本稿は、「[Chinese Journal of Engineering]」により発行された論文「[Mechanism and performance of coal spontaneous combustion with a halide carrier inorganic salt inhibitor]」に基づいています。
1. 概要:
- タイトル: Mechanism and performance of coal spontaneous combustion with a halide carrier inorganic salt inhibitor
- 著者: ZHANG Yan-ni, HOU Yun-chao, LIU Bo, DENG Jun, LIU Chun-hui, YANG Jing-jing, WEN Xin-yu
- 発行年: 2021
- 発行学術誌/学会: Chinese Journal of Engineering
- キーワード: halide carrier inorganic salt; inhibitor; coal spontaneous combustion; differential scanning calorimetry; apparent activation energy
2. 抄録:
Coal spontaneous combustion seriously restricts the safe production of coal mines, and adding an inhibitor is one of the effective methods to prevent coal spontaneous combustion. To improve the pertinence and high efficiency of the inhibitor, this paper considered the intrinsic properties and external conditions that affect the occurrence of coal spontaneous combustion, combined with the characteristics that the rare earth hydrotalcite can effectively improve the thermal stability, coupling, and flame retardancy of the coal and the halide inhibitor. The halide inhibitor can enhance the permeability, dispersion, and uniformity of the rare earth hydrotalcite as a carrier. The halide carrier inorganic salt inhibitor was prepared. To study the inhibition mechanism and performance of the halide carrier inorganic salt inhibitor on coal spontaneous combustion, differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) was used to test the variation law of parameters, such as stage characteristics, characteristic temperature, thermal effect, and apparent activation energy in the process of coal spontaneous combustion under the action of a rare earth hydrotalcite, MgCl2 and a halide carrier inorganic salt inhibitor. Test results reveal that the OH of the rare earth hydrotalcite laminate can generate a weak hydrogen bond with acidic functional groups such as –COOH in coal molecules so that the activity of the acidic functional groups is weakened. Mg²⁺ complexes with –COO⁻ in coal molecules to form –COOMg–, resulting in the weakening of the C=O activity in –COO⁻, which is the main mechanism of the halide carrier inorganic salts inhibiting coal spontaneous combustion. The endothermic peak of the DSC curve appears as a double peak or multi-peak after the addition of halide carrier inorganic salts to the coal sample. Compared with the raw coal, the peak temperature is shifted back by 50–60 °C, the T₁ temperature is shifted back by 90–100 °C, and the total heat release decreased by 19–27 kJ·g⁻¹. Furthermore, the apparent activation energy of each stage of the coal body is effectively improved. Results revealed that the halide carrier inorganic salt inhibitor could effectively inhibit the reaction process of coal spontaneous combustion.
3. はじめに:
石炭は主要なエネルギー源であり、その生産と消費は世界的に重要です。しかし、中国の炭層の約75%は自然発火しやすく、資源の損失とCO2排出の大きな原因となっています。効果的な抑制剤の開発は、炭鉱における熱運動災害を防ぎ、安全な生産を確保するために不可欠です。
現在の抑制剤には、主にハロゲン化物塩、不活性ガス、高分子エマルジョンなどがあります。これらはそのメカニズムに基づいて、化学的抑制と物理的抑制に分類できます。物理的抑制は可燃物や発火源を制御するのに対し、化学的抑制は石炭分子中の活性官能基を破壊または捕捉することにより微視的レベルで作用し、それによって石炭-酸素再結合プロセスを遅らせます。
ハロゲン化物抑制剤は、その良好な被覆性と吸水性のために広く使用されています。しかし、大量に必要であること、装置への腐食性、抑制時間が短いなどの欠点があります。希土類ハイドロタルサイトは機能性材料として、良好な熱安定性、イオン交換性、調整可能な層組成を提供し、さまざまな用途に適しています。希土類ハイドロタルサイトをハロゲン化物抑制剤に添加すると、石炭-抑制剤系の熱安定性、カップリング性、難燃性を向上させることができます。逆に、ハロゲン化物抑制剤を担体として使用すると、希土類ハイドロタルサイトの低い浸透性、分散性、均一性の悪さを克服できます。本研究は、希土類ハイドロタルサイトとMgCl2を用いてハロゲン化物担体無機塩抑制剤を調製し、理論的分析と実験的試験を通じてその抑制特性とメカニズムを調査し、新規で効率的な石炭自然発火抑制剤開発のための基礎データと理論的支援を提供することを目的としています。
4. 研究の概要:
研究トピックの背景:
石炭の自然発火は、炭鉱操業における重大な安全上の危険であり、資源の損失と環境汚染を引き起こします。抑制剤の適用は、そのような事故を防ぐための重要な戦略です。
従来の研究の状況:
ハロゲン化物塩、不活性ガス、高分子エマルジョンなど、さまざまな抑制剤が開発されてきました。ハロゲン化物塩は一般的ですが、高用量、腐食性、短期的な有効性などの欠点があります。希土類ハイドロタルサイトは、熱安定性と難燃性の向上に有望であることが示されています。これまでの研究では、MgCl2などの個々の成分や複合抑制剤が検討されており、相乗効果の可能性が示唆されています。
研究の目的:
本研究は、希土類ハイドロタルサイトとMgCl2を組み合わせることにより、新規のハロゲン化物担体無機塩抑制剤を開発することを目的としました。この複合抑制剤の石炭自然発火に対する抑制メカニズムと性能を理解することに焦点を当て、より効率的で的を絞った抑制剤を作成するための基礎を提供することを目指しました。
研究の核心:
研究の核心は、希土類ハイドロタルサイトとMgCl2を用いたハロゲン化物担体無機塩抑制剤の調製でした。これらの抑制剤を石炭試料に適用することにより、抑制効果を評価しました。示差走査熱量測定(DSC)を用いて、石炭酸化中の特性温度、熱効果、見かけの活性化エネルギーなどの熱挙動を分析しました。走査型電子顕微鏡(SEM)およびエネルギー分散型X線分光法(EDS)を、処理された石炭試料の微細構造および元素分析に使用しました。
5. 研究方法論
研究デザイン:
本研究では実験的デザインを採用しました。希土類ハイドロタルサイトの合成、異なる抑制剤配合物(希土類ハイドロタルサイト単独、MgCl2単独、およびそれらの組み合わせとしてのハロゲン化物担体無機塩抑制剤)の調製、およびこれらの抑制剤による石炭試料の処理が含まれていました。その後、熱分析および微細構造特性評価を通じて抑制剤の性能を評価しました。
データ収集および分析方法:
- 材料: 彬長(Bin-chang)非粘着炭を研究対象として使用しました。希土類ハイドロタルサイトは共沈法を用いて合成しました。MgCl2を別の抑制剤成分として使用しました。
- 試料調製: 石炭試料(0.105–0.15 mm)を異なる抑制剤溶液(組成は原著論文のTable 2に詳述)と混合し、乾燥させました。
- 示差走査熱量測定 (DSC): NETZSCH DSC200F3装置を使用しました。10 mgの試料を空気雰囲気下(25 mL·min⁻¹)、昇温速度5 °C·min⁻¹で30 °Cから450 °Cまで試験しました。
- 走査型電子顕微鏡 (SEM) およびエネルギー分散型X線分光法 (EDS): MAX-50 EDS付属のQUANTA FEG-450 SEMを使用して、試料の微細形態および元素組成を観察しました。
- 速度論的分析: DSCデータから、アレニウス式および導出された速度論モデル(原著論文の式(5))を用いて、石炭酸化の異なる段階における見かけの活性化エネルギー(E)を計算しました。
研究トピックと範囲:
- 異なる抑制剤で処理された石炭試料の微細形態および元素分布の調査。
- 希土類ハイドロタルサイト、MgCl2、およびハロゲン化物担体無機塩抑制剤の影響下における石炭自然発火の熱放出特性(段階特性、特性温度、熱効果)の分析。
- ハロゲン化物担体無機塩抑制剤の抑制メカニズムの解明。
- 抑制剤の有無による石炭酸化プロセスの異なる段階における見かけの活性化エネルギーの決定。
6. 主な結果:
主な結果:
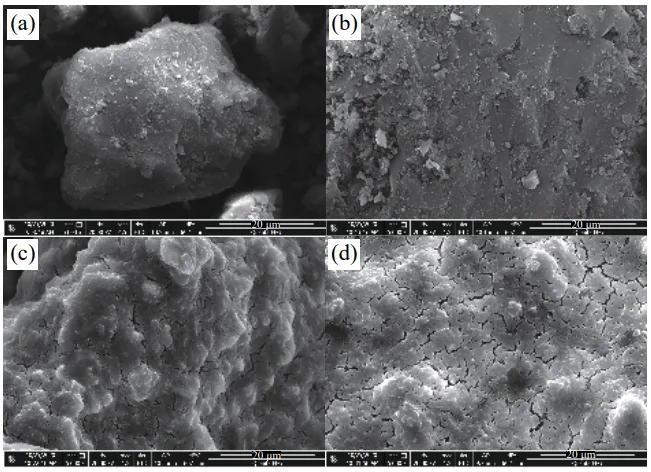
- 微細構造と組成 (SEM/EDS): 化学的共沈法は、抑制剤と石炭との複合度を効果的に向上させました。担体として作用するMgCl2は、石炭表面における希土類ハイドロタルサイトの浸透、分散、均一性を高めました。
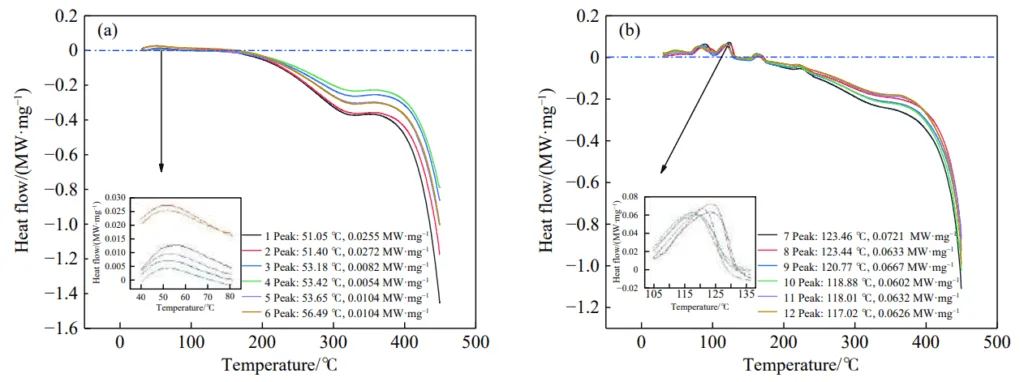
- 熱挙動 (DSC):
- ハロゲン化物担体無機塩抑制剤を石炭試料に添加すると、DSC曲線に二重または複数の吸熱ピークが現れました。
- 未処理石炭と比較して、吸熱プロセスのピーク温度は50–60 °C高温側にシフトしました。
- 顕著な熱放出の開始温度(T₁温度)は90–100 °C高温側にシフトしました。
- 酸化中に放出された総熱量は19–27 kJ·g⁻¹減少しました。
- 抑制メカニズム:
- 希土類ハイドロタルサイトのラミネート上の-OH基は、石炭分子中の酸性官能基(例:-COOH)と弱い水素結合を形成し、それによってこれらの酸性基の活性を低下させることができます。
- MgCl2由来のMg²⁺イオンは、石炭中の-COO⁻基と錯体(-COOMg-を形成)を形成し、-COO⁻基内のC=O結合活性を弱めます。これが、ハロゲン化物担体無機塩が石炭の自然発火を抑制する主要なメカニズムです。
- ハロゲン化物担体無機塩抑制剤は、物理的(例:MgCl2による被覆、水分保持)および化学的抑制効果の両方を示し、吸熱相を遅延させ、吸収熱量を増加させ、その後の酸化段階での熱放出を大幅に減少させました。
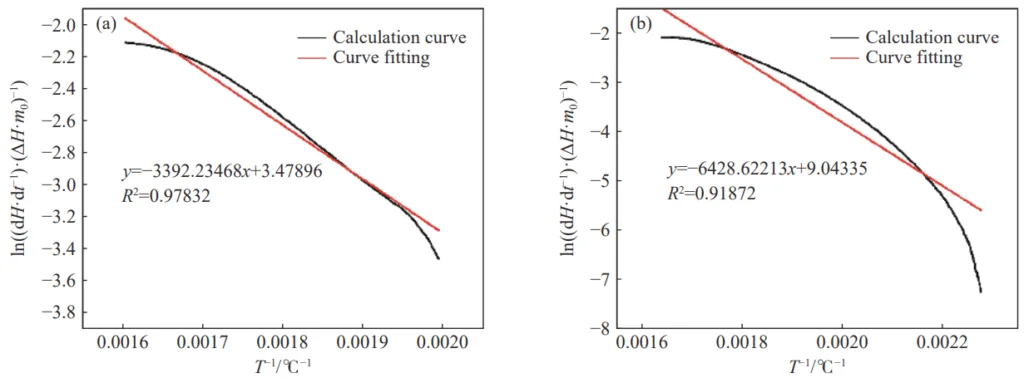
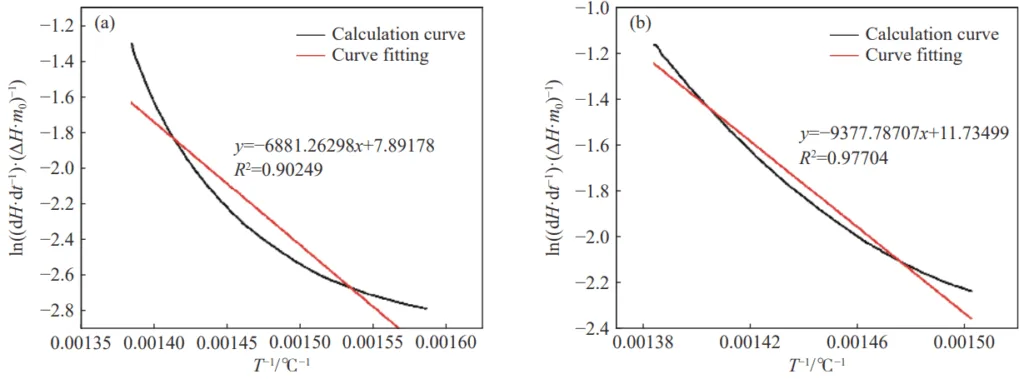
- 見かけの活性化エネルギー: 抑制剤、特にハロゲン化物担体無機塩抑制剤の添加は、石炭酸化の遅い熱放出段階と速い熱放出段階の両方で見かけの活性化エネルギーを効果的に増加させ、燃焼に対するより高いエネルギー障壁、したがってより優れた抑制を示しました。
図の名称リスト:
- Fig.1 Test sample SEM: (a) sample 1; (b) sample 2; (c) sample 7; (d) sample 8
- Fig.2 Test sample EDS: (a) sample 1; (b) sample 2; (c) sample 7; (d) sample 8
- Fig.3 Curve of the heat release rate of the test sample: (a) sample 1–6; (b) sample 7–12
- Fig.4 Heat release rate curve: (a) sample 1; (b) sample 2; (c) sample 3; (d) sample 4; (e) sample 5; (f) sample 6; (g) sample 7; (h) sample 8; (i) sample 9; (j) sample 10; (k) sample 11; (l) sample 12
- Fig.5 Apparent activation energy curve of the test sample during the slow heat release stage: (a) sample 1; (b) sample 7
- Fig.6 Apparent activation energy curve of the test sample during the rapid heat release stage: (a) sample 1; (b) sample 7
7. 結論:
本研究により、以下の主な結論が得られました。
- 微細構造分析(SEM/EDS)により、化学的共沈法が抑制剤と石炭の複合度を高めることが確認されました。MgCl2は担体として効果的に作用し、希土類ハイドロタルサイトの浸透性、分散性、均一性を向上させます。DSC分析により、明確な熱反応段階(吸熱、緩慢な発熱、急速な発熱)が明らかになり、様々な抑制剤の熱反応性と抑制メカニズムの違いが浮き彫りになりました。
- ハロゲン化物担体無機塩抑制剤は、石炭の自然発火に対して物理的および化学的な二重の抑制効果を発揮します。これは巨視的には、特性温度(吸熱ピーク温度およびT₁温度)の遅延、複数の吸熱ピークの出現、吸熱量の増加を伴う吸熱段階の延長、および様々な酸化段階における発熱量の大幅な減少として現れます。
- 希土類ハイドロタルサイトは、ハロゲン化物抑制剤の効率を効果的に高め、石炭の蓄熱を抑制し、自然発火の発生を遅らせ、石炭の各酸化段階における見かけの活性化エネルギーを効果的に増加させます。したがって、ハロゲン化物担体無機塩抑制剤は、石炭の自然発火反応プロセスを効果的に抑制することができ、より効率的な抑制剤を開発するための新しい道筋を提供します。
8. 参考文献:
- [1] Zhang Y N, Chen L, Zhao J Y, et al. Evaluation of the spontaneous combustion characteristics of coal of different metamorphic degrees based on a temperature-programmed oil bath experimental system. J Loss Prev Process Ind, 2019, 60: 17
- [2] Zhang Y N, Hou Y C, Zhao J Y, et al. Heat release characteristic of key functional groups during low-temperature oxidation of coal. Combust Sci Technol, 2020: 1
- [3] Zhao J Y, Deng J, Chen L, et al. Correlation analysis of the functional groups and exothermic characteristics of bituminous coal molecules during high-temperature oxidation. Energy, 2019, 181: 136
- [4] Guo W J. Experimental test and examination of the influential factors of the coal spontaneous combustion. J Saf Environ, 2018, 18(4): 1307 (郭文杰. 煤自燃特性影响因素的试验研究. 安全与环境学报, 2018, 18(4): 1307)
- [5] Zhu H T, Li Y N, Zhai Q Y, et al. Preparation and performance research of hydrotalcites containing rare earth element. Henan Chem Ind, 2019, 36(7): 15 (朱洪涛, 李岩娜, 翟秋月, 等. 稀土元素类水滑石的制备及其性能研究. 河南化工, 2019, 36(7): 15)
- [6] Liu Y Z, Duan T X, Deng Q, et al. Preparation of calcined hydrotalcite and adsorption of Cr(VI). Guangzhou Chem Ind, 2020, 48(15): 109 (刘奕祯, 段天欣, 邓仟, 等. 焙烧水滑石的制备及其吸附 Cr(VI)的研究. 广州化工, 2020, 48(15): 109)
- [7] Pang Y Q, Zhang Q. Research of inhibitor suppression on coal spontaneous combustion by magnesium chloride. Datong Coal Sci Technol, 2020(3): 51 (庞叶青, 张奇. 阻化剂氯化镁抑制煤自燃的实验研究. 同煤科技, 2020(3): 51)
- [8] Xu H Y. Experimental study of thermogravimetric kinetics on the composite inhibitor for inhibiting coal spontaneous combustion. Min Res Dev, 2019, 39(6): 79 (许红英. 复合阻化剂抑制煤自燃的热重动力学实验研究. 矿业研究与开发, 2019, 39(6): 79)
- [9] Ma D J, Tang Y B. Influence of associated metal elements in coal on low-temperature oxidation characteristics of coal. Coal Sci Technol, 2019, 47(2): 203 (马冬娟, 唐一博. 煤中伴生金属元素对煤低温氧化特性的影响. 煤炭科学技术, 2019, 47(2): 203)
- [10] Wang F S, Wang J T, Dong X W, et al. Experimental research on resistance characteristics of hypophosphite to coal spontaneous combustion. Saf Coal Mines, 2020, 51(5): 45 (王福生, 王建涛, 董宪伟, 等. 次磷酸盐对煤自燃的阻化特性实验研究. 煤矿安全, 2020, 51(5): 45)
- [11] Jin Y F, Li Y H, Liu B. Research on inhibiting effects of LDHs on coal spontaneous combustion. Coal Technol, 2017, 36(10): 101 (金永飞, 李毅恒, 刘博. 稀土类水滑石的煤自燃阻化效果研究. 煤炭技术, 2017, 36(10): 101)
- [12] Yang J X, Bai Z J. Experimental study on inhibition characteristic of LDHs inhibitor to bituminous coal. Saf Coal Mines, 2018, 49(8): 35 (杨计先, 白祖锦. LDHs阻化剂对烟煤的阻化特性实验研究. 煤矿安全, 2018, 49(8): 35)
- [13] Zhou X, Yuan H K, He P, et al. Effect of surface modifier on properties of Zn-Mg-Al hydrotalcites as heat stabilizer. Fine Chem, 2018, 35(8): 1389 (周喜, 袁浩坤, 何鹏, 等. 表面改性剂对Zn-Mg-Al水滑石热稳定剂性能影响. 精细化工, 2018, 35(8): 1389)
- [14] Wu W R, Liu T, Liu Z H, et al. Research progress of coal self ignition inhibitor. Appl Chem Ind, 2017, 46(2): 356 (武卫荣, 刘涛, 刘振辉, 等. 煤自燃阻化剂的研究进展. 应用化工, 2017, 46(2): 356)
- [15] Zhang Y T, Shi X Q, Li Y Q, et al. Inhibiting effects of Zn/Mg/Al layer double hydroxide on coal spontaneous combustion. J China Coal Soc, 2017, 42(11): 2892 (张玉涛, 史学强, 李亚清, 等. 锌镁铝层状双氢氧化物对煤自燃的阻化特性. 煤炭学报, 2017, 42(11): 2892)
- [16] Li J H, Wang B, Zhang A S, et al. Research on inhibition effect of halogen inhibitor on coal seam of Guotun Coal Mine. Coal Chem Ind, 2020, 43(5): 142 (李进海, 王兵, 张安山, 等. 卤盐阻化剂对郭屯煤矿煤层的阻化效果研究. 煤炭与化工, 2020, 43(5): 142)
- [17] Dong X W, Ai Q X, Wang F S, et al. Research on thermal characteristics in the process of coal oxidation inhibition. J Saf Sci Technol, 2016, 12(4): 70 (董宪伟, 艾晴雪, 王福生, 等. 煤氧化阻化过程中的热特性研究. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2016, 12(4): 70)
- [18] Zhou K Q, Gao R, Qian X D. Self-assembly of exfoliated molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanosheets and layered double hydroxide (LDH): towards reducing fire hazards of epoxy. J Hazard Mater, 2017, 338: 343
- [19] Wu B, Lou P, Wang C. Analysis of coal spontaneous combustion control by inhibitor. China Coal, 2014, 40(6): 117 (吴兵, 娄鹏, 王超. 阻化剂防治煤自燃效果分析. 中国煤炭, 2014, 40(6): 117)
- [20] Zheng L F. Test and analysis on salty retardants performance to restrain coal oxidized spontaneous combustion. Coal Sci Technol, 2010, 38(5): 70 (郑兰芳. 抑制煤氧化自燃的盐类阻化剂性能分析. 煤炭科学技术, 2010, 38(5): 70)
- [21] Li X P, Chen Y G, Zhang J S, et al. Study on the inhibition effect of chlorine salt composite inhibitor on spontaneous combustion of different coal samples. Coal Eng, 2020, 52(2): 106 (李绪萍, 陈映光, 张金山, 等. 氯盐复合阻化剂对不同煤样自燃阻化效果的研究. 煤炭工程, 2020, 52(2): 106)
- [22] Yang Y. Mechanism and Performance of Inhibitor Based on Oxidation Characteristic of the Spontaneous Combustion of Coal [Dissertation]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Science and Technology, 2015 (杨漪. 基于氧化特性的煤自燃阻化剂机理及性能研究[学位论文]. 西安: 西安科技大学, 2015)
- [23] Zhang X H, Ding F, Zhang Y T, et al. Experimental study on LDHs composite inhibitor to coal resistance property. Coal Sci Technol, 2017, 45(1): 84 (张辛亥, 丁峰, 张玉涛, 等. LDHs复合阻化剂对煤阻化性能的试验研究. 煤炭科学技术, 2017, 45(1): 84)
- [24] Duan Z Y, Wang F. Influence of MgCl2 on initial oxidation and secondary oxidation of coal. Saf Coal Mines, 2017, 48(6): 13 (段志勇, 王飞. MgCl2对煤一次氧化与二次氧化影响的实验研究. 煤矿安全, 2017, 48(6): 13)
- [25] Zhao J Y, Zhang Y L, Deng J, et al. Key functional groups affecting the release of gaseous products during spontaneous combustion of coal. Chin J Eng, 2020, 42(9): 1139 (赵婧昱, 张永利, 邓军, 等. 影响煤自燃气体产物释放的主要活性官能团. 工程科学学报, 2020, 42(9): 1139)
9. 著作権:
- 本資料は、「ZHANG Yan-ni, HOU Yun-chao, LIU Bo, DENG Jun, LIU Chun-hui, YANG Jing-jing, WEN Xin-yu」による論文です。「Mechanism and performance of coal spontaneous combustion with a halide carrier inorganic salt inhibitor」に基づいています。
- 論文の出典: https://doi.org/10.13374/j.issn2095-9389.2020.12.25.001
本資料は上記の論文に基づいて要約したものであり、商業目的での無断使用を禁じます。
Copyright © 2025 CASTMAN. All rights reserved.