本論文概要は、[論文タイトル: 離散形状の形状に対する新しいハイブリッド抜き勾配解析法]と題された論文に基づき、[出版社: Computer-Aided Design]に掲載された論文を要約したものです。
1. 概要:
- タイトル: A new hybrid method for demoldability analysis of discrete geometries (離散形状の形状に対する新しいハイブリッド抜き勾配解析法)
- 著者: Jorge Manuel Mercado-Colmenero, M. A. R. Paramio, Jesus Maria Perez-Garcia, Cristina Martin-Doñate
- 発表年: 2022年 (論文掲載時点、ファイル内の著作権表示は2025年)
- 掲載ジャーナル/学会誌: Computer-Aided Design
- キーワード: Demoldability analysis, geometric analysis, injection molding, computer aided manufacturing (抜き勾配解析、形状解析、射出成形、コンピュータ支援製造)
2. 研究背景:
- 研究テーマの社会的/学術的背景: 射出成形は、複雑な形状や自由曲面を持つプラスチック部品の製造に広く用いられていますが、金型設計プロセスにおいて、抜き勾配解析は品質と製造コストに大きな影響を与える重要な段階です。設計の初期段階で抜き勾配を迅速に検証し、製造不能領域を特定することが重要です。既存の商用CADシステムは、抜き勾配解析に多くの手作業を必要とし、CADツールの習熟度と製造経験が求められます。
- 既存研究の限界: 既存の研究は、モデラーに依存していたり、GPUのような追加のコンピューティングデバイスを必要としたり、すべての種類のプラスチック部品の解析に有効ではないという欠点があります。
- 研究の必要性: 設計および製造時間の短縮、製品の精度と品質の向上、設計変更への迅速な対応のために、プラスチック部品の抜き勾配解析プロセスの自動化が必要です。既存の方法の限界を克服し、あらゆる種類のプラスチック部品に適用可能な新しい抜き勾配解析法の開発が求められています。
3. 研究目的と研究課題:
- 研究目的: プラスチック射出成形部品の抜き勾配自動解析のための新しい方法論を提示すること。特に、三角形メッシュで離散化された部品形状に基づいて、メッシュノードとファセットの両方に対するハイブリッド離散抜き勾配解析法を開発することを目的としています。
- 主な研究課題:
- 離散化されたプラスチック部品形状(三角形メッシュ)を用いて、抜き勾配を効果的に解析できるか?
- メッシュノードとファセットの両方を考慮するハイブリッド解析法は、既存の方法よりも正確で効率的な抜き勾配解析を提供するのか?
- 開発されたアルゴリズムは、多様な形状のプラスチック部品およびCADシステムに独立して適用可能か?
- 開発されたアルゴリズムは、アンダーカット領域だけでなく、抜き勾配不能領域を正確に検出し、設計者に有用な情報を提供できるか?
- 研究仮説: 提示されたハイブリッド離散抜き勾配解析法は、既存の方法の限界を克服し、多様なプラスチック部品の抜き勾配解析を自動化することで、設計時間の短縮と品質向上に貢献するであろう。
4. 研究方法:
- 研究デザイン: 新しいハイブリッド抜き勾配解析アルゴリズムの開発と実装。
- データ収集方法: 産業現場で製造されたプラスチック部品5種類と、実部品2種類(合計7種類)を対象にアルゴリズムを適用し、検証。
- 分析方法: 開発されたアルゴリズムをC++言語で実装し、多様な形状のプラスチック部品に適用して抜き勾配解析性能と計算コストを評価。IsoobstructingアルゴリズムとInprojectアルゴリズムの計算コストを比較分析。
- 研究対象と範囲: プラスチック射出成形部品、三角形メッシュベースの離散形状モデル、抜き勾配解析、コンピュータ支援製造。
5. 主な研究成果:
- 主な研究成果: 開発されたハイブリッド抜き勾配解析アルゴリズムは、プラスチック部品の抜き勾配を効果的に解析し、抜き勾配可能領域、不可能領域、サイドコア必要領域などを正確に識別します。アルゴリズムは、初期離散形状モデルを入力として受け取り、部品の製造情報を含む新しい仮想離散形状モデルを生成します。
- 統計的/定性的分析結果: 多様なケーススタディを通じて、アルゴリズムの有効性を検証しました。特に、InprojectアルゴリズムはIsoobstructingアルゴリズムに比べて計算時間が6%程度と非常に効率的であることが示されました。
- データ解釈: 開発されたアルゴリズムはCADモデラーに依存せず、多様な形状のプラスチック部品に適用可能です。また、アンダーカット領域だけでなく、抜き勾配不能領域を検出し、設計者が設計の初期段階で問題を解決できるように支援します。
- 図表リスト: (英語版と同様のリストを記載)
- * Figla.- Converting a CAD model to a virtual faceted model.
- * Figlb.- Definition of facets and nodes, triangular shell elements.
- * Fig 2- Defining the set of nodes / facets belonging to Plk.
- * Fig 3- Representation of facets Fi for the level k of Ik, definition of Ck
- * Fig 4.- Projection of facets Fi and contour border Fr(Ck) for the level k of Ik .
- * Fig5.- Partial demoldability analysis for a plane (Plk)
- * Fig6.- Result of the algorithm InProject in the analysis (+V₂).
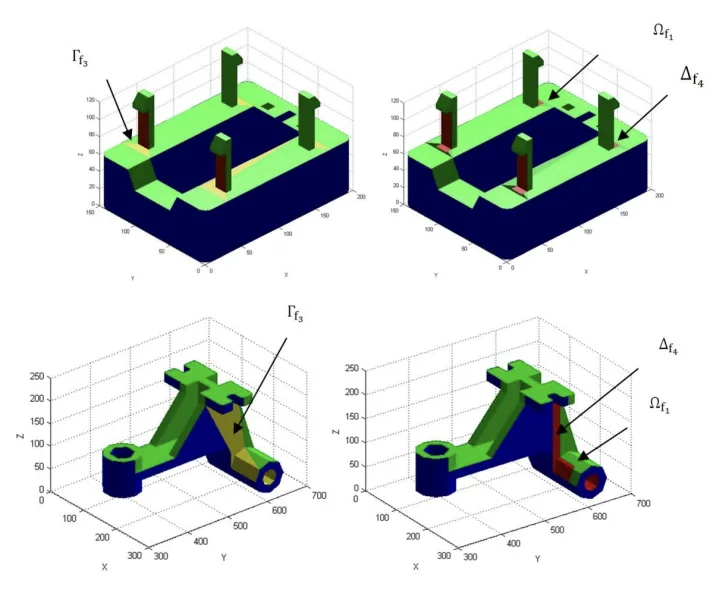
- * Fig7.- Example of location of the region Of₁
- * Fig8.- Example of location of the region [If U Af₄].
- * Fig 9.- Example location of demoldable facets, perpendicular to V2.
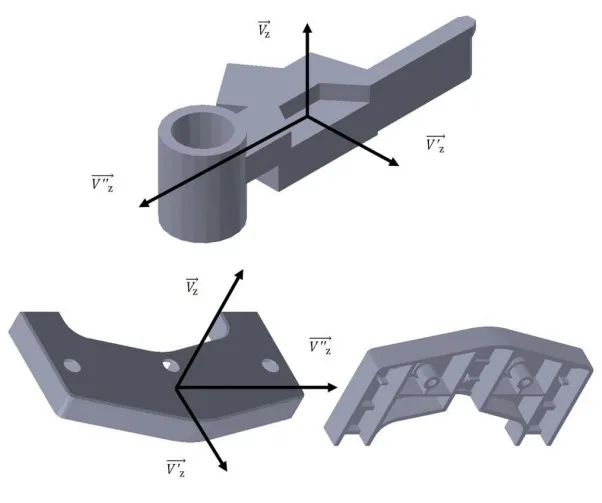
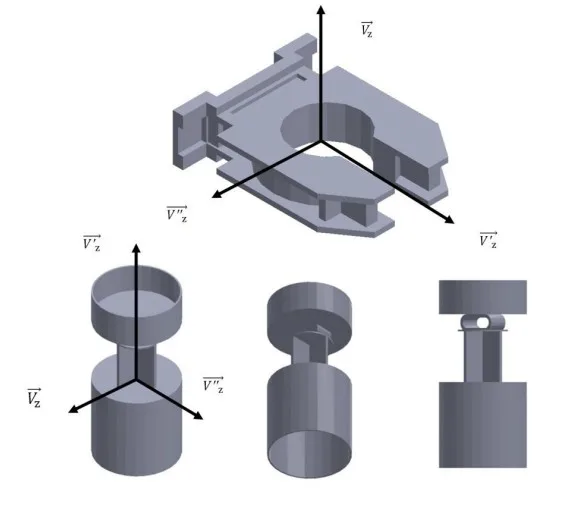
- * Fig 10.- Reorientation of the geometry as the new direction of analysis, and comparison of results of different analyses performed.
- * Fig 11.- Results of the analysis of demoldability in +Vz, -Vz after the implementation of the boundary conditions 3.3.2
- * Fig12.- Example of resolution of semi-demoldable facets, Boolean operation (intersection and subtraction).
- * Fig 13a.- Allocation of non-demoldable facets to side core facets, Example I.
- * Fig13b.- Allocation of non-demoldable facets to side core facets, Example II.
- * Fig 14.- Geometric definition of the parting line.
- * Fig 15.- Optimizing the geometrical definition of the parting line.
- * Fig 16.- Case A and B, demoldable parts by means of upper and lower cavities.
- * Fig 17.- Parts C, D with resoluble demolding regions by means of side cores.
- * Fig18.- Part E, parts with non-demoldable regions.
- * Fig 19.- Cases F and G. Parts with non demoldable regions, geometrically modified to improve their demoldability.
- * Fig20.- Results of demoldability, Cases A, B, C, D, E.
- * Fig21.- Results of demoldability, Cases F, G original part and Cases F',G' optimized part..
- * Fig22.- CPU Computational Cost of Demoldability Algorithm.
- * Fig23.- Formal definition of Gauss points of a facet.
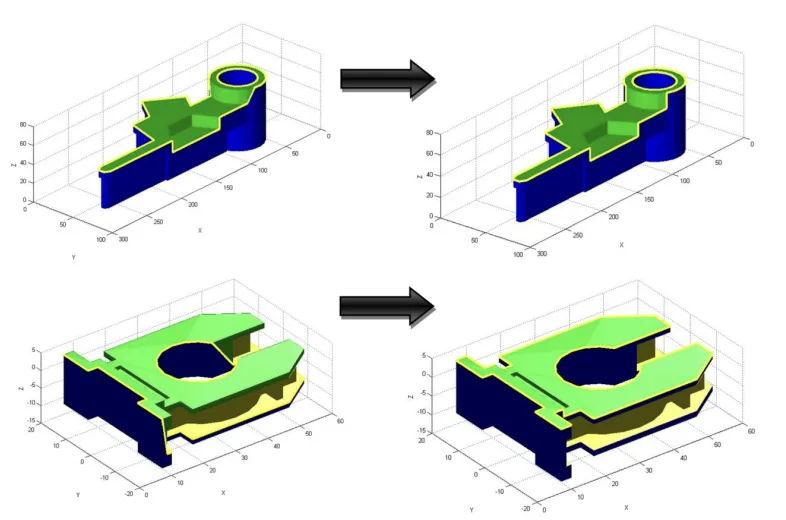
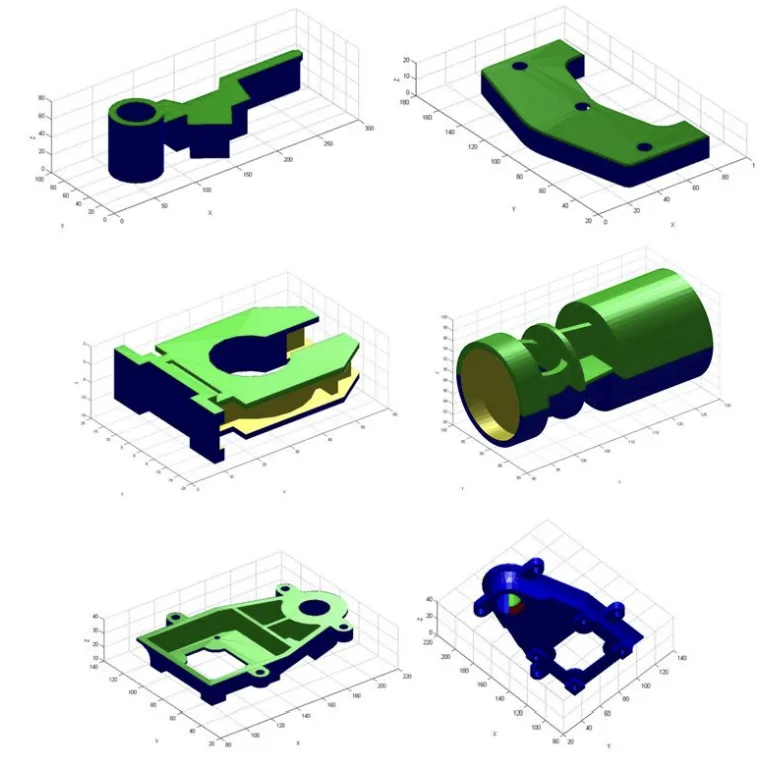
Parts F and G have been used as an example of optimizing the geometry of the part as a methodology in order to enhance its demoldability, Table 2 shows the results of applying the demoldability analysis algorithm over both parts.
6. 結論と考察:
- 主な成果の要約: 本研究では、プラスチック部品の抜き勾配解析のための新しいハイブリッド法を提示しました。この方法は、離散メッシュモデルと仮想形状の概念を組み合わせ、メッシュノードとファセットの両方を解析します。開発されたアルゴリズムは、様々な産業部品に適用され、抜き勾配解析の効率性と精度を実証しました。
- 研究の学術的意義: 本研究は、既存の抜き勾配解析法の限界を克服し、ハイブリッド離散要素ベースの新しいアプローチを提示することで、金型設計分野の発展に貢献します。特に、Inprojectアルゴリズムの高い計算効率は、複雑な形状の部品解析への適用可能性を高めます。
- 実用的な示唆: 開発されたアルゴリズムは、プラスチック部品設計者が設計の初期段階で抜き勾配を自動的に検証し、製造可能性を評価するのに役立ちます。これは、設計時間の短縮、製造コストの削減、製品品質の向上に貢献できます。
- 研究の限界: 本研究は、特定の種類のプラスチック部品および射出成形プロセスに焦点を当てています。多様なプラスチック材料および成形条件に対するアルゴリズムの性能検証と最適化が必要です。
7. 今後のフォローアップ研究:
- 今後の研究方向:
- 多様なプラスチック材料および射出成形条件に対するアルゴリズムの性能評価と最適化の研究。
- 開発されたアルゴリズムを商用CAD/CAEシステムに統合し、実用性を高める研究。
- 金型冷却システム設計、エジェクタシステム設計など、他の金型設計段階との連携研究。
- アルゴリズムの計算効率をさらに向上させるためのGPU活用研究。
- さらなる探求領域:
- 複雑な形状および微細形状部品に対する抜き勾配解析の精度向上研究。
- 抜き勾配解析結果に基づいた自動金型設計システム開発研究。
8. 参考文献:
- [1] Chen L.L., Woo T.C. Computational geometry on the sphere with application to automated machining. ASME Transactions. Journal of Mechanical Design 114, 288-295.
- [2] Chen L.L., Chou S.Y, Woo T.C. Parting directions for mould and die design. Computer Aided Design 1993;25 (12): 762-8.
- [3] Chen L.L., Chou S.Y, Woo T.C. Partial visibility for selecting a parting direction in mold and die design. Journal of Manufacturing Systems 1995; 14 (5):.
- [4] Weinstein M, Manoochehri S. Optimal parting direction of molded and cast parts for manufacturability. Journal of Manufacturing Systems 1997; 16(1):1-12.
- [5] Fu M.W, Fuh J.Y.H., Nee A.Y.C. Undercut feature recognition in an injection mould design system. Computer Aided Design 1999; 31(12):777-790.
- [6] Fu M.W., Fuh J,Y.H., Nee A.Y.C. Generation of optimal parting direction based on undercut features in injection molded parts. IIE Transactions 1999; 31: 947-55.
- [7] Fu M.W, Nee A.Y.C., Fuh J.Y.H. The application of surface visibility and moldability to parting line generation. Computer Aided Design 2002; 34(6): 469-480.
- [8] Fu M.W., Nee A.Y.C., Fuh J.Y.H. A core and cavity generation method in injection mold design. International Journal of Production Research 2001; 39:121-38.
- [9] Fu M.W., The application of surface demoldability and moldability to side core design in die and mold CAD. Computer Aided Design 2008; 40(5): 567-575.
- [10] Ran JQ, Fu MW. Design of internal pins in injection mold CAD via the automatic recognition of undercut features. Computer Aided Design . 2010;42(7):582-597.
- [11] Wuerger D, Gadh R. Virtual prototyping of die design part one: theory and formulation. J Concurrent Engng: Res Appl 1997; 5(4):307–15.
- [12] Wuerger D, Gadh R. Virtual prototyping of die design part two: algorithmic, computational, and practical considerations. J Concurrent Engng: Res Appl 1997; 5(4):317–26.
- [13] Kurth GR, Gath R. Virtual prototyping of die-design: determination of die-open directions for neat-net shape manufactured parts with extruded or rotational features. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems 1997; 10(1):69- 81.
- [14] Lu HY, Lee WB. Detection of interference elements and release directions in die-cast and injection-moulded components. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part B Journal of Engineering Manufacture 2000; 214(6):431–41.
- [15] Yin ZP, Han Ding, You-Lun Xiong: Virtual prototyping of mold design: geometric mouldability analysis for near-net-shape manufactured parts by feature recognition and geometric reasoning. Computer-Aided Design 2001: 33(2): 137-154
- [16] Ye X.G. Fuh JYH, Lee K.S.: A hybrid method for recognition of undercut features from molded part. ComputerAided Design 2001; 33(14):1023-34.
- [17] Ye X.G. Fuh JYH, Lee K.S.: Automotive undercut feature recognition for side core design of injection molds. Journal of Mechanical Design 2004; 126:519-26.
- [18] Zhang Chunjie, Zhou Xionghui, Li Congxin. Feature extraction from freeform molded parts for moldability analysis. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology. 2010;48(1-4):273-82.
- [19] Bassi R., Reddy NV, Bedi S.Automatic recognition of intersecting features of side core design in two piece permanent molds. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology. 2010;50(5-8):421-39.
- [20] Surti A., Reddy NV. Non discretized approach to visibility analysis for automatic mold feature recognition using step part model. Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Systems. 2012;11(1): 1-16.
- [21] Singh R, Madan J, Kumar R. Automated identification of complex undercut features for side core design for die casting parts. Journal of Engineering Manufacture. 2014;228(9):1138-1152.
- [22] Nee A.Y.C., Fu, M.W., Fuh J.Y.H., Lee K.S., Zhang Y.F. Determination of optimal parting direction in plastic injection mould design. Annals of the CIRP.1997:,46(1): 429-432.
- [23] Nee A.Y.C., Fu M.W., Fuh J.Y.H, Lee K.S., Zhang Y.F. Automatic determination of 3D parting Lines and Surfaces in Plastic Injection Mould Design. Annals of the CIRP. 1998: 47(1): 95-99.
- [24] Hui K.C., Tan S.T. Mould design with sweep operations, a heuristic search approach.Computer Aided Design . 1992; 24 (2): 81-92.
- [25] Ravi B., Srinivasan M.N. Decision criteria for computer aided parting surface design-Computer Aided Design.1990; 22(1):11-18.
- [26] Rappaport D, Rosenbloom A. Moldable and castable polygons. Comput Geom: Theory Appl 1994;4:219–33.
- [27] Ahn, H.K., Berg, M.T. de, Bose, J., Cheng, S.W., Halperin, D. & Matouvsek, J. Separating an object from its cast. In Proceedings 13th Annual ACM Symposium on Computational Geometry 1997; 61-83. New York, U.S.A.: ACM Press.
- [28] Ahn, De Berg, Bose, Cheng ,Halperin , Matousek , Swartzkopf, Separating an object from its cast. Computer Aided Design. 2002;34: 547-59,.
- [29] Chen X, McMains S. Finding all undercut-free parting directions for extrusions. In: Geometric modeling and processing. Lecture notes in computer science, 2006; 4077: 514–27.
- [30] Mcmains S, Chen X. Determining moldability and parting directions for polygons with curved edges.In: International mechanical engineering congress and exposition. ASME Anaheim , CA; 2004.
- [31] Mcmains S, Chen X. finding undercut free directions for polygons with curved edges. ASME Journal of Computing and Information Science in Engineering.2006; 6(1):60-68.
- [32] Yin ZP, Han Ding, Han-Xiong Li, You-Lun Xiong: Geometric mouldability analysis by geometric reasoning and fuzzy decision making. Computer Aided Design. 2004; 36(1): 37-50.
- [33] Chen YH, Wang YZ, Leung TM. An investigation of parting direction based on dexel and fuzzy decision making. International Journal of Production Research.2000;38:1357–75.
- [34] Huang J, Gupta SK, Stoppel K. Generating sacrificial multi-piece molds using accessibility driven spatial partitioning. Computer Aided Design 2003;35(3):1147–60.
- [35] Dhaliwal S, Gupta SK, Huang J, Computing exact global accessibility cones for polyhedral objects. In ASME Design for Manufacturing Conference Baltimore MD, September 2000.
- [36] Dhaliwal S, Gupta SK, Huang J, Priyadarshi A. Algorithms for computing global accessibility cones. Journal of Computing and Information Science in Engineering 2003;3(3):200–9.
- [37] Priyadarshi A.K.L., Gupta S.K. Geometric Algorithms for automated design of multipiece permanent molds. Computer Aided Design 2004; 36(3): 241-260.
- [38] Bourne D, Corney J, Gupta S.K. Recent advances and future challenges in automated manufacturing planning. Journal of Computing and Information Science in Engineering 2011; 11(2).
- [39] Chen Y, Rosen D. A region based approach to automated design of multipiece molds with application to rapid tooling .In ASME Design Engineering Technical conference, Pittsburgh PA, 2001;613-623.
- [40] Chen Y, Rosen DW. A reverse glue approach to automated construction of multi-piece molds. J. Comput Inf Sci Eng 2003;3(3):219–30.
- [41] Ganter M.A., Tuss L.L. Computer-Assisted Parting Line Development for Cast Pattern Production. AFS Transactions 1990; 795-800 .
- [42] Wong T., Tan S.T., Sze W.S. Parting line formation by slicing a trimmed surface model.Proceedings of the 1996 ASME Design Engineering Technical Conference and Computers in Engineering Conference 1996.August 18-22, Irvine, California.
- [43] Rubio M.A.,Pérez J.M., Rios J. A Procedure for plastic parts demoldability analysis Robotics and Computer Integrated Manufacturing 2006; 22(1):81-92.
- [44] Martin Doñate C, Rubio Paramio, M. A. New methodology for demoldability analysis based on volume discretization algorithms. Computer Aided Design.2013; 45(2): 229-240.
- [45] Martin Donate Cristina, Rubio Paramio Miguel Angel, Mesa Villar Aurelio. Método de validación automatizada de la fabricabilidad de diseños de objetos tridimensionales en base a su geometría. Patent number: ES2512940
- [46] Khardekar R, McMains S. Finding mold removal directions using graphics hardware. In: ACM workshop on general purpose computing on graphics processors; 2004, pp. C-19, (abstract).
- [47] Khardekar, Burton and McMains. Finding feasible mold parting directions using graphics hardware. Computer Aided Design 2006; 38(4):327-41.
- [48] Chakraborty P., Reddy NV. Automatic determination of parting directions, parting lines and parting surfaces for two piece permanent moulds. Journal of Materials Processing Technology 2000;209(5):2464-76.
- [49] Singh R, Madan J. Systematic approach for automated determination of parting line for die-cast parts. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing. 2013;29(5):346-366.
- [50] Shin K.H. Lee K.W. Design of side cores of injection molds from automatic detection of interference faces. Journal of Design and Manufacturing 1993;3:225-36
- [51] Banerjee A.G., Gupta S.K.Geometrical algorithms for automated design of side actions in injection moulding of complex parts. Computer Aided Design. 2007;39(10): 882-897.
- [52]Li W, Martin RR, Langbein FC. Molds for meshes: Computing smooth parting lines and undercut removal. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering 2009; 6(3):423-32.
9. 著作権:
- この資料は、[論文著者: Jorge Manuel Mercado-Colmenero 他3名]の論文: [論文タイトル: A new hybrid method for demoldability analysis of discrete geometries] に基づいて作成されました。
- 論文ソース: [DOI URL: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cad.2022.103432]
本資料は上記の論文に基づいて要約されたものであり、商業目的での無断使用は禁止されています。
Copyright © 2025 CASTMAN. All rights reserved.