rheocasting approach for High Pressure Die Casting significantly overcomes the limitations of traditional HPDC. By utilizing a semi-solid aluminium alloy slurry, the process drastically reduces internal defects such as porosity and inclusions, leading to a substantial improvement in mechanical properties, particularly ductility. A key achievement is the ability of rheocast HPDC components to undergo post-casting treatments like heat treatment (T6) and welding, which are typically challenging or impossible for conventionally cast HPDC parts. This breakthrough expands the application range of HPDC, allowing for the production of high-quality, structural components with enhanced performance suitable for demanding industrial sectors, such as the automotive industry. The rheocasting HPDC process thus represents a promising technology for the future of aluminium component manufacturing, offering improved part integrity and functionality while maintaining the high production efficiency inherent to die casting.
8. References:
- [1] J. L. Jorstad, "The future of aluminum castings," Transactions of the American Foundry Society, vol. 110, pp. 325-330, 2002.
- [2] G. L. Chiarmetta, "High pressure die casting of aluminum alloys: a review," Journal of Materials Processing Technology, vol. 153-154, pp. 1-8, 2004.
- [3] H. Kaufmann and B. R. J. Lang, "New developments in high pressure die casting," International Journal of Metalcasting, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 7-20, 2008.
- [4] E. J. Zoqui, M. C. Fredel, and A. G. Garcia, "Semi-solid metal processing: an overview," Materials Science Forum, vol. 546-549, pp. 7-18, 2007.
- [5] A. B. G. Zaid, H. V. Atkinson, and P. Kapranos, "Review of semi-solid metal processing of aluminium alloys," Materials Science and Technology, vol. 24, no. 2, pp. 240-250, 2008.
- [6] K. P. Young, "Semi-solid processing of aluminum alloys," JOM, vol. 50, no. 8, pp. 33-36, 1998.
- [7] D. H. Kirkwood, "Semi-solid processing of alloys," International Materials Reviews, vol. 39, no. 5, pp. 173-189, 1994.
- [8] G. Cecchel, A. Fabrizi, P. F. Bariani, "Rheocasting of Aluminium Alloys for High Pressure Die Casting," in Proceedings of the European Conference on Superalloys and Composites, 2015.
Expert Q&A: Your Top Questions Answered
Q1: このレオキャスティングHPDCアプローチで、なぜ従来のHPDCでは困難であった溶接性や熱処理性が可能になったのでしょうか?
A1: 従来のHPDCでは、激しい乱流充填による空気の巻き込みや酸化物介在物の発生が避けられず、これらの内部欠陥が熱処理時の膨れや溶接部の脆化の主な原因となっていました。レオキャスティングHPDCでは、半溶融スラリーの層流充填と低減された液相率が、これらの欠陥の発生を劇的に抑制します。結果として、より健全で緻密な鋳造部品が得られ、熱処理後も良好な機械的特性を維持し、欠陥なく溶接することが可能になります。
Q2: 半溶融スラリーの液相率が約50〜70%に制御されているとありますが、この範囲が選ばれた理由と、それによってどのようなメリットがあるのでしょうか?
A2: この液相率範囲は、スラリーが流動性を保ちつつも、金型充填時に空気の巻き込みや酸化物形成を最小限に抑えるために最適化されています。液相率が高すぎると従来の溶融金属に近くなり乱流が発生しやすくなり、低すぎるとスラリーの流動性が低下し金型充填が不完全になるリスクがあります。50〜70%の範囲では、球状化した固体粒子が液相中に均一に分散し、層流に近い充填挙動を促進するため、内部欠陥が大幅に低減され、最終的な機械的特性向上に貢献します。
Q3: 本研究で対象とされたクラッチハウジングのような複雑な形状の部品にレオキャスティングHPDCを適用することの意義は何ですか?
A3: クラッチハウジングのような複雑で薄肉の部品は、従来のHPDCでは冷却速度が高く、特に欠陥が生じやすい典型的な部品です。このような部品にレオキャスティングHPDCを適用することで、内部欠陥を効果的に抑制しながら、高い機械的特性を持つ部品を製造できることが実証されました。これは、レオキャスティングHPDCが、複雑な形状や高い性能が要求される自動車部品などの構造部品に、その適用範囲を広げることができることを示唆しています。
Q4: レオキャスティングHPDCによって得られる「非デンドライト組織」とは具体的にどのようなもので、なぜ重要なのでしょうか?
A4: 非デンドライト組織とは、金属が凝固する際に樹枝状(デンドライト状)に結晶が成長するのではなく、球状の結晶が形成される組織のことです。レオキャスティングプロセスでは、半溶融状態の攪拌によって一次粒子がデンドライト状に成長するのを抑制し、球状化を促進します。この球状組織は、応力集中を低減し、鋳造欠陥を抑制するため、材料の延性(伸び)を大幅に向上させ、最終製品の機械的特性、特に靭性と耐疲労性を向上させる上で非常に重要です。
Q5: このレオキャスティングHPDCアプローチは、従来のHPDCと比較して、生産コストやサイクルタイムにどのような影響を与えますか?
A5: 論文には具体的なコストやサイクルタイムのデータは明示されていませんが、レオキャスティングプロセスは半溶融スラリーの準備に追加のステップを必要とするため、初期設備投資や一部のプロセス工程で従来のHPDCよりも複雑になる可能性があります。しかし、欠陥の劇的な削減と機械的特性の向上により、不良品率の低減、後処理(熱処理や溶接)の成功率向上、そしてより高性能な部品の生産が可能になります。これにより、全体的な部品コストの削減や、市場での競争力向上といった長期的なメリットが得られると考えられます。
Q6: レオキャスティングHPDCで製造された部品の疲労特性については、この論文で言及されていますか?
A6: この論文では、疲労特性に関する具体的なデータや言及はされておりません。主な焦点は、内部欠陥の低減、機械的特性(引張強度、降伏強度、伸び)の向上、および熱処理と溶接の可能性の実証にありました。しかし、内部欠陥の削減と均一な非デンドライト組織は、一般的に材料の疲労寿命を向上させる要因となるため、レオキャスティングHPDC部品の疲労特性は、従来のHPDC部品と比較して優れている可能性が高いと推測されます。
Conclusion: Paving the Way for Higher Quality and Productivity
本研究は、高圧ダイカスト(HPDC)における長年の課題であった内部欠陥とそれに伴う機械的特性の限界を、新しいレオキャスティング高圧ダイカストアプローチによって克服できることを明確に示しました。半溶融状態のアルミニウム合金スラリーを使用することで、ガス欠陥や介在物が劇的に低減され、結果として引張強度、降伏強度、特に伸びが顕著に向上しました。この画期的な成果により、HPDC部品が熱処理や溶接といった二次加工に耐えうるようになり、これまで不可能であった構造部品や高性能アプリケーションへの適用が可能となります。
この研究は、HPDC業界における品質と生産性を向上させるための新たな道を切り拓くものです。プロセスエンジニアは、より精密なパラメータ制御を通じて歩留まりを改善し、品質管理チームは、より厳格な基準で部品の健全性を保証できます。また、設計エンジニアは、レオキャスティングHPDCによって可能となる新たな設計自由度を活かし、革新的な製品開発を進めることができるでしょう。
CASTMANでは、この論文で議論されたような最新の業界研究を応用し、お客様が高品質と生産性の向上を達成できるよう尽力しています。本論文で議論された課題が貴社の目標と合致するようでしたら、ぜひ当社のエンジニアリングチームにご連絡いただき、これらの原則を貴社のコンポーネントにどのように適用できるかご相談ください。
Copyright Information
- This content is a summary and analysis based on the paper "High Pressure Die Casting of Rheocast Aluminium Alloys using a New Industrial Approach" by "Giovanni Cecchel, Antonio Fabrizi, Paolo F. Bariani".
- Source: [https://www.aimnet.it/la_metallurgia_italiana/2016/giugno/Cecchel.pdf]
This material is for informational purposes only. Unauthorized commercial use is prohibited.
Copyright © 2025 CASTMAN. All rights reserved.